
Explain the structure of a typical flower with the help of a diagram.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Flowers are the reproductive structures found in angiosperms. They are modified shoots of a plant. The structure of a flower is made up of different whorls and a stalk that holds them.
Complete answer:
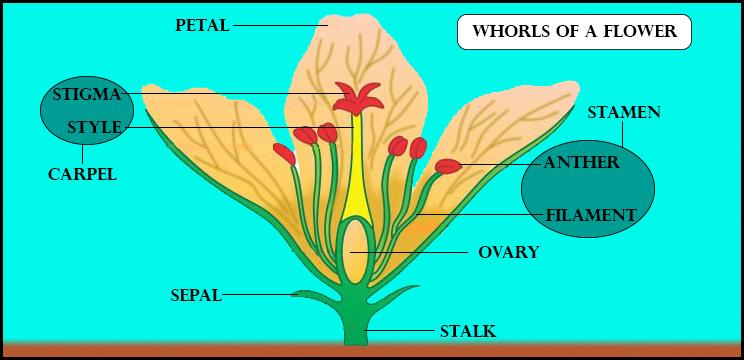
Flowers are the reproductive structures found in flowering plants i.e. the angiosperms. The structure of a typical flower mainly contains the following parts called whorls from outside to inside:
-Stalk- The part by which the flower is attached to the branch is called its stalk. It is also known as the pedicel.
-Sepals- Sepals are the small, green coloured, leaf-shaped structures that are found on the outermost part of a flower. They are considered to be a modified form of leaves. They provide protection to the flower in their stage of budding and they support the petals when the flowers bloom.
-Petals- Petals are the pigmented or coloured, modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of the flowers. They may be brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract the insects for pollination or maybe white in case of flowers that bloom at night to increase visibility.
-Stamen- Stamens are the pollen-producing, male reproductive parts of a flower that usually consist of a long slender stalk called the filament, with the anthers at the tip which are the chambers for pollen production.
-Pistil - Pistils are the ovule producing, female reproductive organs of a flower. They are the innermost whorl of a flower. The pistil consists of three parts namely the stigma, style, and ovary.
Note:
-In some flowers, the sepals may be fused to the petals. Such a fused whorl is known as tepals.
-These flowers give rise to the fruits in angiosperms. The ovary of the pistil forms the fleshy fruit, while the ovules form the seeds.
-Since, flowers are not found in gymnosperms, they produce cones which act as reproductive structures.
Complete answer:

Flowers are the reproductive structures found in flowering plants i.e. the angiosperms. The structure of a typical flower mainly contains the following parts called whorls from outside to inside:
-Stalk- The part by which the flower is attached to the branch is called its stalk. It is also known as the pedicel.
-Sepals- Sepals are the small, green coloured, leaf-shaped structures that are found on the outermost part of a flower. They are considered to be a modified form of leaves. They provide protection to the flower in their stage of budding and they support the petals when the flowers bloom.
-Petals- Petals are the pigmented or coloured, modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of the flowers. They may be brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract the insects for pollination or maybe white in case of flowers that bloom at night to increase visibility.
-Stamen- Stamens are the pollen-producing, male reproductive parts of a flower that usually consist of a long slender stalk called the filament, with the anthers at the tip which are the chambers for pollen production.
-Pistil - Pistils are the ovule producing, female reproductive organs of a flower. They are the innermost whorl of a flower. The pistil consists of three parts namely the stigma, style, and ovary.
Note:
-In some flowers, the sepals may be fused to the petals. Such a fused whorl is known as tepals.
-These flowers give rise to the fruits in angiosperms. The ovary of the pistil forms the fleshy fruit, while the ovules form the seeds.
-Since, flowers are not found in gymnosperms, they produce cones which act as reproductive structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




