
Explain each of these shapes and write the number of lines of symmetry in each shape.
i.Scalene triangle
ii.Isosceles triangle
iii.Equilateral triangle
iv.Rectangle
v.Square
vi.Parallelogram
vii.Rhombus
viii..Line
ix.Line Segment
x.Angle
xi.Isosceles trapezium
xii.Kite
xiii.Arrow
xiv.Circle
xv.Semi-circle
xvi.Regular pentagon
xvii.Regular Hexagon
Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint: We are given the names of $ 17 $ shapes here. We will first explain all the types of shapes given here in a sentence or two. A line of symmetry is a line that cuts a shape exactly in half. There can be multiple lines of symmetry for a given figure. We will analyze the number of lines of symmetry through diagrams.
Complete step-by-step answer:
i.Scalene triangle
A scalene triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of all three sides are different and all angles are different is called a scalene triangle.
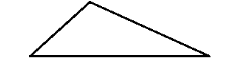
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
ii.Isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of two sides of the triangle are equal and the two angles opposite to equal sides are equal is called an isosceles triangle.
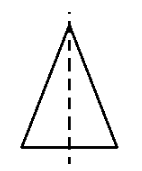
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
iii.Equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of all three sides of the triangle are equal and all angles are equal is called an equilateral triangle.
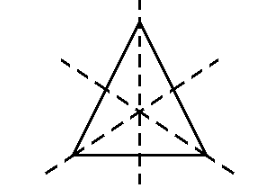
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 3 $ .
iv.Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral in which all angles as right angles and the lengths of opposite sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 2 $ .
v.Square
A square is a quadrilateral whose all angles have right angles and the lengths of all four sides are equal.
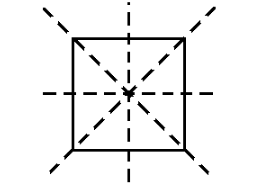
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 4 $ .
vi.Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral whose opposite angles are equal and the lengths of opposite sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
vii.Rhombus
A rhombus is a parallelogram whose all sides are equal.
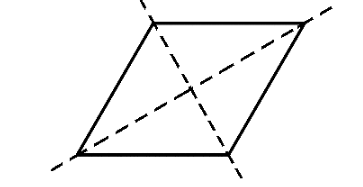
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 2 $ .
viii.Line
Line is a long thin mark made by a pen or a pencil. It has length but no width and is a one-dimensional figure. A line goes endless on both sides.
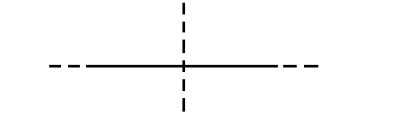
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
ix.Line Segment
Line segment is a measurable piece of line segment. It has a fixed length.
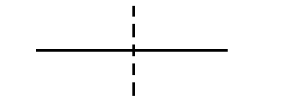
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
x.Angle
Angle is a figure obtained when two rays meet at a point.
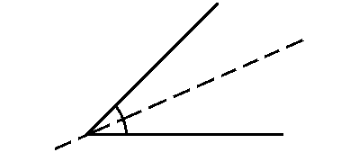
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xi.Isosceles trapezium
An isosceles trapezium is a quadrilateral whose one pair of opposite sides is parallel and another pair of opposite sides is equal.
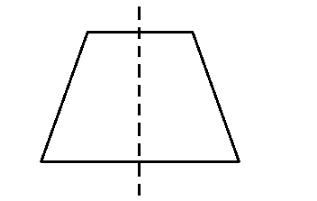
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xii.Kite
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides, and the sides of the first pair are equal and the sides of the second pair are equal.
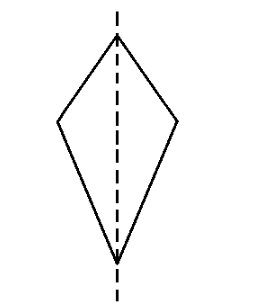
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xiii.Arrow
An arrow is a projectile moving towards a point. It has no width. It has a head and a tail.
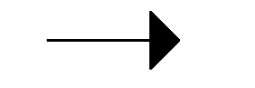
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
xiv.Circle
A circle is a figure obtained by drawing a curve around a fixed point at a fixed length from that point.
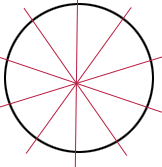
Number of lines of symmetry is infinite.
xv.Semi-circle
A semi-circle is a figure obtained by cutting a circle in half.
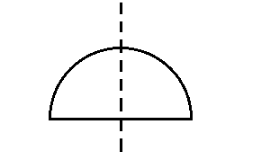
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xvi.Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon is a pentagon whose all five sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 5 $ .
xvii.Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a hexagon whose all six sides are equal.
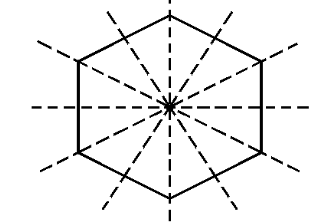
Number of lines of symmetry is $ 6 $ .
Note: A line of symmetry is a line that cuts a shape or a figure in half. The lines of symmetry can be perpendicular to the sides of a polygon. It can be diagonals of the polygon also.
In cases of each line and line segment, the number of lines of symmetry is 1 because there would be only one point at which if cut, the shape would be cut in half.
In the case of a circle, the number of lines of symmetry is infinite because infinite numbers of diameters can be drawn which would cut a circle in half.
For a regular polygon, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides of the polygon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
i.Scalene triangle
A scalene triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of all three sides are different and all angles are different is called a scalene triangle.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
ii.Isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of two sides of the triangle are equal and the two angles opposite to equal sides are equal is called an isosceles triangle.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
iii.Equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which the lengths of all three sides of the triangle are equal and all angles are equal is called an equilateral triangle.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 3 $ .
iv.Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral in which all angles as right angles and the lengths of opposite sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 2 $ .
v.Square
A square is a quadrilateral whose all angles have right angles and the lengths of all four sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 4 $ .
vi.Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral whose opposite angles are equal and the lengths of opposite sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
vii.Rhombus
A rhombus is a parallelogram whose all sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 2 $ .
viii.Line
Line is a long thin mark made by a pen or a pencil. It has length but no width and is a one-dimensional figure. A line goes endless on both sides.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
ix.Line Segment
Line segment is a measurable piece of line segment. It has a fixed length.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
x.Angle
Angle is a figure obtained when two rays meet at a point.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xi.Isosceles trapezium
An isosceles trapezium is a quadrilateral whose one pair of opposite sides is parallel and another pair of opposite sides is equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xii.Kite
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides, and the sides of the first pair are equal and the sides of the second pair are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xiii.Arrow
An arrow is a projectile moving towards a point. It has no width. It has a head and a tail.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 0 $ .
xiv.Circle
A circle is a figure obtained by drawing a curve around a fixed point at a fixed length from that point.

Number of lines of symmetry is infinite.
xv.Semi-circle
A semi-circle is a figure obtained by cutting a circle in half.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 1 $ .
xvi.Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon is a pentagon whose all five sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 5 $ .
xvii.Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a hexagon whose all six sides are equal.

Number of lines of symmetry is $ 6 $ .
Note: A line of symmetry is a line that cuts a shape or a figure in half. The lines of symmetry can be perpendicular to the sides of a polygon. It can be diagonals of the polygon also.
In cases of each line and line segment, the number of lines of symmetry is 1 because there would be only one point at which if cut, the shape would be cut in half.
In the case of a circle, the number of lines of symmetry is infinite because infinite numbers of diameters can be drawn which would cut a circle in half.
For a regular polygon, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides of the polygon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




