
Explain in detail the process of development of female gametophyte. Draw diagram.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: In most of the flowering plants, one of the megaspores is functional whereas the other three degenerate. The functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte.
Complete answer:
- The female reproductive part of a flower is known as gynoecium. Gynoecium consists of one or more pistils. Each pistil has three parts: stigma, style, and ovary. The ovarian cavity or locule is present inside the ovary. The placenta is located inside the locule. Ovules or megasporangium occur from the placenta. Each ovule has an embryo sac or female gametophyte in the nucellus.
- One diploid cell grows into a diploid megaspore mother cell in the nucleus of the developing ovule. This mother cell megaspore divides by meiosis to create four haploid megaspores arranged in a linear tetrad.
- One of the megaspores is usable, while the other three degenerate into angiosperms. The lower chalazal megaspore is formed by the female gametophyte.The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically into two nucleuses. They are called primary micropylar and primary chalazal nuclei.
- The second division produces a pair of nuclei at the micropylar end and a pair of nuclei at the chalazal end. The third division results in the creation of four nuclei at each pole. One nucleus from each pole then goes towards the middle to become polar nucleus, which fuse together and give rise to a secondary nucleus (2n).
- Out of these, the central one is the egg cell, while the two lateral cells are known as synergids. The three nuclei towards the chalazal end are also organized into three thin-walled cells named antipodal cells.
- The structure comprising egg apparatus, secondary nucleus and antipodal is termed as female gametophyte or embryo sac. As a result, the average angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-cell.
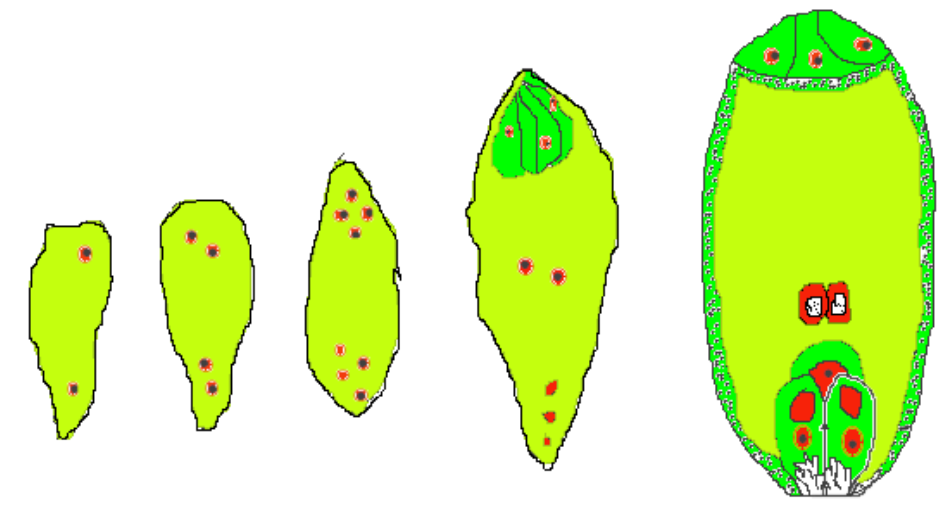
Fig: Development of female gametophyte
Note: The mechanism of formation of megaspores from the mother cell of megaspores is called megasporogenesis. Ovules typically distinguish a single mother cell megaspore (MMC) in the micropylar region of the nucleus. It is a large cell with a thick cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. The MMC is undergoing a meiotic division.
Complete answer:
- The female reproductive part of a flower is known as gynoecium. Gynoecium consists of one or more pistils. Each pistil has three parts: stigma, style, and ovary. The ovarian cavity or locule is present inside the ovary. The placenta is located inside the locule. Ovules or megasporangium occur from the placenta. Each ovule has an embryo sac or female gametophyte in the nucellus.
- One diploid cell grows into a diploid megaspore mother cell in the nucleus of the developing ovule. This mother cell megaspore divides by meiosis to create four haploid megaspores arranged in a linear tetrad.
- One of the megaspores is usable, while the other three degenerate into angiosperms. The lower chalazal megaspore is formed by the female gametophyte.The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically into two nucleuses. They are called primary micropylar and primary chalazal nuclei.
- The second division produces a pair of nuclei at the micropylar end and a pair of nuclei at the chalazal end. The third division results in the creation of four nuclei at each pole. One nucleus from each pole then goes towards the middle to become polar nucleus, which fuse together and give rise to a secondary nucleus (2n).
- Out of these, the central one is the egg cell, while the two lateral cells are known as synergids. The three nuclei towards the chalazal end are also organized into three thin-walled cells named antipodal cells.
- The structure comprising egg apparatus, secondary nucleus and antipodal is termed as female gametophyte or embryo sac. As a result, the average angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-cell.

Fig: Development of female gametophyte
Note: The mechanism of formation of megaspores from the mother cell of megaspores is called megasporogenesis. Ovules typically distinguish a single mother cell megaspore (MMC) in the micropylar region of the nucleus. It is a large cell with a thick cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. The MMC is undergoing a meiotic division.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




