
Explain Clemmenson’s reduction with an example.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: Clemmenson’s reduction is a reduction reaction which involves formation of saturated hydrocarbons from carbonyl compounds. This reaction is similar to Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction except for the reagents and catalysts used and the pH conditions.
Complete step by step answer:
- In Clemmenson’s reduction, aldehydes or ketones which are not sensitive to acids are reduced to alkanes when heated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- Clemmenson’s reduction is a deoxygenation reaction which involves removal of oxygen from carbonyl compounds to form alkanes.
- In this reaction, $C=O$ is reduced to $-C{{H}_{2}}-$ group.
- Clemmenson’s reduction is most commonly used to convert acyl benzenes to alkyl benzenes.
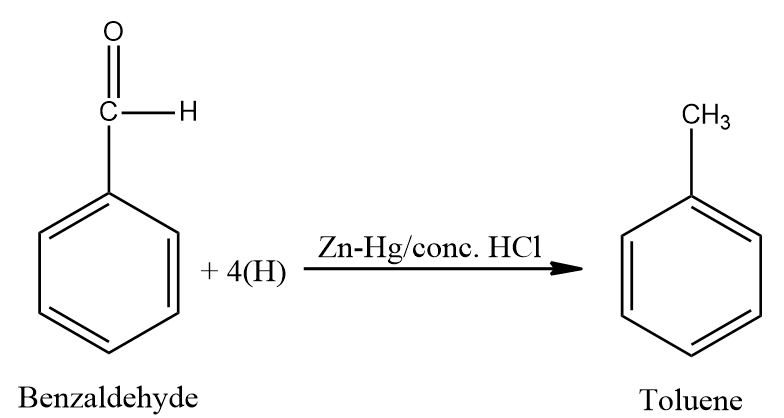
- Benzaldehyde undergoes Clemmenson’s reduction in the presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid to form toluene.
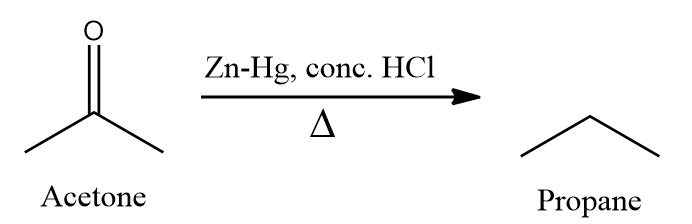
- One more example can be conversion of acetone to n-propane.
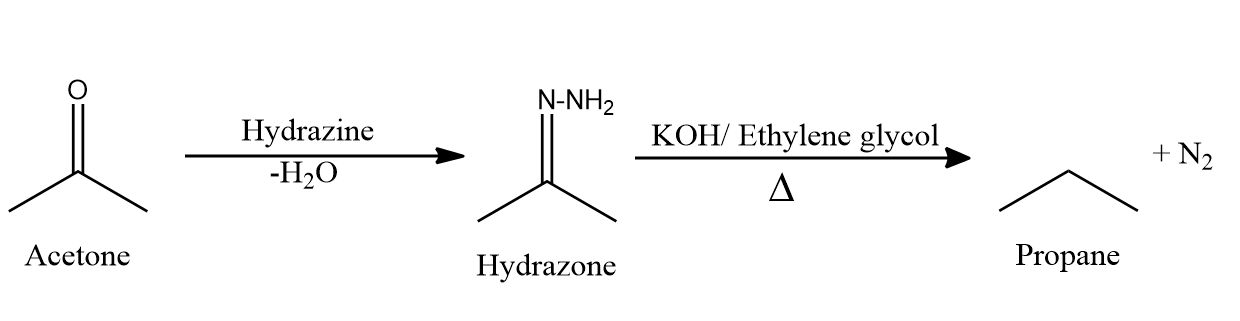
- Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction is also similar to Clemmenson’s reduction reaction.
- In Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction, carbonyl compounds are heated with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide or potassium tert-butoxide in presence of boiling solvents such as ethylene glycol or diethylene glycol to give alkanes.
- First the carbonyl compounds react with hydrazine to form hydrazine which on heating under basic conditions gives alkane with evolution of nitrogen gas.
- The only difference in both the reactions is the reaction conditions and the catalysts used.
Note: Remember Clemmenson’s reaction is a deoxygenation reaction in which carbonyl compounds are reduced to alkanes. Clemmenson’s reaction and Wolff –Kishner reaction yield the same final product. The difference between the two reactions is that Clemmenson’s reaction takes place in acidic condition in the presence of zinc amalgam and heat and Wolff-Kishner’s reaction takes place in basic conditions in the presence of hydrazine and solvent ethylene glycol.
Complete step by step answer:
- In Clemmenson’s reduction, aldehydes or ketones which are not sensitive to acids are reduced to alkanes when heated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- Clemmenson’s reduction is a deoxygenation reaction which involves removal of oxygen from carbonyl compounds to form alkanes.
- In this reaction, $C=O$ is reduced to $-C{{H}_{2}}-$ group.
- Clemmenson’s reduction is most commonly used to convert acyl benzenes to alkyl benzenes.

- Benzaldehyde undergoes Clemmenson’s reduction in the presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid to form toluene.
- One more example can be conversion of acetone to n-propane.

- Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction is also similar to Clemmenson’s reduction reaction.
- In Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction, carbonyl compounds are heated with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide or potassium tert-butoxide in presence of boiling solvents such as ethylene glycol or diethylene glycol to give alkanes.
- First the carbonyl compounds react with hydrazine to form hydrazine which on heating under basic conditions gives alkane with evolution of nitrogen gas.

- The only difference in both the reactions is the reaction conditions and the catalysts used.
Note: Remember Clemmenson’s reaction is a deoxygenation reaction in which carbonyl compounds are reduced to alkanes. Clemmenson’s reaction and Wolff –Kishner reaction yield the same final product. The difference between the two reactions is that Clemmenson’s reaction takes place in acidic condition in the presence of zinc amalgam and heat and Wolff-Kishner’s reaction takes place in basic conditions in the presence of hydrazine and solvent ethylene glycol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




