
Explain with chemical equation, what happens when slaked lime reacts with chlorine?
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The slaked lime is the hydroxide of calcium which in reaction with the chlorine gas produces the compound which has a unique property of disinfection as it acts as an oxidant or basic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Slaked lime is calcium hydroxide present in solid state,$Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}$. It is formed by adding water to CaO, that is, quicklime.
\[CaO(s)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)\to Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}(s)\]
The slightly moist slaked lime on reaction with chlorine forms calcium hypochlorite, calcium chloride and water.
\[2Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}+2C{{l}_{2}}(g)\to Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}(s)+CaC{{l}_{2}}(s)+2{{H}_{2}}O(l)\]
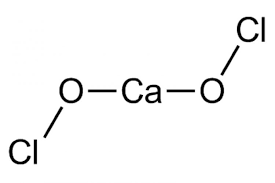
Here, the $Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}$ has a calcium cation $C{{a}^{2+}}$ and two hypochlorite ions $Cl{{O}^{-}}$ which has the chlorine in $(+1)$ charge and oxygen in ${{O}^{2-}}$. Thus, calcium hypochlorite acts as an oxidising agent and is highly basic. It is an exothermic reaction with the release of heat.
The reaction can also be written for dry slaked lime as, $Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}(s)+C{{l}_{2}}(g)\to CaOC{{l}_{2}}(s)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)$, where the $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ formed has $C{{l}^{-}}$ and $Cl{{O}^{-}}$ions along with $C{{a}^{2+}}$.
Both $Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}$and $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$,that is, calcium hypochlorite is known as the bleaching powder and smell of chlorine due to its high availability.
Note: The dilute aqueous solution of slaked lime is known as lime water. The calcium hypochlorite formed is the solid form of chlorine used for chlorination in disinfectants. Therefore, it is used for purification of wastewater or portable water due to its disinfecting ability by the chlorine present having the oxidising nature. Thereby, also, dealing with the taste and odour problem in the disinfected drinking water. It is stored in a cool and dry place, away from any acid, organic materials, and metals.
Complete step by step answer:
Slaked lime is calcium hydroxide present in solid state,$Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}$. It is formed by adding water to CaO, that is, quicklime.
\[CaO(s)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)\to Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}(s)\]
The slightly moist slaked lime on reaction with chlorine forms calcium hypochlorite, calcium chloride and water.
\[2Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}+2C{{l}_{2}}(g)\to Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}(s)+CaC{{l}_{2}}(s)+2{{H}_{2}}O(l)\]

Here, the $Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}$ has a calcium cation $C{{a}^{2+}}$ and two hypochlorite ions $Cl{{O}^{-}}$ which has the chlorine in $(+1)$ charge and oxygen in ${{O}^{2-}}$. Thus, calcium hypochlorite acts as an oxidising agent and is highly basic. It is an exothermic reaction with the release of heat.
The reaction can also be written for dry slaked lime as, $Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}(s)+C{{l}_{2}}(g)\to CaOC{{l}_{2}}(s)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)$, where the $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ formed has $C{{l}^{-}}$ and $Cl{{O}^{-}}$ions along with $C{{a}^{2+}}$.
Both $Ca{{(OCl)}_{2}}$and $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$,that is, calcium hypochlorite is known as the bleaching powder and smell of chlorine due to its high availability.
Note: The dilute aqueous solution of slaked lime is known as lime water. The calcium hypochlorite formed is the solid form of chlorine used for chlorination in disinfectants. Therefore, it is used for purification of wastewater or portable water due to its disinfecting ability by the chlorine present having the oxidising nature. Thereby, also, dealing with the taste and odour problem in the disinfected drinking water. It is stored in a cool and dry place, away from any acid, organic materials, and metals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




