
Explain series connections of Resistors and derive the formula of equivalent resistance.
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Resistor is an electrical component that is used to convert the current into the voltage or the voltage into the current. Resistors are said to be in series when they are connected in one line. Here, we will use ohm’s law to calculate the formula of equivalent resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circuit carrying a current $I$ in which three resistors are connected in series. A voltage $V$ is connected to the circuit.
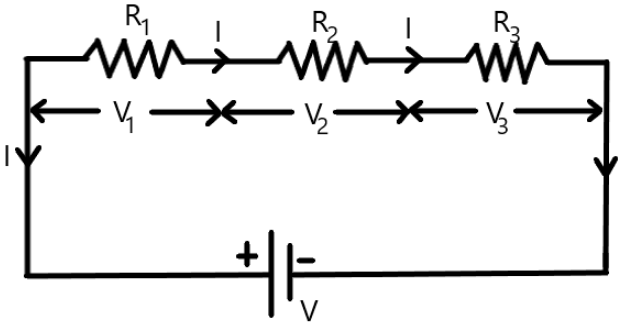
Here, ${R_1}$ , ${R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ are the resistors that are connected in series and ${V_1}$ , ${V_2}$ and ${V_3}$ are the voltage drops across the respective resistors.
Now, as the resistors are connected in series, the current flowing through the circuit will be the same across all the resistors. Now, the voltage $V$ across the circuit is given by
$V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} + ....$
Now, if a resistor $R$ is placed in the place of these three resistors ${R_1}$ , ${R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ such that the current in the circuit remains the same, then $R$ is called the equivalent resistance.
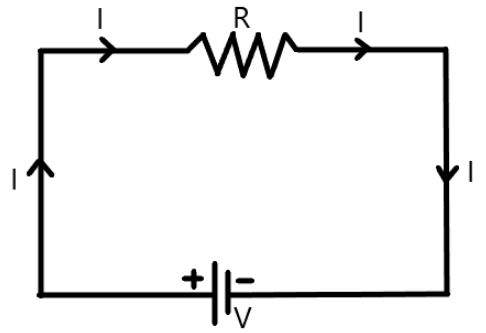
Therefore, for an equivalent resistance, $V = IR$.
Now, the voltage drop across the resistance ${R_1}$ is ${V_1} = I{R_1}$.
The voltage drop across the resistance ${R_2}$ is ${V_2} = I{R_2}$.
The voltage drop across the resistance ${R_3}$ is ${V_3} = I{R_3}$.
Therefore, the voltage $V$ across the circuit is given by,
$V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} + .....$
$ \Rightarrow \,V = I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_3}$
Now, taking $I$ common, we get
$V = I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)$
$ \therefore \,\dfrac{V}{I} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Now, as we know $V = IR$
Therefore, $\dfrac{V}{I} = R$
Therefore, the above equation becomes
$R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Which is the equivalent resistance.
Thus, we can say that the equivalent resistance $R$ in the circuit is the sum of all the individual resistances in the circuit.
Note:All the resistors in the series do not get a source voltage, therefore, they divide the voltage across them. Also, the amount of energy used by the resistors will be the same as the amount of energy used by a single resistor. This energy is also divided across the resistors depending upon their resistances.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circuit carrying a current $I$ in which three resistors are connected in series. A voltage $V$ is connected to the circuit.

Here, ${R_1}$ , ${R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ are the resistors that are connected in series and ${V_1}$ , ${V_2}$ and ${V_3}$ are the voltage drops across the respective resistors.
Now, as the resistors are connected in series, the current flowing through the circuit will be the same across all the resistors. Now, the voltage $V$ across the circuit is given by
$V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} + ....$
Now, if a resistor $R$ is placed in the place of these three resistors ${R_1}$ , ${R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ such that the current in the circuit remains the same, then $R$ is called the equivalent resistance.

Therefore, for an equivalent resistance, $V = IR$.
Now, the voltage drop across the resistance ${R_1}$ is ${V_1} = I{R_1}$.
The voltage drop across the resistance ${R_2}$ is ${V_2} = I{R_2}$.
The voltage drop across the resistance ${R_3}$ is ${V_3} = I{R_3}$.
Therefore, the voltage $V$ across the circuit is given by,
$V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} + .....$
$ \Rightarrow \,V = I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_3}$
Now, taking $I$ common, we get
$V = I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)$
$ \therefore \,\dfrac{V}{I} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Now, as we know $V = IR$
Therefore, $\dfrac{V}{I} = R$
Therefore, the above equation becomes
$R = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Which is the equivalent resistance.
Thus, we can say that the equivalent resistance $R$ in the circuit is the sum of all the individual resistances in the circuit.
Note:All the resistors in the series do not get a source voltage, therefore, they divide the voltage across them. Also, the amount of energy used by the resistors will be the same as the amount of energy used by a single resistor. This energy is also divided across the resistors depending upon their resistances.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




