
Explain hybridization of central atom in: $CO_{3}^{2-}$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Think which atom is the central atom in the given ion. Write the electronic configuration of both carbon and oxygen atoms. Find out the total number of electron pairs present in the system and accordingly figure out the hybridization.
Complete answer:
- Let’s start by counting the number of electron pairs present in the system.
- Carbon has atomic number 6 and oxygen has atomic number 8.
\[C=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}\]
\[O=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}\]
- Number of valence electrons in carbon is 4 and in oxygen is 6.
- Carbonate ion has one carbon atom, three oxygen atoms and -2 charge.
- Therefore, the total number of electrons present in carbonate ion $=4+\left( 3\times 6 \right)+2=24$.
- Therefore, the total number of electron pairs present is $\dfrac{24}{2}=12$.
-So, the Lewis dot structure of $CO_{3}^{2-}$ can be drawn as follows:
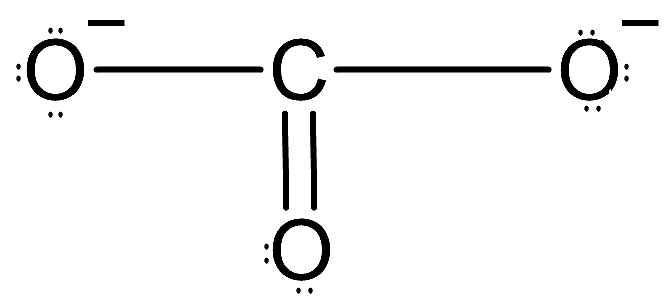
-Here, carbon is the central atom and we can see all twelve electron pairs are present and charge of the ion is also -2. Now, carbon is forming a double bond. We know that doubly bonded carbon is always $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.
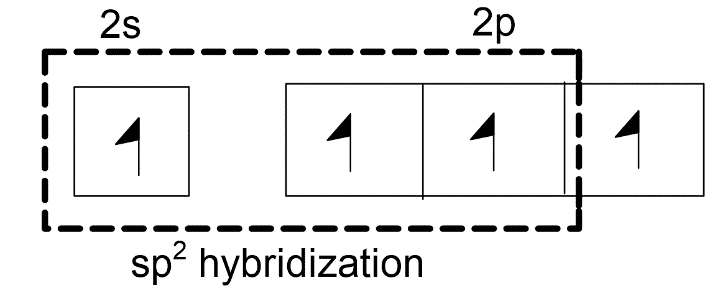
-One 1s orbital and two 2p orbitals will combine to form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized orbitals. One unhybridized 2p orbital of carbon will laterally overlap with one unhybridized 2p orbital of oxygen to form pi-bond. Thus, there is a presence of one double bond in the carbonate ion.
- Therefore, the carbon atom in carbonate ion, $CO_{3}^{2-}$ is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.
Note:
In this type of problems, start by writing electronic configuration and then calculating the total number of electron pairs and then, try drawing the structure to get an accurate answer. Carbonyl ion has trigonal planar geometry.
Complete answer:
- Let’s start by counting the number of electron pairs present in the system.
- Carbon has atomic number 6 and oxygen has atomic number 8.
\[C=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}\]
\[O=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}\]
- Number of valence electrons in carbon is 4 and in oxygen is 6.
- Carbonate ion has one carbon atom, three oxygen atoms and -2 charge.
- Therefore, the total number of electrons present in carbonate ion $=4+\left( 3\times 6 \right)+2=24$.
- Therefore, the total number of electron pairs present is $\dfrac{24}{2}=12$.
-So, the Lewis dot structure of $CO_{3}^{2-}$ can be drawn as follows:

-Here, carbon is the central atom and we can see all twelve electron pairs are present and charge of the ion is also -2. Now, carbon is forming a double bond. We know that doubly bonded carbon is always $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.

-One 1s orbital and two 2p orbitals will combine to form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized orbitals. One unhybridized 2p orbital of carbon will laterally overlap with one unhybridized 2p orbital of oxygen to form pi-bond. Thus, there is a presence of one double bond in the carbonate ion.
- Therefore, the carbon atom in carbonate ion, $CO_{3}^{2-}$ is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.
Note:
In this type of problems, start by writing electronic configuration and then calculating the total number of electron pairs and then, try drawing the structure to get an accurate answer. Carbonyl ion has trigonal planar geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




