
Explain with the help of a labelled ray diagram, the defect of hypermetropia and how it is corrected.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Hypermetropia is a defect of vision in which the image of the object is not formed on the retina but in front of the retina. It is also called long sightedness. Usually for a healthy eye, it is able to see up to infinity but when it becomes weak due to stress and strain the far point decreases. Similarly, the near point up to which an object can be clearly seen is 25 cm.
Complete step by step answer:
In case of hypermetropia the image of an object is not formed on the retina but Infront of the retina, as shown below.
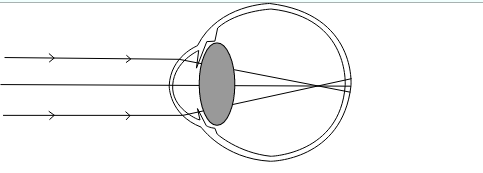
We can see that the light rays coming from the infinity gets converged Infront of the retina but we want them to get focuses on the retina, thus in order to rectify this defect of eye we use a diverging lens that is concave lens which diverges the incoming light rays, then after passing through it they passes through the lens of the eye and finally converges onto the retina. This can be shown below.

Note:
The major cause of the hypermetropia is that the focal length of the eye lens increases and as a result of it the light rays converge in front of the retina. Another cause can be that the eyeball itself becomes too small. To correct this defect, we use a concave lens of appropriate focal length. In Farsightedness one can see distant objects but cannot see nearby objects.
Complete step by step answer:
In case of hypermetropia the image of an object is not formed on the retina but Infront of the retina, as shown below.

We can see that the light rays coming from the infinity gets converged Infront of the retina but we want them to get focuses on the retina, thus in order to rectify this defect of eye we use a diverging lens that is concave lens which diverges the incoming light rays, then after passing through it they passes through the lens of the eye and finally converges onto the retina. This can be shown below.

Note:
The major cause of the hypermetropia is that the focal length of the eye lens increases and as a result of it the light rays converge in front of the retina. Another cause can be that the eyeball itself becomes too small. To correct this defect, we use a concave lens of appropriate focal length. In Farsightedness one can see distant objects but cannot see nearby objects.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




