
Express the process of budding in detail.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: It is a method of asexual reproduction. It can occur from any point of body but can be restricted to a special area in some organisms. It can be external or internal. It can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Hydra and yeast undergo this process.
Complete answer:
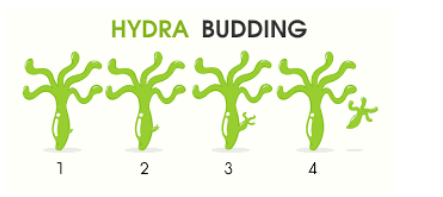
Budding is a method of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develop as an outgrowth or bud from the parent itself by cell division at any point on the body. Bud is a small bulb like projection outgrowing from the parent body. The newborns are identical to the parents except in case of mutations.
In the case of hydra, it uses regenerative cells for reproduction.
When these buds fully mature on the parent body, they detach themselves and become independent individuals.
Budding can be internal or external.
The bud formation on the parent itself is external budding. It is seen in hydra and yeast.
Internal budding is division of the parent itself into two or multiple daughter cells. It is seen in toxoplasma gondii. These buds can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Asymmetrical budding is seen in saccharomyces cerevisiae (a kind of yeast used in brewing and baking). In this case the daughter is smaller than the parent.
Budding can also be seen in multicellular animals such as corals, sponges etc.
Note: Budding is a method of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develop as an outgrowth or bud from the parent itself by cell division at any point on the body. The newborns are identical to the parents except in case of mutations. It can be external or internal. It can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Hydra and yeast undergo this process.
Complete answer:
Budding is a method of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develop as an outgrowth or bud from the parent itself by cell division at any point on the body. Bud is a small bulb like projection outgrowing from the parent body. The newborns are identical to the parents except in case of mutations.
In the case of hydra, it uses regenerative cells for reproduction.
When these buds fully mature on the parent body, they detach themselves and become independent individuals.
Budding can be internal or external.
The bud formation on the parent itself is external budding. It is seen in hydra and yeast.
Internal budding is division of the parent itself into two or multiple daughter cells. It is seen in toxoplasma gondii. These buds can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Asymmetrical budding is seen in saccharomyces cerevisiae (a kind of yeast used in brewing and baking). In this case the daughter is smaller than the parent.
Budding can also be seen in multicellular animals such as corals, sponges etc.

Note: Budding is a method of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develop as an outgrowth or bud from the parent itself by cell division at any point on the body. The newborns are identical to the parents except in case of mutations. It can be external or internal. It can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Hydra and yeast undergo this process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




