
Explain the term perianth.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: It is the non-reproductive part of the flower that forms an envelope surrounding the sexual parts of flowers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Calyx and corolla are collectively called the perianth. Perianth enclosed the reproductive part of flowers. It is divided into outer and inner whorls. The sepals are the outermost layer which is usually green and encloses the flower bud. They are collectively called the calyx. However, the petals are the next layer of floral appendages internal to the calyx. The sepals and petals in flowers are accessory parts or sterile appendages that protect the flower buds and attract pollinators.
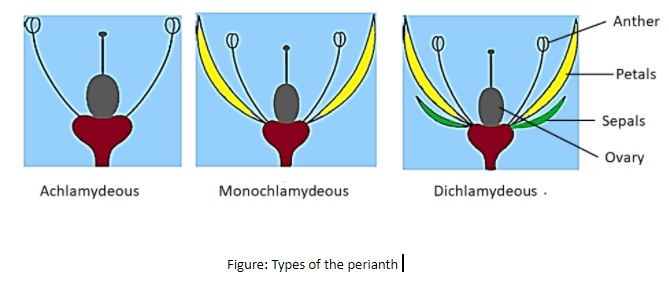
In some plants, the calyx and corolla are separately called dichlamydeous while in some plants they both are indistinguishable and called monochlamydeous. A flower without perianth is called achlamydeous. If the perianth is not differentiated into the calyx and the corolla, called perigon.
The symmetry of flowers decided by the perianth. When the perianth is bisected over the central axis from any point the symmetrical halves are produced, the flower is called actinomorphic. When flowers are bisected and produce only one line that produces symmetrical halves, called zygomorphic.
Types of perianth:
Aposepalous: When the sepals are free, the calyx is called aposepalous.
Synsepalous: If the sepals are partially or wholly fused, the calyx is called as synsepalous.
Asepalous: A flower without calyx is called as asepalous
Sympetalous: The petals are united to form a tubular corolla, called sympetalous.
Apopetalus: If the petals are free, the corolla is called apopetalous.
Note: -In the mosses and liverworts, the perianth is the sterile tube-like tissue that surrounds the female reproductive structure.
-In flowers, sepals and petals are collectively called tepals.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Calyx and corolla are collectively called the perianth. Perianth enclosed the reproductive part of flowers. It is divided into outer and inner whorls. The sepals are the outermost layer which is usually green and encloses the flower bud. They are collectively called the calyx. However, the petals are the next layer of floral appendages internal to the calyx. The sepals and petals in flowers are accessory parts or sterile appendages that protect the flower buds and attract pollinators.
In some plants, the calyx and corolla are separately called dichlamydeous while in some plants they both are indistinguishable and called monochlamydeous. A flower without perianth is called achlamydeous. If the perianth is not differentiated into the calyx and the corolla, called perigon.
The symmetry of flowers decided by the perianth. When the perianth is bisected over the central axis from any point the symmetrical halves are produced, the flower is called actinomorphic. When flowers are bisected and produce only one line that produces symmetrical halves, called zygomorphic.
Types of perianth:
Aposepalous: When the sepals are free, the calyx is called aposepalous.
Synsepalous: If the sepals are partially or wholly fused, the calyx is called as synsepalous.
Asepalous: A flower without calyx is called as asepalous
Sympetalous: The petals are united to form a tubular corolla, called sympetalous.
Apopetalus: If the petals are free, the corolla is called apopetalous.

Note: -In the mosses and liverworts, the perianth is the sterile tube-like tissue that surrounds the female reproductive structure.
-In flowers, sepals and petals are collectively called tepals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




