
Explain how the properties of iron can be changed by the addition of carbon?
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: As carbon atoms are larger than the iron atoms, so when they go inside the interstices of the crystal lattice of iron, imperfections are created and the iron becomes harder.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about impurity defects. Foreign atoms can occupy interstitial or substitutional sites in a crystal. Defects in the ionic solids can be found out by adding impurity ions. If the impurity ions have different valence states than that of the host ions, vacancies are created. For example, addition of $SrC{{l}_{2}}$ to NaCl yields solids solutions where each $S{{r}^{2+}}$ ion replaces two $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions. $S{{r}^{2+}}$ion occupies the site of one Nation whereas the other site remains vacant. Thus, it produces cation vacancies equal to the number of the $S{{r}^{2+}}$ ions occupying substitutional sites.
In the metallic crystal of iron, the atoms are held very tightly to each other by application of strong metallic bonds. So, in order to deform the crystal structure, a lot of force needs to be applied. However, there are some vacancies created in the crystal structure of iron.
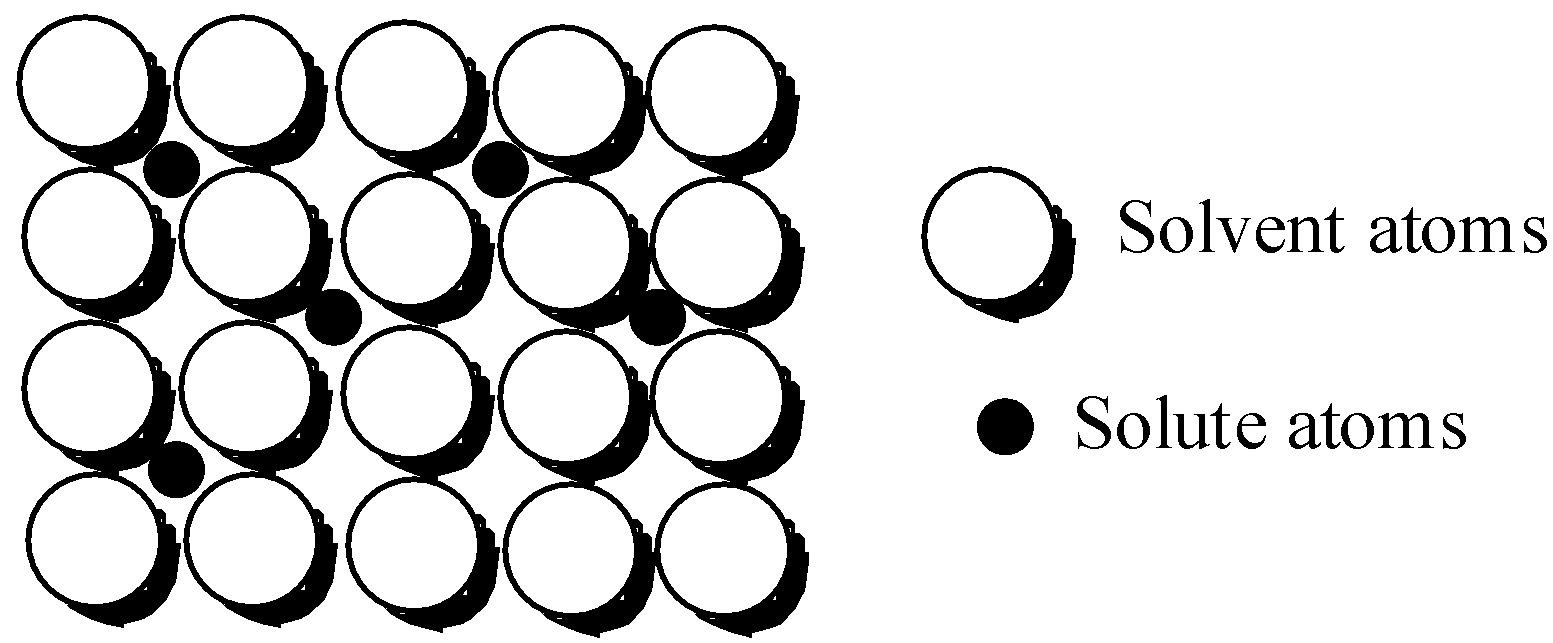
But, the carbon atom is larger in size than the iron atom, so it is larger to fit inside the perfectly arranged interstices of the crystal lattice. As a result, a lot of imperfections are created and no more vacant space is left out. Iron is relatively soft, but after introducing carbon, the layers do not slide past each other easily and this makes the iron harder.
Note:
The process of introducing an external element in a metal crystal lattice to improve its properties is called doping.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about impurity defects. Foreign atoms can occupy interstitial or substitutional sites in a crystal. Defects in the ionic solids can be found out by adding impurity ions. If the impurity ions have different valence states than that of the host ions, vacancies are created. For example, addition of $SrC{{l}_{2}}$ to NaCl yields solids solutions where each $S{{r}^{2+}}$ ion replaces two $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions. $S{{r}^{2+}}$ion occupies the site of one Nation whereas the other site remains vacant. Thus, it produces cation vacancies equal to the number of the $S{{r}^{2+}}$ ions occupying substitutional sites.
In the metallic crystal of iron, the atoms are held very tightly to each other by application of strong metallic bonds. So, in order to deform the crystal structure, a lot of force needs to be applied. However, there are some vacancies created in the crystal structure of iron.
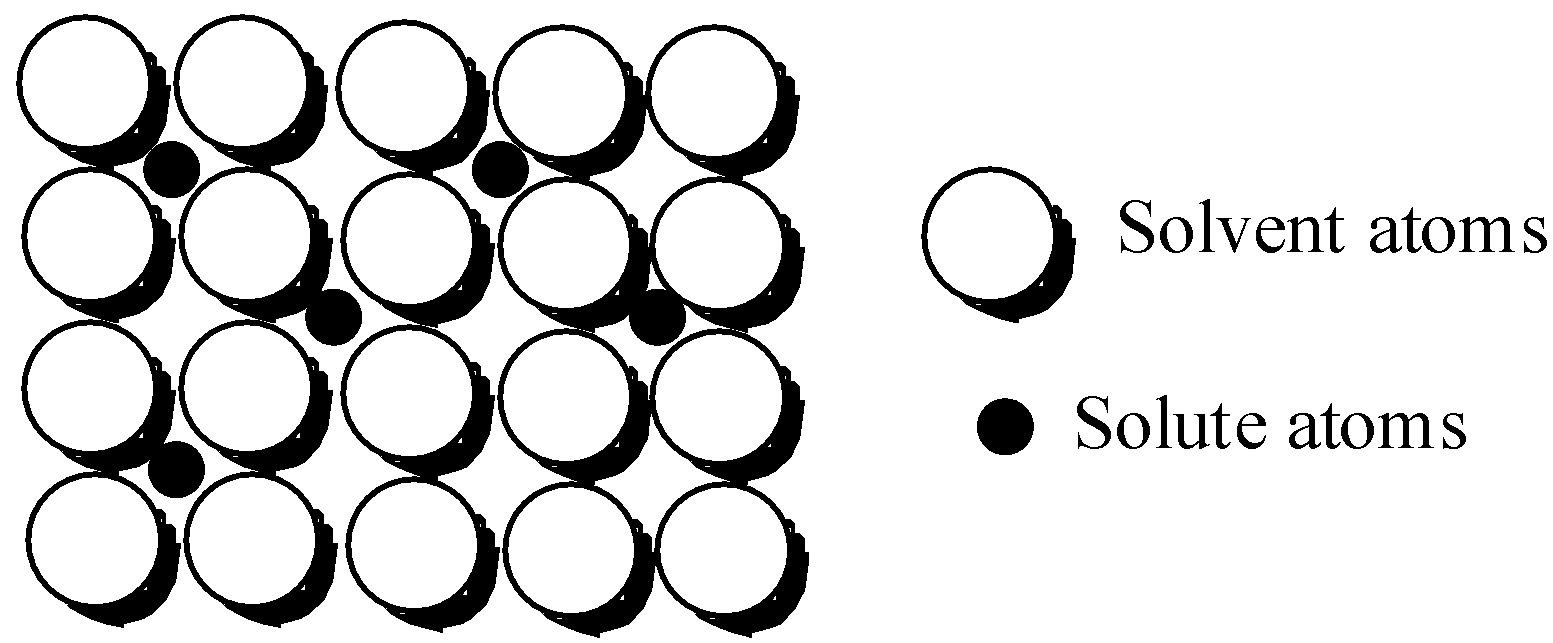
But, the carbon atom is larger in size than the iron atom, so it is larger to fit inside the perfectly arranged interstices of the crystal lattice. As a result, a lot of imperfections are created and no more vacant space is left out. Iron is relatively soft, but after introducing carbon, the layers do not slide past each other easily and this makes the iron harder.
Note:
The process of introducing an external element in a metal crystal lattice to improve its properties is called doping.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




