
Explain cleansing action of soap.
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Soap is nothing but sodium or potassium salts of long chains of carboxylic acids. Soap contains two ends having dissimilar properties. One end has hydrophobic character and another end has hydrophilic character.
Complete step by step answer:
When soap is added to water then soap forms two ions (cation and anion).
We can see the dissociation of soap in the following equation.
\[\underset{\text{Sodium palmitate (Soap)}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{14}}COONa}}\,\to \underset{\text{Palmitate ion (Soap anion)}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{14}}CO{{O}^{-}}}}\,+\underset{\text{sodium cation}}{\mathop{N{{a}^{+}}}}\,\]
The soap anion contains two ends.
One end is called hydrophilic end (contains carboxyl group) and the other end called hydrophobic end (contains hydrocarbon chain).
The hydrophilic part is soluble in water and the hydrophobic part is soluble in oils or grease.
When soap is added to water then the long hydrocarbon chains arrange themselves to form micelles and trap the dirt at the center of the cluster.
In micelles hydrophilic part exposes to outside the micelle and hydrophobic part exposes towards the dirt or grease.
The micelles suspended in water like a particle in colloidal solution.
The micelles formed in the solution don’t come nearer to one another to form a precipitate because they repel each other due to ion-ion repulsions.
Therefore the dust stays or is trapped inside (hydrophobic end) of the micelle itself and easily removed by rinsing with water.
Thus micelles formed by soap remove dirt by cleaning with water.
The structure of the micelles looks like as follows.
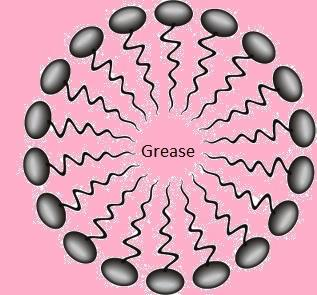
Note: Hydrophobic means water hating, hydrophilic means water loving. That is why the hydrophobic end in micelles is not exposed to aqueous solution and the hydrophilic end in micelles is exposed toward water. The hydrophobic end of micelle is exposed towards the grease or dirt.
Complete step by step answer:
When soap is added to water then soap forms two ions (cation and anion).
We can see the dissociation of soap in the following equation.
\[\underset{\text{Sodium palmitate (Soap)}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{14}}COONa}}\,\to \underset{\text{Palmitate ion (Soap anion)}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{14}}CO{{O}^{-}}}}\,+\underset{\text{sodium cation}}{\mathop{N{{a}^{+}}}}\,\]
The soap anion contains two ends.
One end is called hydrophilic end (contains carboxyl group) and the other end called hydrophobic end (contains hydrocarbon chain).
The hydrophilic part is soluble in water and the hydrophobic part is soluble in oils or grease.
When soap is added to water then the long hydrocarbon chains arrange themselves to form micelles and trap the dirt at the center of the cluster.
In micelles hydrophilic part exposes to outside the micelle and hydrophobic part exposes towards the dirt or grease.
The micelles suspended in water like a particle in colloidal solution.
The micelles formed in the solution don’t come nearer to one another to form a precipitate because they repel each other due to ion-ion repulsions.
Therefore the dust stays or is trapped inside (hydrophobic end) of the micelle itself and easily removed by rinsing with water.
Thus micelles formed by soap remove dirt by cleaning with water.
The structure of the micelles looks like as follows.

Note: Hydrophobic means water hating, hydrophilic means water loving. That is why the hydrophobic end in micelles is not exposed to aqueous solution and the hydrophilic end in micelles is exposed toward water. The hydrophobic end of micelle is exposed towards the grease or dirt.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




