
Explain the work of an Electric Generator with a diagram.
Answer
527.4k+ views
Hint: An electric generator is an electronic device used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of electromagnetic induction. Construct the diagram by following its working scheme. Additionally, explain the phenomena of electromagnetic induction for the generator itself and how current is produced.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A generator or dynamo is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The term generator is wrongly used to describe this device because it does not generate energy in any manner rather just converts its one form into another. This is due to the universal law of conservation of energy which states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, rather just converted from one form to another.
This device works in accordance with Faraday’s law which states that when a conductor is present in a varying magnetic field it results in the induction of an emf, which in turn is equal to the rate of change of flux of the setup. The following figure shows an electric generator.
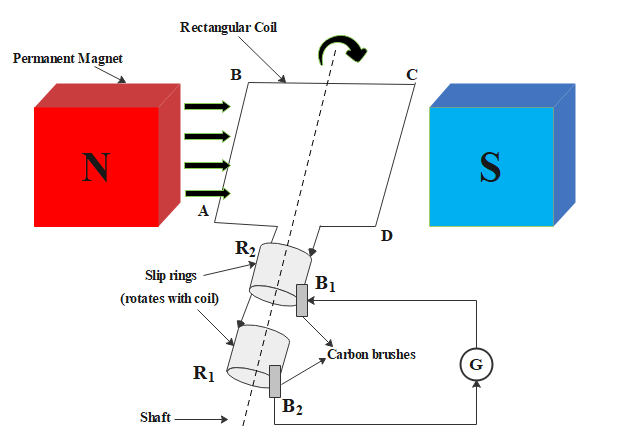
There are two types of electric generator:
i. A.C. Generator
ii. D.C. Generator
Components of Generator:
i. Field magnet
ii. Armature
iii. Slip rings
iv. Brushes
v. Source of energy
Working of the generator:
When the armature coil of the generator starts rotating, the magnetic flux linked with it tends to change and so an induced current flows via the coil. Based on the original position of the coil, in accordance with Fleming’s right-hand rule, the induced current flows in the circuit. In the first cycle of the coil the current moves in a particular direction such that one brush acts as the positive terminal and the other as a negative terminal. In the other half, this polarity changes and current flows in the opposite direction from the initial one. Thus the direction of current produced changes direction every half cycle. Hence in this way, the mechanical rotation of the coil produces electrical energy, i.e., mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy with the help of an electric generator.
Note: Electrical generator is also known as a dynamo. The mechanical power for the generator can be provided in numerous ways like hydraulic turbines at dams or waterfalls, steam turbines using steam produced by combustion of fossil fuels, and wind turbines, etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A generator or dynamo is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The term generator is wrongly used to describe this device because it does not generate energy in any manner rather just converts its one form into another. This is due to the universal law of conservation of energy which states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, rather just converted from one form to another.
This device works in accordance with Faraday’s law which states that when a conductor is present in a varying magnetic field it results in the induction of an emf, which in turn is equal to the rate of change of flux of the setup. The following figure shows an electric generator.

There are two types of electric generator:
i. A.C. Generator
ii. D.C. Generator
Components of Generator:
i. Field magnet
ii. Armature
iii. Slip rings
iv. Brushes
v. Source of energy
Working of the generator:
When the armature coil of the generator starts rotating, the magnetic flux linked with it tends to change and so an induced current flows via the coil. Based on the original position of the coil, in accordance with Fleming’s right-hand rule, the induced current flows in the circuit. In the first cycle of the coil the current moves in a particular direction such that one brush acts as the positive terminal and the other as a negative terminal. In the other half, this polarity changes and current flows in the opposite direction from the initial one. Thus the direction of current produced changes direction every half cycle. Hence in this way, the mechanical rotation of the coil produces electrical energy, i.e., mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy with the help of an electric generator.
Note: Electrical generator is also known as a dynamo. The mechanical power for the generator can be provided in numerous ways like hydraulic turbines at dams or waterfalls, steam turbines using steam produced by combustion of fossil fuels, and wind turbines, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




