
Express tan A in terms of sin A.
Answer
619.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, we will write tan A in terms of sin A and cos A (that is $\tan A=\dfrac{\sin A}{\cos A}$). We will then square both the sides. We can then express ${{\cos }^{2}}A=1-{{\sin }^{2}}A$ to get ${{\tan }^{2}}A$ in terms of ${{\sin }^{2}}A$. We can then get the value of tan A by performing the square root on both sides of the equation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We first try to understand the trigonometric properties in terms of a right triangle ABC (as shown below).
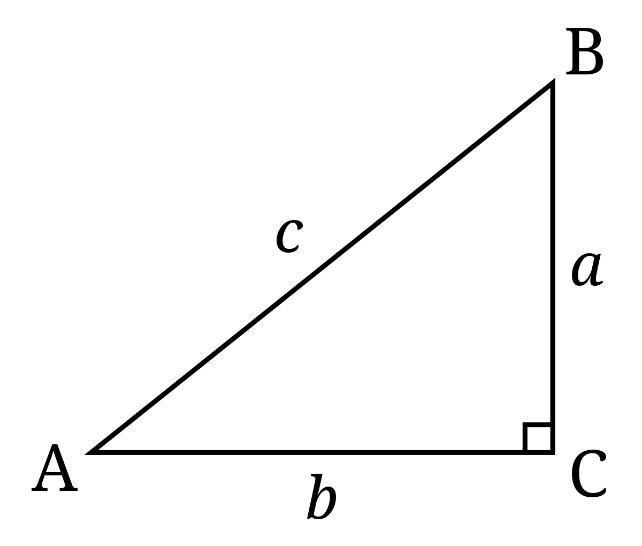
Now, by definition, we have,
sin A = $\dfrac{a}{c}$ -- (1)
cos A = $\dfrac{b}{c}$ -- (2)
tan A = $\dfrac{a}{b}$
Thus, we can see that $\dfrac{\sin A}{\cos A}=\tan A$ . Now, to proceed forward, we square both LHS and RHS, thus, we get,
${{\left( \dfrac{\sin A}{\cos A} \right)}^{2}}={{\tan }^{2}}A$
$\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{{{\cos }^{2}}A} \right)={{\tan }^{2}}A$ -- (A)
Now, we square (1) and (2) individually and then adding them, we get,
${{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{c}^{2}}}$ -- (3)
Now, we can use the Pythagoras theorem on the right triangle. We have,
${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$
We put this in (3), we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{c}^{2}}} \\
& {{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can substitute the value of ${{\cos }^{2}}A=1-{{\sin }^{2}}A$ in (A), we get,
$\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A} \right)={{\tan }^{2}}A$
Now, simplifying further, we get,
To find tan A in terms of sin A, we just perform square root on both RHS and LHS, we get.
\[\tan A=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A}}\]
\[\tan A=\dfrac{\sin A}{\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A}}\] -- (B)
Thus, equation (B) gives us the relation between tan A and sin A.
Note: It is generally important to remember few results like ${{\cos }^{2}}A=1-{{\sin }^{2}}A$ , since this result greatly helps us in arriving at the results faster. Generally, for finding any trigonometric angle in terms of other trigonometric angles (say cot A in terms of cos A), we have to square both the terms to use the known results and then we can perform square root to get the desired relation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We first try to understand the trigonometric properties in terms of a right triangle ABC (as shown below).

Now, by definition, we have,
sin A = $\dfrac{a}{c}$ -- (1)
cos A = $\dfrac{b}{c}$ -- (2)
tan A = $\dfrac{a}{b}$
Thus, we can see that $\dfrac{\sin A}{\cos A}=\tan A$ . Now, to proceed forward, we square both LHS and RHS, thus, we get,
${{\left( \dfrac{\sin A}{\cos A} \right)}^{2}}={{\tan }^{2}}A$
$\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{{{\cos }^{2}}A} \right)={{\tan }^{2}}A$ -- (A)
Now, we square (1) and (2) individually and then adding them, we get,
${{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{c}^{2}}}$ -- (3)
Now, we can use the Pythagoras theorem on the right triangle. We have,
${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$
We put this in (3), we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{c}^{2}}} \\
& {{\sin }^{2}}A+{{\cos }^{2}}A=1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can substitute the value of ${{\cos }^{2}}A=1-{{\sin }^{2}}A$ in (A), we get,
$\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A} \right)={{\tan }^{2}}A$
Now, simplifying further, we get,
To find tan A in terms of sin A, we just perform square root on both RHS and LHS, we get.
\[\tan A=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}A}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A}}\]
\[\tan A=\dfrac{\sin A}{\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}A}}\] -- (B)
Thus, equation (B) gives us the relation between tan A and sin A.
Note: It is generally important to remember few results like ${{\cos }^{2}}A=1-{{\sin }^{2}}A$ , since this result greatly helps us in arriving at the results faster. Generally, for finding any trigonometric angle in terms of other trigonometric angles (say cot A in terms of cos A), we have to square both the terms to use the known results and then we can perform square root to get the desired relation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




