
Explain the nature of covalent bond using the bond formation in $C{{H}_{3}}Cl$.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons between a pair of atoms. In the given compound there is 1 carbon atom to which 3 hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom is attached and they share electrons among themselves to gain mutual stability.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability.
Generally, there are three types of covalent bonding that we know about. They are-
Single bond- When there is a sharing of two electrons between a pair of atoms and gives rise to a sigma bond between the atoms, the sigma bond formed is the single bond.
Double bond- When four electrons are shared by the two atoms, it gives rise to a sigma bond and a pi-bond which is known as the double bond.
Triple bond- When six electrons are shared by the two atoms, there exists one sigma and two pi-bonds thus forming a triple bond.
Now, let us discuss the nature of the covalent bond in $C{{H}_{3}}Cl$. Here, carbon will complete its octet by sharing electrons and not by gaining or losing electrons which will require more energy and eventually destabilize it.
The atoms here will share their valence shell electrons and this bonding is known as covalent bonding.
We know the atomic number of carbon is 6 i.e. it’s electronic configuration is 2, 4. It will need 4 more electrons to complete its octet. Therefore, it will share these 4 electrons with the three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom.
Similarly, the atomic number of chlorine is 17 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7 i.e. it needs 1electron to gain stable configuration.
And hydrogen’s atomic number is 1 and it needs one more electron to gain stability. Each hydrogen atom shares an electron with carbon.
All these electrons are shared and thus each atom gains mutual stability giving rise to a stable, covalently bonded compound.
Pictorially we can show this sharing as-
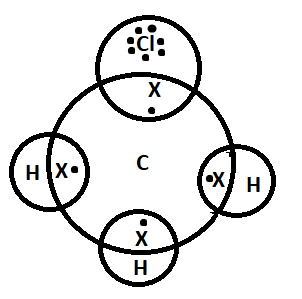
Note: In order to form a covalent bond, the atoms need to be in a specific arrangement which will allow the overlapping between the orbitals. It is difficult to break a sigma bond because sigma bonds are stronger than pi- bonds. A sigma bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals along the axis and pi-bond is formed by overlapping of two lobes of the atomic orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability.
Generally, there are three types of covalent bonding that we know about. They are-
Single bond- When there is a sharing of two electrons between a pair of atoms and gives rise to a sigma bond between the atoms, the sigma bond formed is the single bond.
Double bond- When four electrons are shared by the two atoms, it gives rise to a sigma bond and a pi-bond which is known as the double bond.
Triple bond- When six electrons are shared by the two atoms, there exists one sigma and two pi-bonds thus forming a triple bond.
Now, let us discuss the nature of the covalent bond in $C{{H}_{3}}Cl$. Here, carbon will complete its octet by sharing electrons and not by gaining or losing electrons which will require more energy and eventually destabilize it.
The atoms here will share their valence shell electrons and this bonding is known as covalent bonding.
We know the atomic number of carbon is 6 i.e. it’s electronic configuration is 2, 4. It will need 4 more electrons to complete its octet. Therefore, it will share these 4 electrons with the three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom.
Similarly, the atomic number of chlorine is 17 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7 i.e. it needs 1electron to gain stable configuration.
And hydrogen’s atomic number is 1 and it needs one more electron to gain stability. Each hydrogen atom shares an electron with carbon.
All these electrons are shared and thus each atom gains mutual stability giving rise to a stable, covalently bonded compound.
Pictorially we can show this sharing as-

Note: In order to form a covalent bond, the atoms need to be in a specific arrangement which will allow the overlapping between the orbitals. It is difficult to break a sigma bond because sigma bonds are stronger than pi- bonds. A sigma bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals along the axis and pi-bond is formed by overlapping of two lobes of the atomic orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




