
Explain metal deficiency defect due to cation vacancies?
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Cation vacancies imply that cation is not present at its Lattice position and this missing cation may be present or absent in the crystal. Based on the presence or absence of missing cation from its Lattice position figure out possible defects.
Complete answer:
First we should know about the cationic vacancies. Cationic vacancies are possible when cation is not present in its Lattice position. There are defects where cation lattice position is vacant but the number of cations and anions will be balanced because both cations and anions missing will be equal or cation will be occupying an interstitial position. There are 2 types of nonstoichiometric defects which are either due to the presence of excess anions or excess cations.
When there are cationic vacancies these cations will be absent in the crystal. This will cause a charge imbalance. To balance this charge imbalance neighboring cations of missing cation will gain extra positive charge. This balances the charge on the crystal.
But there will be a lesser number of metal ions compared to crystals without vacancies which results in a change of composition of the crystal. That’s why this defect is called a non stoichiometric defect. This defect is possible only when there are two or more oxidation states of the metal ion. So, this defect is possible with d-block elements that show two or more oxidation states.
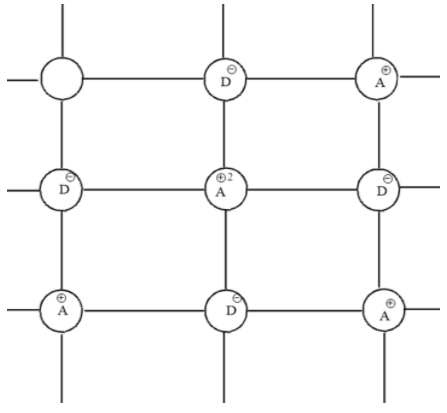
Note: Check the density and composition of crystal with each type of defect. Cation vacancy does not always result in a decrease in density. Also, check the fraction of metal ions which are in higher oxidation state to balance the charge of the crystal.
Complete answer:
First we should know about the cationic vacancies. Cationic vacancies are possible when cation is not present in its Lattice position. There are defects where cation lattice position is vacant but the number of cations and anions will be balanced because both cations and anions missing will be equal or cation will be occupying an interstitial position. There are 2 types of nonstoichiometric defects which are either due to the presence of excess anions or excess cations.
When there are cationic vacancies these cations will be absent in the crystal. This will cause a charge imbalance. To balance this charge imbalance neighboring cations of missing cation will gain extra positive charge. This balances the charge on the crystal.
But there will be a lesser number of metal ions compared to crystals without vacancies which results in a change of composition of the crystal. That’s why this defect is called a non stoichiometric defect. This defect is possible only when there are two or more oxidation states of the metal ion. So, this defect is possible with d-block elements that show two or more oxidation states.

Note: Check the density and composition of crystal with each type of defect. Cation vacancy does not always result in a decrease in density. Also, check the fraction of metal ions which are in higher oxidation state to balance the charge of the crystal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




