
Explain the manufacturing of Ethanol from Molasses.
Answer
592.8k+ views
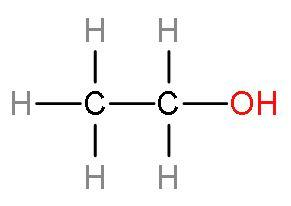
Hint: Ethanol consists of two carbon atoms and an alcohol group whose rest valencies are filled with hydrogen atoms. Ethanol is a colourless liquid. The structure of ethanol:
Molasses from which ethanol is produced, is obtained from the juice extracted from sugarcane is boiled down until the sugars crystallises and precipitates out. The sweety syrup left out after crystallization is molasses.
- Ethanol is obtained commercially by fermentation.
Complete answer:
Let us see the manufacturing of ethanol from molasses:
- The sugar in molasses, sugarcane or fruits such as grapes is converted to glucose and fructose $\left( {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}} \right)$ in the presence of an enzyme called invertase.
The reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{11}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}\xrightarrow{\text{Invertase}}\text{2}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}}$
- Glucose and Fructose undergo fermentation in the presence of another enzyme named zymase which is found in yeast. For making wine, grapes are the source of sugars and yeast. The reaction is $\begin{align}
& {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}}\xrightarrow{\text{zymase}}\text{2}{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OH}+\text{2C}{{\text{O}}_{2}} \\
& \text{glucose ethanol} \\
\end{align}$
- As grapes ripen, the quantity of sugar increases and yeast grows on their outer skin. When grapes are crushed, sugar and the enzymes come in contact and the process of fermentation starts. Fermentation takes place in anaerobic conditions meant in absence of air. Carbon dioxide is released during fermentation. If air gets into fermentation mixture, the oxygen gas oxidises ethanol to ethanoic acid which destroys the taste of alcoholic drinks.
Additional Information:
Applications of ethanol:
(1)- The largest use of ethanol is as an engine fuel and fuel additive.
(2)- Ethanol is commonly consumed psychoactive drugs.
(3)- Ethanol increases the secretion of acids in the stomach.
(4)- It is used in medical wipes and in antibacterial hand sanitizers as an antiseptic for its antifungal effects.
(5)- It is used as a solvent in the paint industry.
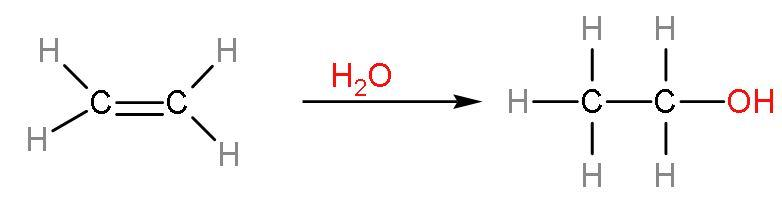
Note: The commercial alcohol is made unfit for drinking by mixing in it some pyridine (a foul smelling liquid) and copper sulphate (to give it a colour). It is called the denaturation of alcohols. The action of zymase is hindered once the percentage of alcohol formed exceeds 14%. Now, at large scale ethanol is produced by hydration of ethenes. The process is

Molasses from which ethanol is produced, is obtained from the juice extracted from sugarcane is boiled down until the sugars crystallises and precipitates out. The sweety syrup left out after crystallization is molasses.
- Ethanol is obtained commercially by fermentation.
Complete answer:
Let us see the manufacturing of ethanol from molasses:
- The sugar in molasses, sugarcane or fruits such as grapes is converted to glucose and fructose $\left( {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}} \right)$ in the presence of an enzyme called invertase.
The reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{11}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}\xrightarrow{\text{Invertase}}\text{2}{{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}}$
- Glucose and Fructose undergo fermentation in the presence of another enzyme named zymase which is found in yeast. For making wine, grapes are the source of sugars and yeast. The reaction is $\begin{align}
& {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_{6}}\xrightarrow{\text{zymase}}\text{2}{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OH}+\text{2C}{{\text{O}}_{2}} \\
& \text{glucose ethanol} \\
\end{align}$
- As grapes ripen, the quantity of sugar increases and yeast grows on their outer skin. When grapes are crushed, sugar and the enzymes come in contact and the process of fermentation starts. Fermentation takes place in anaerobic conditions meant in absence of air. Carbon dioxide is released during fermentation. If air gets into fermentation mixture, the oxygen gas oxidises ethanol to ethanoic acid which destroys the taste of alcoholic drinks.
Additional Information:
Applications of ethanol:
(1)- The largest use of ethanol is as an engine fuel and fuel additive.
(2)- Ethanol is commonly consumed psychoactive drugs.
(3)- Ethanol increases the secretion of acids in the stomach.
(4)- It is used in medical wipes and in antibacterial hand sanitizers as an antiseptic for its antifungal effects.
(5)- It is used as a solvent in the paint industry.
Note: The commercial alcohol is made unfit for drinking by mixing in it some pyridine (a foul smelling liquid) and copper sulphate (to give it a colour). It is called the denaturation of alcohols. The action of zymase is hindered once the percentage of alcohol formed exceeds 14%. Now, at large scale ethanol is produced by hydration of ethenes. The process is

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




