
Expand the given expression: \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = ?\]
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Here in this question let us consider two squares, one of side a and other of side b. Side a is twice than the side of the other square i.e. side b. Smaller square is inside the larger square at one of its corners. So, by simply subtracting the area of these squares will give us the required formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
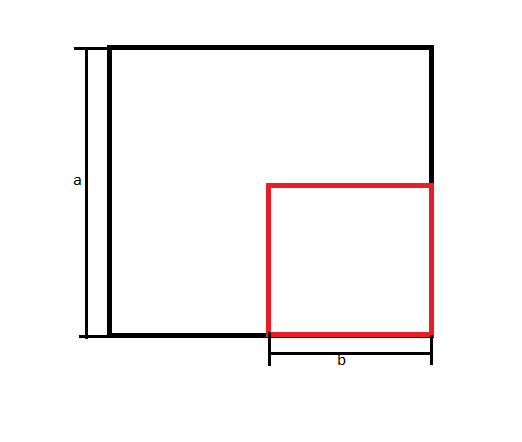
As we all know that the area of the square is \[{{\rm{(side)}}^2}\]
So the area of larger square is \[{{\rm{a}}^2}\]
And the area of the smaller square is \[{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
Now subtract the area of the smaller square from the bigger square, we get \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
As shown in the figure now we have to find out the area of the green shaded region to find the value of the \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
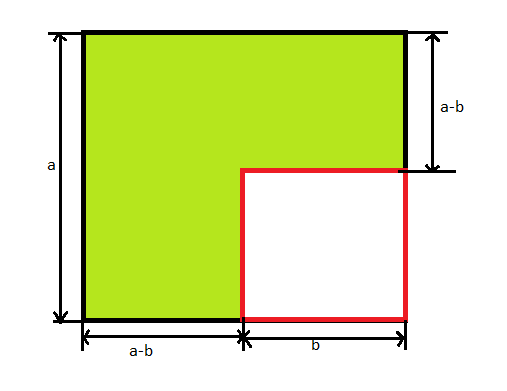
So, area of the shaded portion = \[{\rm{((a - b)}} \times {\rm{a) + ((a - b)}} \times {\rm{b)}}\]
Now by taking \[{\rm{(a - b)}}\] common in the above equation, we get
So, area of the shaded portion = \[{\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
\[\therefore {{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
Hence \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\].
Note: Algebraic identities in maths refer to an equation that is always true regardless of the values assigned to the variables. Algebraic identities are equations where the value of the left-hand side of the equation is identically equal to the value of the right-hand side of the equation. An algebraic identity is an equality that holds for any values of its variables. We have to remember that mathematics can be solved by using this approach and also we have to remember the basic mathematics identity. It is very important that we learn about algebraic identities in maths.
\[{\left( {{\rm{a }} + {\rm{ b}}} \right)^2}\; = {\rm{ }}{{\rm{a}}^2}\; + {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ab }} + {\rm{ }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
\[{\left( {{\rm{a - b}}} \right)^2}\; = {\rm{ }}{{\rm{a}}^2}\; - {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ab }} + {\rm{ }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
\[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:

As we all know that the area of the square is \[{{\rm{(side)}}^2}\]
So the area of larger square is \[{{\rm{a}}^2}\]
And the area of the smaller square is \[{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
Now subtract the area of the smaller square from the bigger square, we get \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
As shown in the figure now we have to find out the area of the green shaded region to find the value of the \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]

So, area of the shaded portion = \[{\rm{((a - b)}} \times {\rm{a) + ((a - b)}} \times {\rm{b)}}\]
Now by taking \[{\rm{(a - b)}}\] common in the above equation, we get
So, area of the shaded portion = \[{\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
\[\therefore {{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
Hence \[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\].
Note: Algebraic identities in maths refer to an equation that is always true regardless of the values assigned to the variables. Algebraic identities are equations where the value of the left-hand side of the equation is identically equal to the value of the right-hand side of the equation. An algebraic identity is an equality that holds for any values of its variables. We have to remember that mathematics can be solved by using this approach and also we have to remember the basic mathematics identity. It is very important that we learn about algebraic identities in maths.
\[{\left( {{\rm{a }} + {\rm{ b}}} \right)^2}\; = {\rm{ }}{{\rm{a}}^2}\; + {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ab }} + {\rm{ }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
\[{\left( {{\rm{a - b}}} \right)^2}\; = {\rm{ }}{{\rm{a}}^2}\; - {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ab }} + {\rm{ }}{{\rm{b}}^2}\]
\[{{\rm{a}}^2}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{b}}^2} = {\rm{(a - b)}}({\rm{a + b)}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Full Form of IASDMIPSIFSIRSPOLICE class 7 social science CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





