
How is ethene converted into ethyl magnesium bromide?
Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint :A Grignard reagent is an organo-magnesium compound which is very important reagent in chemistry. It can be described by the chemical formula $ R - Mg - X $ , where R refers to an alkyl or aryl group and X refers to a halogen like chlorine or bromine. They are generally produced by reacting an aryl or alkyl halide with magnesium.
Ethyl magnesium bromide is a commercially available chemical, usually present as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as a solvent.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Most of the organic chlorides, bromides and iodides react with certain metals to give compounds containing carbon-metal bonds. Such compounds are known as organo-metallic compounds or Grignard reagents. An important class of organo-metallic compounds discovered by Victor Grignard in 1900 is alkyl magnesium halide, $ R - Mg - X $ , referred to as Grignard Reagents. These reagents are obtained by the reaction of haloalkanes or haloarenes with magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether.
For preparing ethyl magnesium bromide we treat ethene with Hydrogen Bromide in the presence of dry ether.
$ C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{Dry{\text{ }}Ether}]{{HBr}}C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Mg - Br $
The complete mechanism of the reaction is given as below:
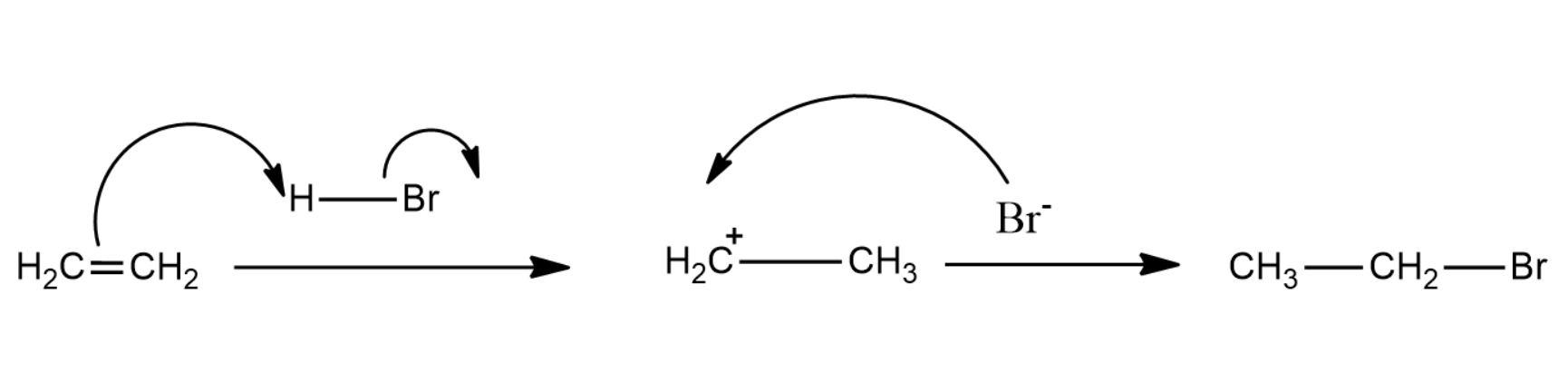
Here the Hydrogen bromide will break the double bond and thus form a carbocation. Bromine ions will react with the carbocation to form ethyl bromide.
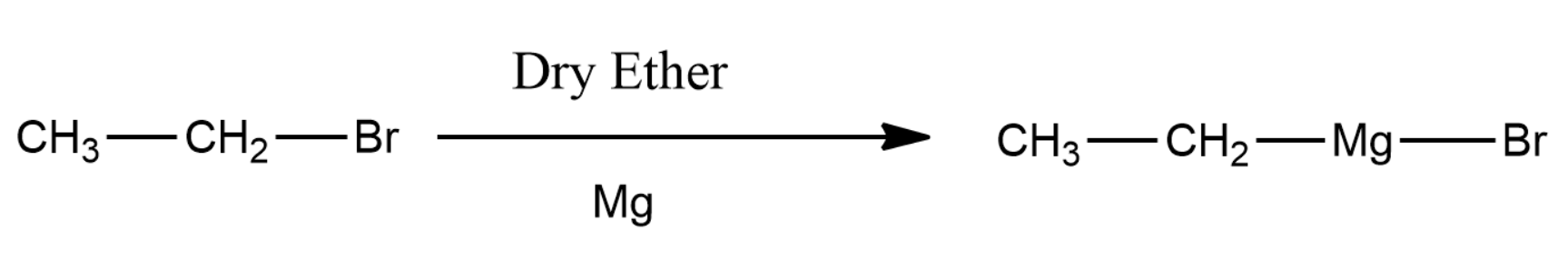
The formed ethyl bromide will react with magnesium metal and thus forms ethyl magnesium Bromide.
Note :
Grignard reagents are highly reactive to any source of proton to give hydrocarbons. One of the very best examples of proton sources is water, and in turn convert them to corresponding hydrocarbons. It is therefore absolutely necessary to avoid even traces of moisture from a Grignard reagent. This is why it is absolutely necessary to use dry ether while preparing Grignard reagent.
Ethyl magnesium bromide is a commercially available chemical, usually present as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as a solvent.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Most of the organic chlorides, bromides and iodides react with certain metals to give compounds containing carbon-metal bonds. Such compounds are known as organo-metallic compounds or Grignard reagents. An important class of organo-metallic compounds discovered by Victor Grignard in 1900 is alkyl magnesium halide, $ R - Mg - X $ , referred to as Grignard Reagents. These reagents are obtained by the reaction of haloalkanes or haloarenes with magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether.
For preparing ethyl magnesium bromide we treat ethene with Hydrogen Bromide in the presence of dry ether.
$ C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{Dry{\text{ }}Ether}]{{HBr}}C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Mg - Br $
The complete mechanism of the reaction is given as below:

Here the Hydrogen bromide will break the double bond and thus form a carbocation. Bromine ions will react with the carbocation to form ethyl bromide.

The formed ethyl bromide will react with magnesium metal and thus forms ethyl magnesium Bromide.
Note :
Grignard reagents are highly reactive to any source of proton to give hydrocarbons. One of the very best examples of proton sources is water, and in turn convert them to corresponding hydrocarbons. It is therefore absolutely necessary to avoid even traces of moisture from a Grignard reagent. This is why it is absolutely necessary to use dry ether while preparing Grignard reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




