
Ethane-1,2-diol has the given structure. Without breaking the $C - C$ bond, there are five possible oxidation products. What is the total number of aldehyde groups and carboxylic acid groups in these five products?
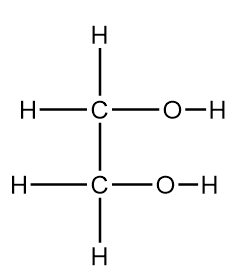
A. $ - CHO:3;\; - COOH:3$
B. $ - CHO:3;\; - COOH:4$
C. $ - CHO:4;\; - COOH:3$
D. $ - CHO:4;\; - COOH:4$

Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: In organic chemistry, the oxidation and reduction of compounds is described on the basis of addition and removal of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. During a reaction, if addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms takes place then it is said to be oxidation reaction while if addition of hydrogen atoms or removal of oxygen atoms takes place then it is said to be reduction reaction
Complete answer:
For oxidizing alcohols, various oxidizing reagents can be used like chromic acid $\left( {{H_2}Cr{O_4}} \right)$, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), potassium dichromate $\left( {{K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}} \right)$, etc. Ethane-1,2-diol which is also known as ethylene glycol is an odourless, sweet tasting viscous liquid and oxidized to form various products. The possible oxidation products without cleavage of carbon-carbon single bond are as follows:
1. When only one hydroxyl group is oxidized to aldehyde group:
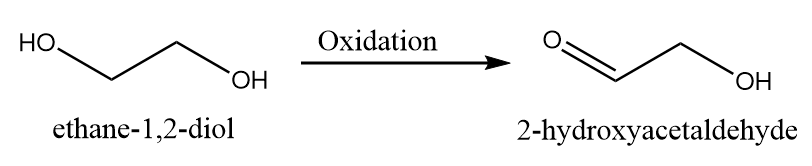
2. When both the hydroxyl groups are oxidized to aldehyde group:
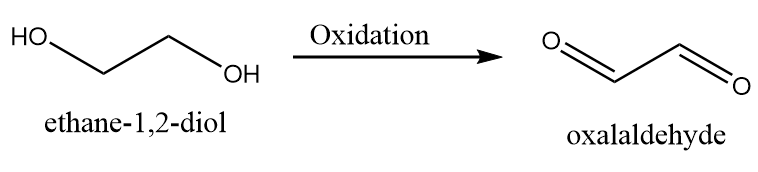
3. When one hydroxyl group is oxidized to aldehyde while other is oxidized to carboxylic acid:
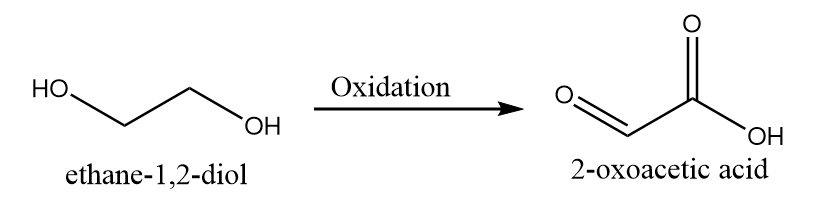
4. When only one hydroxyl group is oxidized to carboxylic acid group:
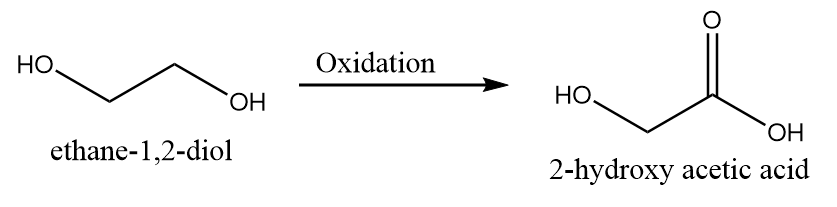
5. When both the hydroxyl groups are oxidized to carboxylic acid group:
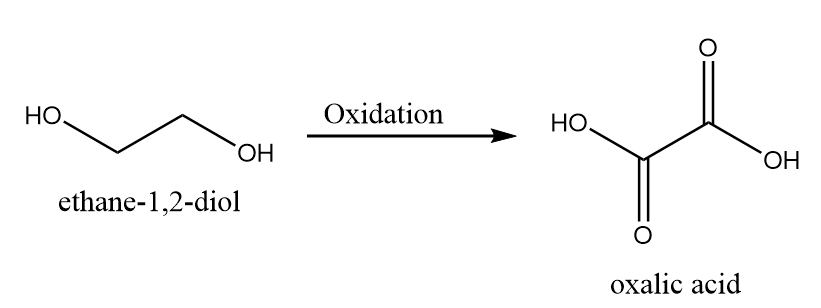
Hence, the total four aldehyde groups and four carboxylic acid groups are formed in the possible oxidation product.
Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that in ethylene glycol, both the hydroxyl groups are attached to primary carbon atoms. That’s why the groups are oxidized to the aldehyde group. If in case, the hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon atom, then it will be oxidized to the ketonic group.
Complete answer:
For oxidizing alcohols, various oxidizing reagents can be used like chromic acid $\left( {{H_2}Cr{O_4}} \right)$, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), potassium dichromate $\left( {{K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}} \right)$, etc. Ethane-1,2-diol which is also known as ethylene glycol is an odourless, sweet tasting viscous liquid and oxidized to form various products. The possible oxidation products without cleavage of carbon-carbon single bond are as follows:
1. When only one hydroxyl group is oxidized to aldehyde group:

2. When both the hydroxyl groups are oxidized to aldehyde group:

3. When one hydroxyl group is oxidized to aldehyde while other is oxidized to carboxylic acid:

4. When only one hydroxyl group is oxidized to carboxylic acid group:

5. When both the hydroxyl groups are oxidized to carboxylic acid group:

Hence, the total four aldehyde groups and four carboxylic acid groups are formed in the possible oxidation product.
Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that in ethylene glycol, both the hydroxyl groups are attached to primary carbon atoms. That’s why the groups are oxidized to the aldehyde group. If in case, the hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon atom, then it will be oxidized to the ketonic group.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




