
Explain the construction of a motor with a diagram.
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint:A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors generate force in the form of torque through the interaction between the motor’s magnetic field and the electric current in the wire winding. The torque generated is applied to the motor’s shaft.
Complete step by step answer:
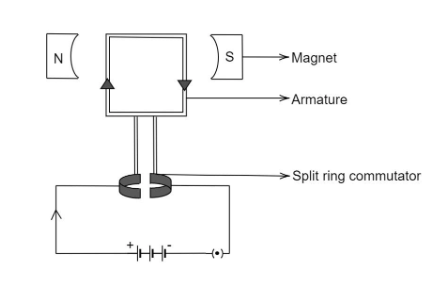
The working principle of DC Motor mainly depends upon Fleming Left-Hand rule. As can be seen in the diagram, the armature coil is placed between the magnetic poles. An external DC source, a battery, is connected to the armature coil and current starts flowing through it. Since the current-carrying armature coil lies inside a magnetic field, they will experience a force which tends to rotate the armature.
Here, the arm of the armature coil near the North Pole of the magnet carries current in the upward direction along the plane of this screen. By applying Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, the direction of force F, experienced by this arm will be downwards perpendicular to the plane of this screen. A similar force will be experienced by the arm of the armature near the South Pole. Thus the armature coil tends to rotate in an anti-clockwise direction.
The direction of the current in the armature coil is reversed after every half rotation with the help of the split-ring commutator, to keep the coil rotating in the same direction. This reversal of current helps to develop a continuous and unidirectional torque.
Note:Electric motors find a vast array of applications in our daily life, mainly including blowers, fans, machine tools, pumps, turbines, power tools, alternators, compressors, rolling mills, ships, movers, paper mills, vacuum cleaners, dishwashers, computer printers, etc.
Complete step by step answer:

The working principle of DC Motor mainly depends upon Fleming Left-Hand rule. As can be seen in the diagram, the armature coil is placed between the magnetic poles. An external DC source, a battery, is connected to the armature coil and current starts flowing through it. Since the current-carrying armature coil lies inside a magnetic field, they will experience a force which tends to rotate the armature.
Here, the arm of the armature coil near the North Pole of the magnet carries current in the upward direction along the plane of this screen. By applying Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, the direction of force F, experienced by this arm will be downwards perpendicular to the plane of this screen. A similar force will be experienced by the arm of the armature near the South Pole. Thus the armature coil tends to rotate in an anti-clockwise direction.
The direction of the current in the armature coil is reversed after every half rotation with the help of the split-ring commutator, to keep the coil rotating in the same direction. This reversal of current helps to develop a continuous and unidirectional torque.
Note:Electric motors find a vast array of applications in our daily life, mainly including blowers, fans, machine tools, pumps, turbines, power tools, alternators, compressors, rolling mills, ships, movers, paper mills, vacuum cleaners, dishwashers, computer printers, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




