
Explain the non-linear shape of ${H_2}S$ and non-planar shape of $PC{l_3}$ using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint:Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory is a theory used in chemical bonding to predict the geometry of molecules from the number of electron pairs (both bonding and non-bonding) surrounding the central atom.
Formula used:
Steric number $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {V + M - C + A} \right)$
Where V is the number of valence electron of central atom
M is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom
C is the amount of positive charge on the ion
A is the amount of negative charge on the ion
Complete step-by-step answer:Steric number in ${H_2}S$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6 + 2} \right) = \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
According to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, tetrahedral geometry is the most favored geometry for steric number four as it leads to the least repulsion between the four bond pairs.
In ${H_2}S$, out of total electron pairs, two will be bonding and two will be non-bonding or lone pairs. Now, since two lone pairs are present, it will lead to distortion in geometry as we know according to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, the order of repulsion is as follows:
$L.P. - L.P. > L.P. - B.P. > B.P. - B.P.$
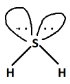
Because of this the shape of ${H_2}S$ will be bent and hence non-linear.
Steric number in $PC{l_3}$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5 + 3} \right) = \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
According to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, tetrahedral geometry is the most favored geometry for steric number four as it leads to the least repulsion between the four bond pairs.
In $PC{l_3}$, out of total electron pairs, three will be bonding and one will be non-bonding or lone pair. Now, since one lone pair are present, it will lead to distortion in geometry as we know according to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, the order of repulsion is as follows:
$L.P. - L.P. > L.P. - B.P. > B.P. - B.P.$
Hence, $PC{l_3}$ is non-planar unlike $BC{l_3}$which is planar (steric number is three).
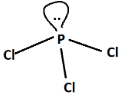
Shape of $PC{l_3}$ is trigonal pyramidal and hence non-planar.
Note:The main principle of the VSEPR theory is that the atoms occupy the positions in order to minimize the repulsions. This minimization of repulsions will in turn lead to a decrease in the energy of the system and hence will make the system stable.
Formula used:
Steric number $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {V + M - C + A} \right)$
Where V is the number of valence electron of central atom
M is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom
C is the amount of positive charge on the ion
A is the amount of negative charge on the ion
Complete step-by-step answer:Steric number in ${H_2}S$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6 + 2} \right) = \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
According to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, tetrahedral geometry is the most favored geometry for steric number four as it leads to the least repulsion between the four bond pairs.
In ${H_2}S$, out of total electron pairs, two will be bonding and two will be non-bonding or lone pairs. Now, since two lone pairs are present, it will lead to distortion in geometry as we know according to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, the order of repulsion is as follows:
$L.P. - L.P. > L.P. - B.P. > B.P. - B.P.$

Because of this the shape of ${H_2}S$ will be bent and hence non-linear.
Steric number in $PC{l_3}$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5 + 3} \right) = \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
According to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, tetrahedral geometry is the most favored geometry for steric number four as it leads to the least repulsion between the four bond pairs.
In $PC{l_3}$, out of total electron pairs, three will be bonding and one will be non-bonding or lone pair. Now, since one lone pair are present, it will lead to distortion in geometry as we know according to Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory, the order of repulsion is as follows:
$L.P. - L.P. > L.P. - B.P. > B.P. - B.P.$
Hence, $PC{l_3}$ is non-planar unlike $BC{l_3}$which is planar (steric number is three).

Shape of $PC{l_3}$ is trigonal pyramidal and hence non-planar.
Note:The main principle of the VSEPR theory is that the atoms occupy the positions in order to minimize the repulsions. This minimization of repulsions will in turn lead to a decrease in the energy of the system and hence will make the system stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




