
How do you evaluate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$ ?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: First, we need to analyze the given information so that we can able to solve the problem.Generally, in Mathematics, the trigonometric Identities are useful whenever trigonometric functions are involved in an expression or an equation and these identities are useful whenever expressions involving trigonometric functions need to be simplified.Here we are asked to calculate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
We need to apply the appropriate trigonometric identities to obtain the required answer.
Formula to be used:
The trigonometric identity that is used to solve the given problem is as follows.
$\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are asked to calculate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
Now we are asked to calculate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
We all know that the value of $\pi $ is ${180^\circ }$
Thus, we have
$\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3 \times {{180}^\circ }} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {3 \times {{90}^\circ }} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {{{270}^\circ }} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {{{270}^\circ } + 0} \right)$
The trigonometric identity that is used to solve the given problem is as follows.
$\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left({{ {270}^\circ } + 0} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - \cos 0$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Hence, $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Note:
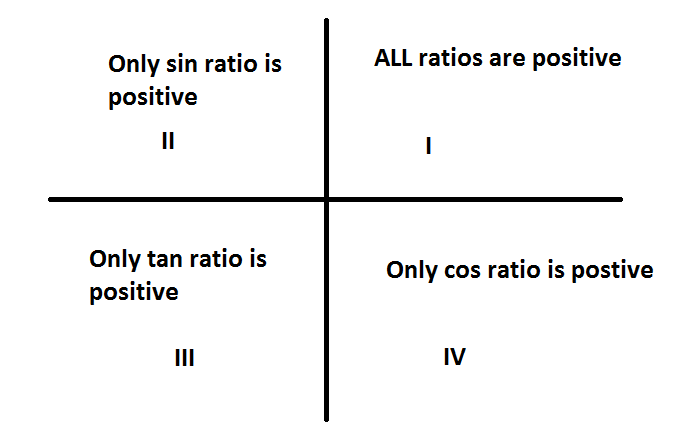
Here in the first quadrant, all ratios are positive. In the second quadrant, only sine is positive, and in the third quadrant, only the tangent ratio is positive. And in the fourth quadrant, only the cosine ratio is positive.
When we are given $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right)$ , we need to understand $\sin 270$ is in between the third and fourth quadrant and $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right)$ is in the fourth quadrant. In the fourth quadrant, only the cos ratio is positive and sin is negative. That’s why we got minus sign in this trigonometric identity $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
We need to apply the appropriate trigonometric identities to obtain the required answer.
Formula to be used:
The trigonometric identity that is used to solve the given problem is as follows.
$\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are asked to calculate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
Now we are asked to calculate $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
We all know that the value of $\pi $ is ${180^\circ }$
Thus, we have
$\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3 \times {{180}^\circ }} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {3 \times {{90}^\circ }} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {{{270}^\circ }} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left( {{{270}^\circ } + 0} \right)$
The trigonometric identity that is used to solve the given problem is as follows.
$\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = \sin \left({{ {270}^\circ } + 0} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - \cos 0$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Hence, $\sin \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {3\pi} \right)}}{2}} \right) = - 1$
Note:

Here in the first quadrant, all ratios are positive. In the second quadrant, only sine is positive, and in the third quadrant, only the tangent ratio is positive. And in the fourth quadrant, only the cosine ratio is positive.
When we are given $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right)$ , we need to understand $\sin 270$ is in between the third and fourth quadrant and $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right)$ is in the fourth quadrant. In the fourth quadrant, only the cos ratio is positive and sin is negative. That’s why we got minus sign in this trigonometric identity $\sin \left( {270 + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




