
Expand \[\sin (45 + x)\]
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: We will use the concepts of trigonometry to solve this problem. We will prove the trigonometric ratios of compound angles and from the result, we will find the required value. We will use some theorems related to parallel line and use the standard ratio \[\cos 45 = \sin 45 = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\].
Complete answer:
Generally, trigonometry deals with ratios and equations related to sides and angles of right-angled triangles. And we can use this trigonometry in a standard way in many situations and cases.
In mathematics, the sine value of an angle is equal to the ratio of side opposite to the angle to hypotenuse.
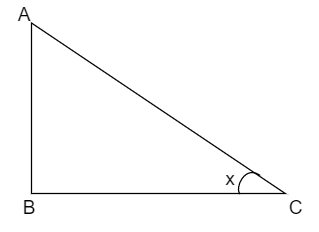
Consider this right triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\] right angled at B. Here, the side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
So, sine value of angle \[x\] is defined as ratio of side opposite to this angle to the length of hypotenuse. So, \[\sin x = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Now consider this figure.
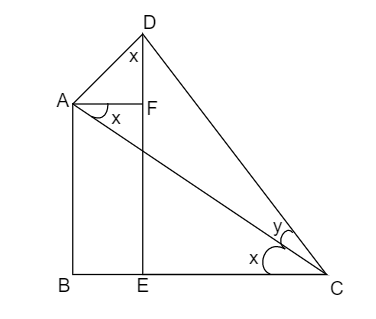
The lines \[AF\] and \[BC\] are parallel. So, by alternate angle theorem, \[\angle BCA = \angle CAF = x\]
And, \[\angle CAF = \angle FDA\]. So, \[\angle FDA = x\]
And also, the line \[AC\] is perpendicular to line \[AD\]. So, \[\angle CAD = {90^ \circ }\].
So, in \[\vartriangle CED\], \[\sin C = \dfrac{{DE}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF + FE}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{FE}}{{DC}}\]
And the length \[FE\] is equal to \[AB\]
So, we get \[\sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{AB}}{{DC}}\]
Now, divide and multiply the first fraction by \[DA\] and the second fraction by \[AC\].
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{AD}}.\dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}.\dfrac{{AC}}{{DC}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ADF\], \[\cos x = \dfrac{{DF}}{{AD}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ADC\], \[\sin y = \dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}}\] and \[\cos y = \dfrac{{AC}}{{DC}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[\sin x = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
So, we can write it as,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \cos x.\sin y + \sin x.\cos y\]
In this, substitute the value of \[y\] as 45 degrees. So, \[\sin (45 + x) = \cos x.\sin 45 + \sin x.\cos 45\]
We know that, \[\cos 45 = \sin 45 = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (45 + x) = \cos x.\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} + \sin x.\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (45 + x) = \dfrac{{\sin x + \cos x}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
This is the required value.
This is a standard result. So, we can find sine values of many angles by changing the values of \[x\] as per our wish and requirement.
Note: We can standardize our result and write it as \[\sin (A \pm B) = \sin A\cos B \pm \sin B\cos A\]
And also, \[\cos (A \pm B) = \cos A\cos B \mp \sin A\sin B\].
And \[\tan (A \pm B) = \dfrac{{\tan A \pm \tan B}}{{1 \mp \tan A\tan B}}\]
These are the compound angles formula. Remember these for your future needs.
Complete answer:
Generally, trigonometry deals with ratios and equations related to sides and angles of right-angled triangles. And we can use this trigonometry in a standard way in many situations and cases.
In mathematics, the sine value of an angle is equal to the ratio of side opposite to the angle to hypotenuse.

Consider this right triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\] right angled at B. Here, the side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
So, sine value of angle \[x\] is defined as ratio of side opposite to this angle to the length of hypotenuse. So, \[\sin x = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Now consider this figure.

The lines \[AF\] and \[BC\] are parallel. So, by alternate angle theorem, \[\angle BCA = \angle CAF = x\]
And, \[\angle CAF = \angle FDA\]. So, \[\angle FDA = x\]
And also, the line \[AC\] is perpendicular to line \[AD\]. So, \[\angle CAD = {90^ \circ }\].
So, in \[\vartriangle CED\], \[\sin C = \dfrac{{DE}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF + FE}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{FE}}{{DC}}\]
And the length \[FE\] is equal to \[AB\]
So, we get \[\sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{AB}}{{DC}}\]
Now, divide and multiply the first fraction by \[DA\] and the second fraction by \[AC\].
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \dfrac{{DF}}{{AD}}.\dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}} + \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}.\dfrac{{AC}}{{DC}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ADF\], \[\cos x = \dfrac{{DF}}{{AD}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ADC\], \[\sin y = \dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}}\] and \[\cos y = \dfrac{{AC}}{{DC}}\]
In \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[\sin x = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
So, we can write it as,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (x + y) = \cos x.\sin y + \sin x.\cos y\]
In this, substitute the value of \[y\] as 45 degrees. So, \[\sin (45 + x) = \cos x.\sin 45 + \sin x.\cos 45\]
We know that, \[\cos 45 = \sin 45 = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (45 + x) = \cos x.\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} + \sin x.\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin (45 + x) = \dfrac{{\sin x + \cos x}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
This is the required value.
This is a standard result. So, we can find sine values of many angles by changing the values of \[x\] as per our wish and requirement.
Note: We can standardize our result and write it as \[\sin (A \pm B) = \sin A\cos B \pm \sin B\cos A\]
And also, \[\cos (A \pm B) = \cos A\cos B \mp \sin A\sin B\].
And \[\tan (A \pm B) = \dfrac{{\tan A \pm \tan B}}{{1 \mp \tan A\tan B}}\]
These are the compound angles formula. Remember these for your future needs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




