
How do you evaluate $arccot \left( -2 \right)$ on the scientific calculator?
Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: We explain the function $arccot \left( x \right)$. We express the inverse function of cot in the form of $arccot \left( x \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}x$. We draw the graph of $arccot \left( x \right)$ and the line $x=-2$ to find the intersection point as the solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The given expression is the inverse function of trigonometric ratio cot.
The arcus function represents the angle which on ratio tan gives the value.
So, $arccot \left( x \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}x$. If $arccot \left( x \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}x=\alpha $ then we can say $\cot \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\cot \alpha =x$ will be $n\pi +\alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $arccot \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio tan we have $0\le arccot \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
We now place the value of $x=-2$ in the function of $arccot \left( x \right)$.
Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $arccot \left( -2 \right)=\theta $. This gives $\cot \theta =-2$.
Putting the value in the graph of $arccot \left( x \right)$, we get $\theta =153.43$.
For this we take the line of $x=-2$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $arccot \left( x \right)$.
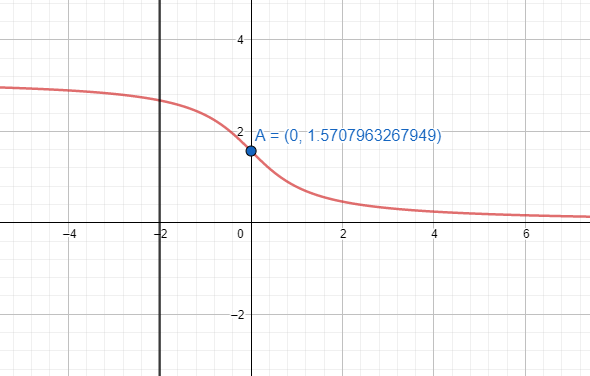
Therefore, the value of $arccot \left( -2 \right)$ is ${{153.43}^{\circ }}$.
Note:
First note that the value $-2$ looks suspiciously like it was intended to be an angle but the argument of the $arccot \left( x \right)$ function is not an angle. The representation can also be done in this manner. We convert the equation in $\arctan \left( x \right)$.
We know $\arctan \left( x \right)=arccot \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-\pi $ for $x<0$.
Complete step by step answer:
The given expression is the inverse function of trigonometric ratio cot.
The arcus function represents the angle which on ratio tan gives the value.
So, $arccot \left( x \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}x$. If $arccot \left( x \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}x=\alpha $ then we can say $\cot \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\cot \alpha =x$ will be $n\pi +\alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $arccot \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio tan we have $0\le arccot \left( x \right)\le \pi $.
We now place the value of $x=-2$ in the function of $arccot \left( x \right)$.
Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $arccot \left( -2 \right)=\theta $. This gives $\cot \theta =-2$.
Putting the value in the graph of $arccot \left( x \right)$, we get $\theta =153.43$.
For this we take the line of $x=-2$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $arccot \left( x \right)$.

Therefore, the value of $arccot \left( -2 \right)$ is ${{153.43}^{\circ }}$.
Note:
First note that the value $-2$ looks suspiciously like it was intended to be an angle but the argument of the $arccot \left( x \right)$ function is not an angle. The representation can also be done in this manner. We convert the equation in $\arctan \left( x \right)$.
We know $\arctan \left( x \right)=arccot \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-\pi $ for $x<0$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




