
Evaluate \[\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)} \right)\].
Answer
461.7k+ views
Hint: In the given problem, we are required to calculate the cosine of an angle whose sine is given to us. Such problems require basic knowledge of trigonometric ratios and formulae. Besides this, knowledge of concepts of inverse trigonometry is extremely essential to answer these questions correctly.
Formula used:
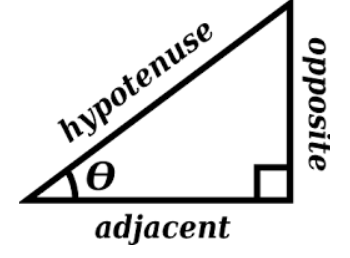
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem, we have to find the value of\[\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)} \right)\].
Hence, we have to find the cosine of the angle whose sine is given to us as $\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)$.
Let us assume $\theta $ to be the concerned angle.
Then, $\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)$
Taking sine on both sides of the equation, we get
$ = \sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{7}$
To evaluate the value of the required expression, we must keep in mind the formulae of basic trigonometric ratios.
We know that, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Hypotenuse}}$and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}}$.
So, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{3}{7}$
Let the length of the perpendicular be$3x$.
Then, length of hypotenuse $ = 7x$.
Now, applying Pythagoras Theorem,
${\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Perpendicular} \right)^2}$
$ = {\left( {7x} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {3x} \right)^2}$
Computing the squares, we get,
$ = 49{x^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + 9{x^2}$
$ = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} = 49{x^2} - 9{x^2}$
$ = \left( {Base} \right) = \sqrt {40{x^2}} $
Simplifying the expression by taking the factor appearing twice in the factorisation of the number outside the square root. So, we get,
$ = \left( {Base} \right) = 2\sqrt {10} x$
So, we get $Base = 2\sqrt {10} x$
Hence, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} x}}{{7x}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} }}{7}$
Therefore, the value of\[\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)} \right)\] is $\dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} }}{7}$.
Note:
The given problem can also be solved by use of some basic trigonometric identities such as ${\sin ^2}\left( \theta \right) + {\cos ^2}\left( \theta \right) = 1$. This method also provides exposure to the applications of trigonometric identities in various mathematical questions.
Formula used:

$\sin \theta = \dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem, we have to find the value of\[\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)} \right)\].
Hence, we have to find the cosine of the angle whose sine is given to us as $\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)$.
Let us assume $\theta $ to be the concerned angle.
Then, $\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)$
Taking sine on both sides of the equation, we get
$ = \sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{7}$
To evaluate the value of the required expression, we must keep in mind the formulae of basic trigonometric ratios.
We know that, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Hypotenuse}}$and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}}$.
So, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{3}{7}$
Let the length of the perpendicular be$3x$.
Then, length of hypotenuse $ = 7x$.
Now, applying Pythagoras Theorem,
${\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Perpendicular} \right)^2}$
$ = {\left( {7x} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {3x} \right)^2}$
Computing the squares, we get,
$ = 49{x^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + 9{x^2}$
$ = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} = 49{x^2} - 9{x^2}$
$ = \left( {Base} \right) = \sqrt {40{x^2}} $
Simplifying the expression by taking the factor appearing twice in the factorisation of the number outside the square root. So, we get,
$ = \left( {Base} \right) = 2\sqrt {10} x$
So, we get $Base = 2\sqrt {10} x$
Hence, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} x}}{{7x}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} }}{7}$
Therefore, the value of\[\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)} \right)\] is $\dfrac{{2\sqrt {10} }}{7}$.
Note:
The given problem can also be solved by use of some basic trigonometric identities such as ${\sin ^2}\left( \theta \right) + {\cos ^2}\left( \theta \right) = 1$. This method also provides exposure to the applications of trigonometric identities in various mathematical questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




