
Explain the Lewis structure diagram of covalent compound $ A{l_2}C{l_6} $ ?
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: Lewis structure diagrams are widely used to depict the bonding between different molecules. This structure also provides the knowledge of lone pairs of electrons present in any atom. Lewis structure basically shows the type and position of different atoms within a molecule.
Complete answer:
The compound $ A{l_2}C{l_6} $ is formed when two molecules of aluminium chloride, $ AlC{l_3} $ , combine with each other to form a dimer molecule. Atomic number of aluminium is $ 13 $ and the electronic configuration is $ \left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^1} $ . There are three electrons in the outermost shell of aluminium. Similarly, electronic configuration of chlorine is $ \left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^5} $ . There are seven electrons in the outermost shell of the chlorine atom.
Aluminium atoms share its three valence electrons with three electrons of chlorine atoms to form covalent bonds. Chlorine atom has seven electrons in its valence electron so it is able to form a covalent bond with one aluminium atom and share its lone pair electron to another aluminium atom to form a coordinate bond.
Since, aluminium is less electronegative element than chlorine atom it will occupy the central position in Lewis structure diagram.
So, final Lewis structure diagram of $ A{l_2}C{l_6} $ will become-
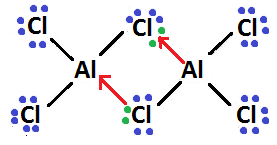
In this Lewis structure, dots over the atom show their electron and black line shows formation of covalent bond while red line shows formation of coordinate bond.
Note:
The Lewis structure diagram is drawn for covalent compounds as well as coordination compounds like $ {H_2}S{O_4} $ . Coordinate covalent are the compounds in which both the electrons which contribute in bond formation come from one atom. If a molecule contains a negative charge then we have to add a pair of electrons to the total number of valence electrons of anions.
Complete answer:
The compound $ A{l_2}C{l_6} $ is formed when two molecules of aluminium chloride, $ AlC{l_3} $ , combine with each other to form a dimer molecule. Atomic number of aluminium is $ 13 $ and the electronic configuration is $ \left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^1} $ . There are three electrons in the outermost shell of aluminium. Similarly, electronic configuration of chlorine is $ \left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^5} $ . There are seven electrons in the outermost shell of the chlorine atom.
Aluminium atoms share its three valence electrons with three electrons of chlorine atoms to form covalent bonds. Chlorine atom has seven electrons in its valence electron so it is able to form a covalent bond with one aluminium atom and share its lone pair electron to another aluminium atom to form a coordinate bond.
Since, aluminium is less electronegative element than chlorine atom it will occupy the central position in Lewis structure diagram.
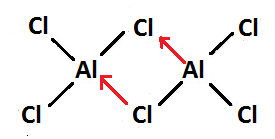
So, final Lewis structure diagram of $ A{l_2}C{l_6} $ will become-


In this Lewis structure, dots over the atom show their electron and black line shows formation of covalent bond while red line shows formation of coordinate bond.
Note:
The Lewis structure diagram is drawn for covalent compounds as well as coordination compounds like $ {H_2}S{O_4} $ . Coordinate covalent are the compounds in which both the electrons which contribute in bond formation come from one atom. If a molecule contains a negative charge then we have to add a pair of electrons to the total number of valence electrons of anions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




