
Explain motion.
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the concept of the motion. Thus, we will define the term motion, the types of motion and their applications or the usage. There are different types of motion. And the motion is classified on the basis of periodicity, path and the speed of the object/body. Path – circular, oscillatory, vibratory, translator and rotator. Periodicity – periodic and non-periodic. Speed – uniform and non-uniform.
Complete answer:
The rate of change in the position of the body/object is called the motion.
There are many types of motion. The motion along a straight path is called the linear motion. One of the types of linear motion is called the rectilinear motion. The rotational motion or the circular motion is the motion along a circular path. The change in the position of the object/body from point to the other through spinning is called the translational motion. The periodic motion or the oscillatory motion or the vibratory motion is a to and fro motion that involves the vibrations.
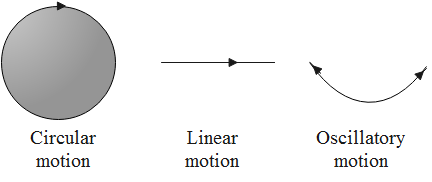
The examples of these motions are: In case of the motion of a swing, swing moves to and fro. As the cyclist moves on a plain road and not on a circular path, the motion will be linear. The stone falls along a linear path. When the string of a sitar is plucked, the string starts to vibrate. In case of the pendulum of a wall clock, the pendulum moves to and fro. A spinning ball spins and changes its position concerning time.
Note: The oscillatory motion is sometimes considered different from the vibration motion according to the situation. For example, in the case of plucking of a sitar string, the motion is considered to be vibration and not oscillatory.
Complete answer:
The rate of change in the position of the body/object is called the motion.
There are many types of motion. The motion along a straight path is called the linear motion. One of the types of linear motion is called the rectilinear motion. The rotational motion or the circular motion is the motion along a circular path. The change in the position of the object/body from point to the other through spinning is called the translational motion. The periodic motion or the oscillatory motion or the vibratory motion is a to and fro motion that involves the vibrations.

The examples of these motions are: In case of the motion of a swing, swing moves to and fro. As the cyclist moves on a plain road and not on a circular path, the motion will be linear. The stone falls along a linear path. When the string of a sitar is plucked, the string starts to vibrate. In case of the pendulum of a wall clock, the pendulum moves to and fro. A spinning ball spins and changes its position concerning time.
Note: The oscillatory motion is sometimes considered different from the vibration motion according to the situation. For example, in the case of plucking of a sitar string, the motion is considered to be vibration and not oscillatory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




