
Evaluate the definite integral:
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos xdx} $
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We know that $\int {\cos xdx} $$ = \sin x$ and while putting upper and lower limits, you will get your answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that integration represents the area under the curve, here we are given to find the integral of the curve $\cos x$ in the limit from $0$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So now let us see by the graph what we need to find.
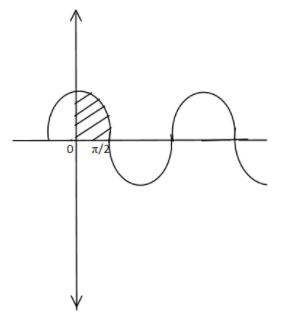
So this is the graph of $\cos x$ and we need to find the $\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x dx} $ that means that we need to find the area which is shaded or the curve of the $\cos x$ from $0$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Now we know that integration of \[\cos x\] gives $\sin x$ and we know the formula that
$\int\limits_a^b {\cos nx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin x}}{n}} \right]_a^b$
$\int\limits_a^b {\cos nx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin nb}}{n} - \dfrac{{\sin na}}{n}} \right]$
So in this question, we are given:
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x dx} $
Now we know that
$\int {\cos nxdx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin nx}}{n}} \right]$ and here $n = 1$
So we get $\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin x} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}$
Here$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ is the upper limit and $0$ is the lower limit.
So upon putting we get
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin 0} \right]$
We know that $\sin 0 = 0,\sin 90 = 1$
We get that
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin 0} \right] = 1$
Note: We should know that if $\dfrac{{df(x)}}{{dx}} = g(x)$, then $\int {g(x)dx} $ gives $f(x)$ or vice-versa similarly.
$\int {\cos x} dx$ gives $\sin x$. So $\dfrac{{d\sin x}} {{dx}} = \cos x$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that integration represents the area under the curve, here we are given to find the integral of the curve $\cos x$ in the limit from $0$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So now let us see by the graph what we need to find.

So this is the graph of $\cos x$ and we need to find the $\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x dx} $ that means that we need to find the area which is shaded or the curve of the $\cos x$ from $0$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Now we know that integration of \[\cos x\] gives $\sin x$ and we know the formula that
$\int\limits_a^b {\cos nx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin x}}{n}} \right]_a^b$
$\int\limits_a^b {\cos nx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin nb}}{n} - \dfrac{{\sin na}}{n}} \right]$
So in this question, we are given:
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x dx} $
Now we know that
$\int {\cos nxdx} = \left[ {\dfrac{{\sin nx}}{n}} \right]$ and here $n = 1$
So we get $\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin x} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}$
Here$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ is the upper limit and $0$ is the lower limit.
So upon putting we get
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin 0} \right]$
We know that $\sin 0 = 0,\sin 90 = 1$
We get that
$\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\cos x} = \left[ {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin 0} \right] = 1$
Note: We should know that if $\dfrac{{df(x)}}{{dx}} = g(x)$, then $\int {g(x)dx} $ gives $f(x)$ or vice-versa similarly.
$\int {\cos x} dx$ gives $\sin x$. So $\dfrac{{d\sin x}} {{dx}} = \cos x$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




