
Ethylene on the addition of hypochlorous acid forms:
(A)
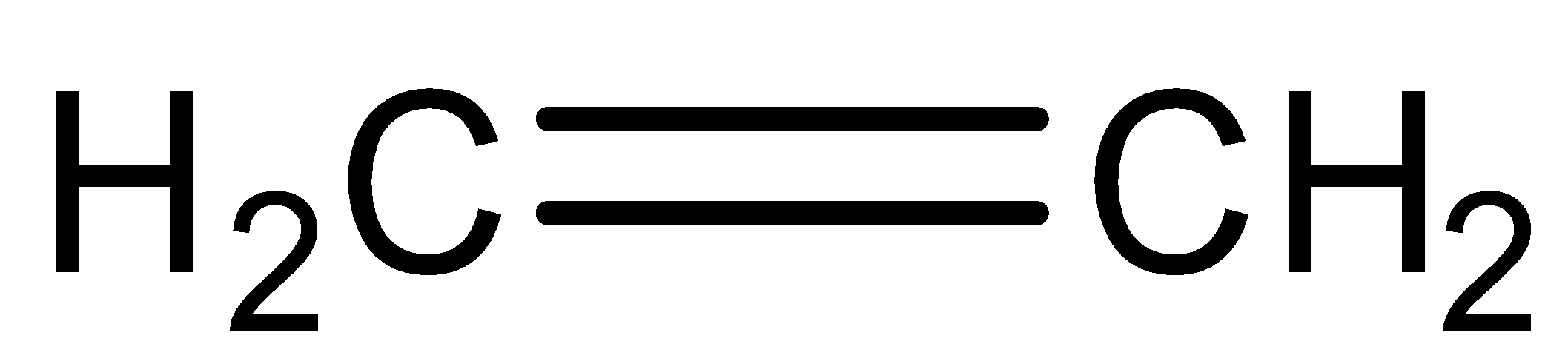
(B)
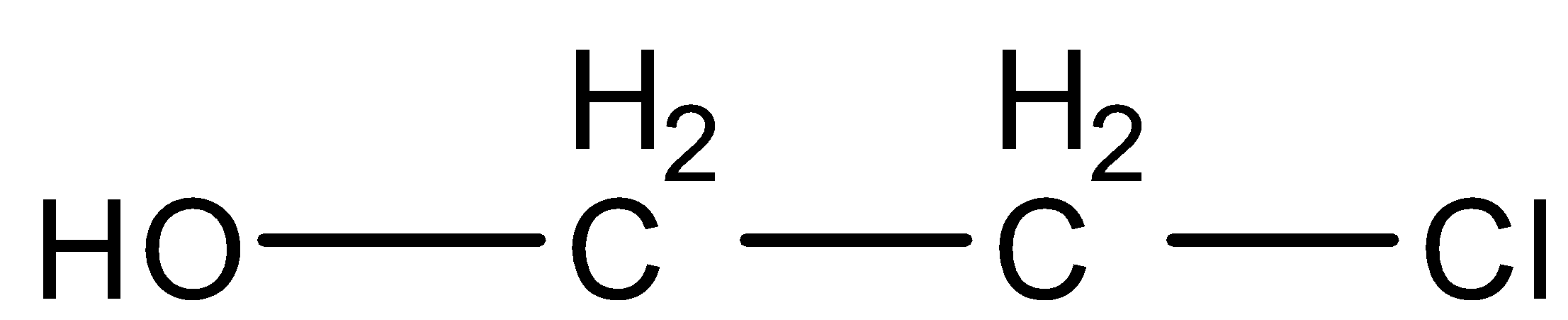
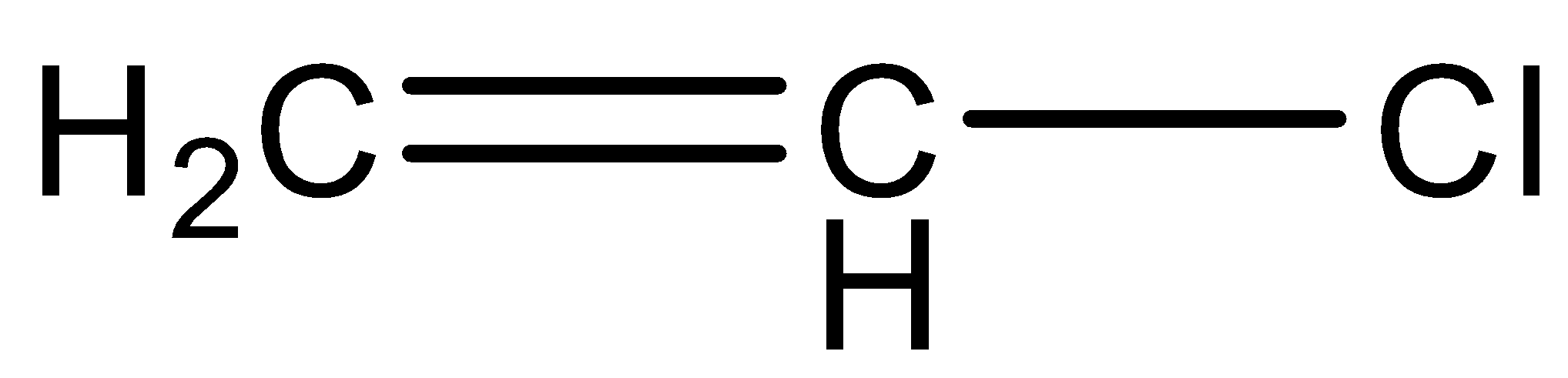
(C)
(D)
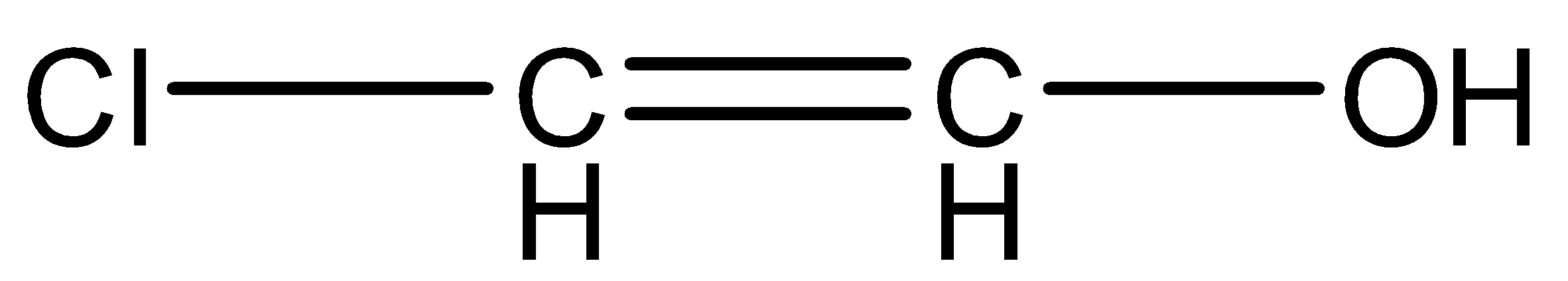
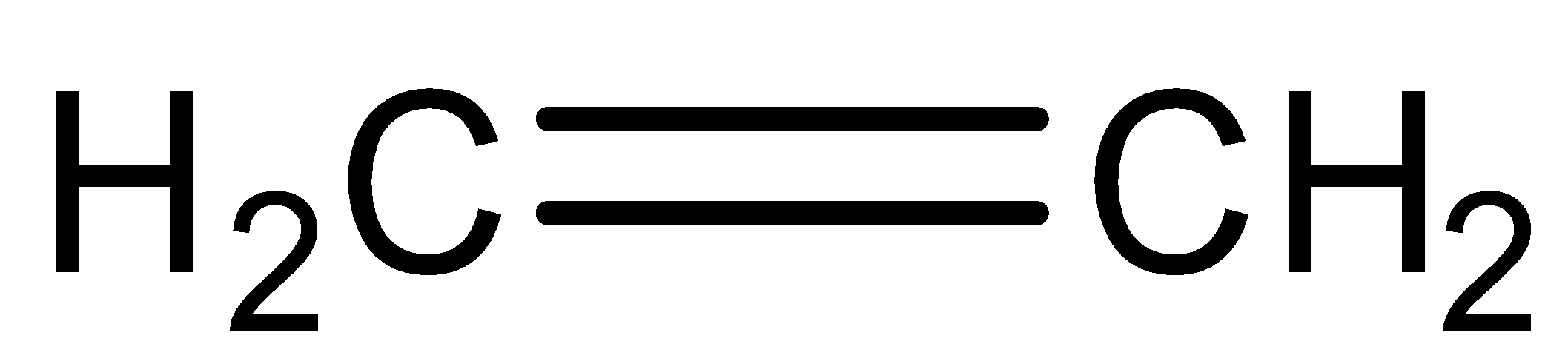
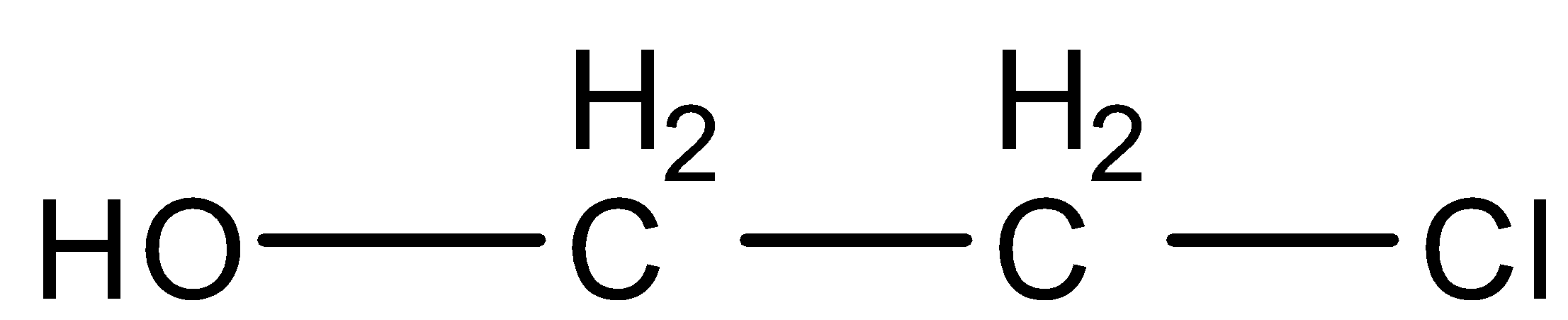

Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction between ethylene
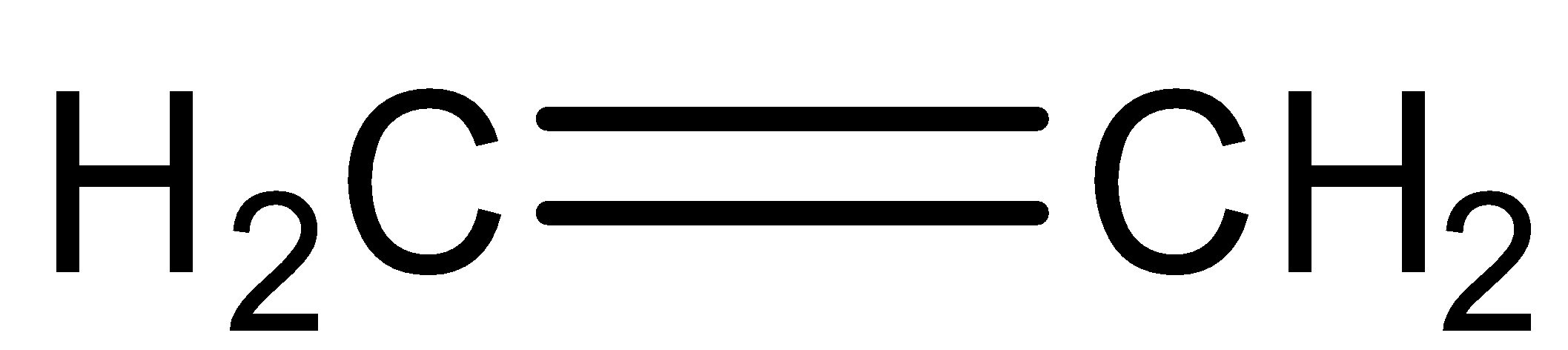 on the addition of hypochlorous acid $ HOCl $ depends on the amount of $ HOCl $ added as well as Markovnikov’s rule. Also, there is breaking as well as the formation of bonds
on the addition of hypochlorous acid $ HOCl $ depends on the amount of $ HOCl $ added as well as Markovnikov’s rule. Also, there is breaking as well as the formation of bonds
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will understand the basic principle used for the reaction that is Markovnikov’s rule. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes and alkynes have proceeded with the addition of halogen atoms to the carbon atom bearing the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. Now we will write the chemical reaction which shows the additional reaction of ethylene and hypochlorous acid. The reaction is given below:

Now we will discuss the reaction step by step. In the first step of the reaction, the double bond of ethylene and the single bond of hypochlorous acid breaks which results in the formation of electrophile and nucleophile. Therefore, there is a negative charge over the hydroxyl group $ O{H^ - } $ and the positive charge is formed over the halogen group $ C{l^ + } $ , which results in the formation of $ ^ + C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ . Now we will discuss the second step of the reaction. In this step, $ O{H^ - } $ gets attached with $ ^ + C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ and forms the final product $ OH - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ . The final product formed is Ethylene chlorohydrin. The IUPAC name of the product formed is $ 2 - chloro - ethanol $ .
Therefore, Ethylene on the addition of hypochlorous acid forms
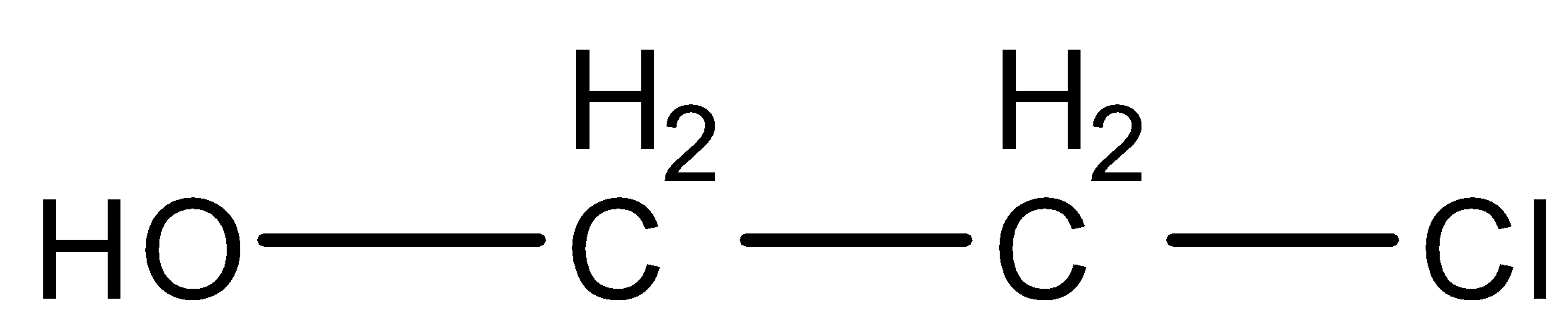 .
.
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note:
The product formed is Ethylene chlorohydrin is an organochlorine compound and hazardous substance. It is used as a solvent and in the manufacture of a variety of industrial agents. It is also used as a xenobiotic metabolite.
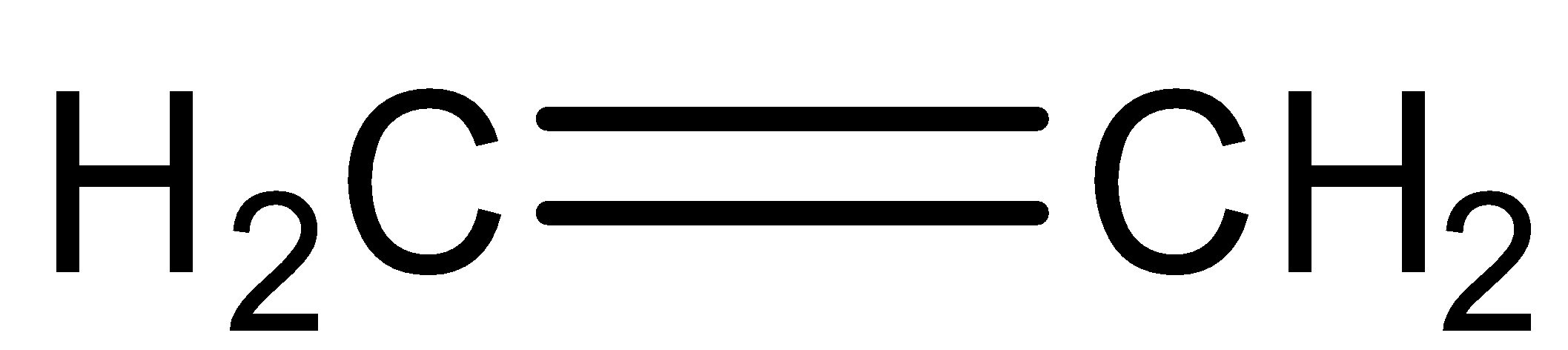
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will understand the basic principle used for the reaction that is Markovnikov’s rule. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes and alkynes have proceeded with the addition of halogen atoms to the carbon atom bearing the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. Now we will write the chemical reaction which shows the additional reaction of ethylene and hypochlorous acid. The reaction is given below:

Now we will discuss the reaction step by step. In the first step of the reaction, the double bond of ethylene and the single bond of hypochlorous acid breaks which results in the formation of electrophile and nucleophile. Therefore, there is a negative charge over the hydroxyl group $ O{H^ - } $ and the positive charge is formed over the halogen group $ C{l^ + } $ , which results in the formation of $ ^ + C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ . Now we will discuss the second step of the reaction. In this step, $ O{H^ - } $ gets attached with $ ^ + C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ and forms the final product $ OH - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl $ . The final product formed is Ethylene chlorohydrin. The IUPAC name of the product formed is $ 2 - chloro - ethanol $ .
Therefore, Ethylene on the addition of hypochlorous acid forms
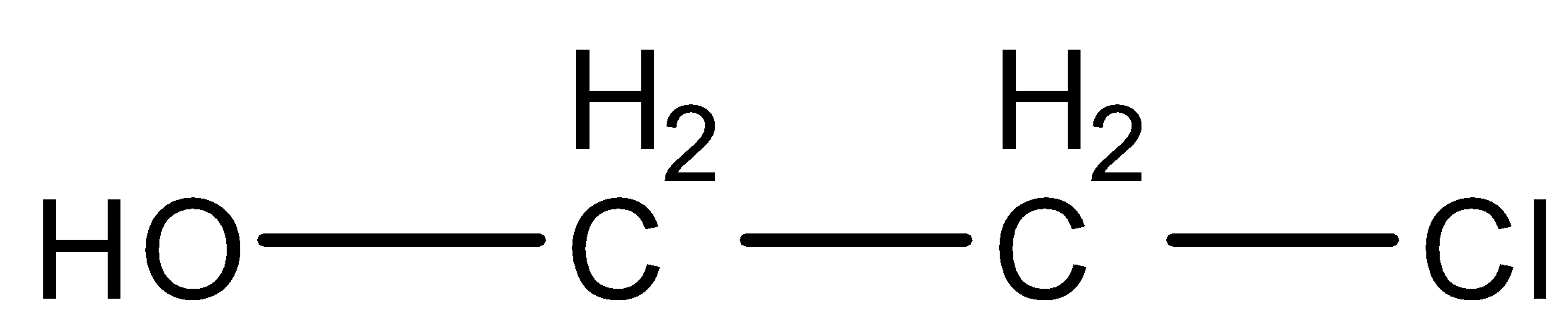
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note:
The product formed is Ethylene chlorohydrin is an organochlorine compound and hazardous substance. It is used as a solvent and in the manufacture of a variety of industrial agents. It is also used as a xenobiotic metabolite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




