
Equivalent weight of hydrated oxalic acid is:
A.$44$
B.$45$
C.$63$
D.$126$
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the oxalic acid is an organic compound which generally exists as a white colored solid crystalline form. And it forms a colorless solution in water. Oxalic acid occurs as a dihydrate containing two water molecules. We have to know that the oxalic acid is represented by the formula - ${C_2}{H_2}{O_4}$. We have to know that the oxalic acids have acid strength greater than acetic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the chemical structure of oxalic acid as,
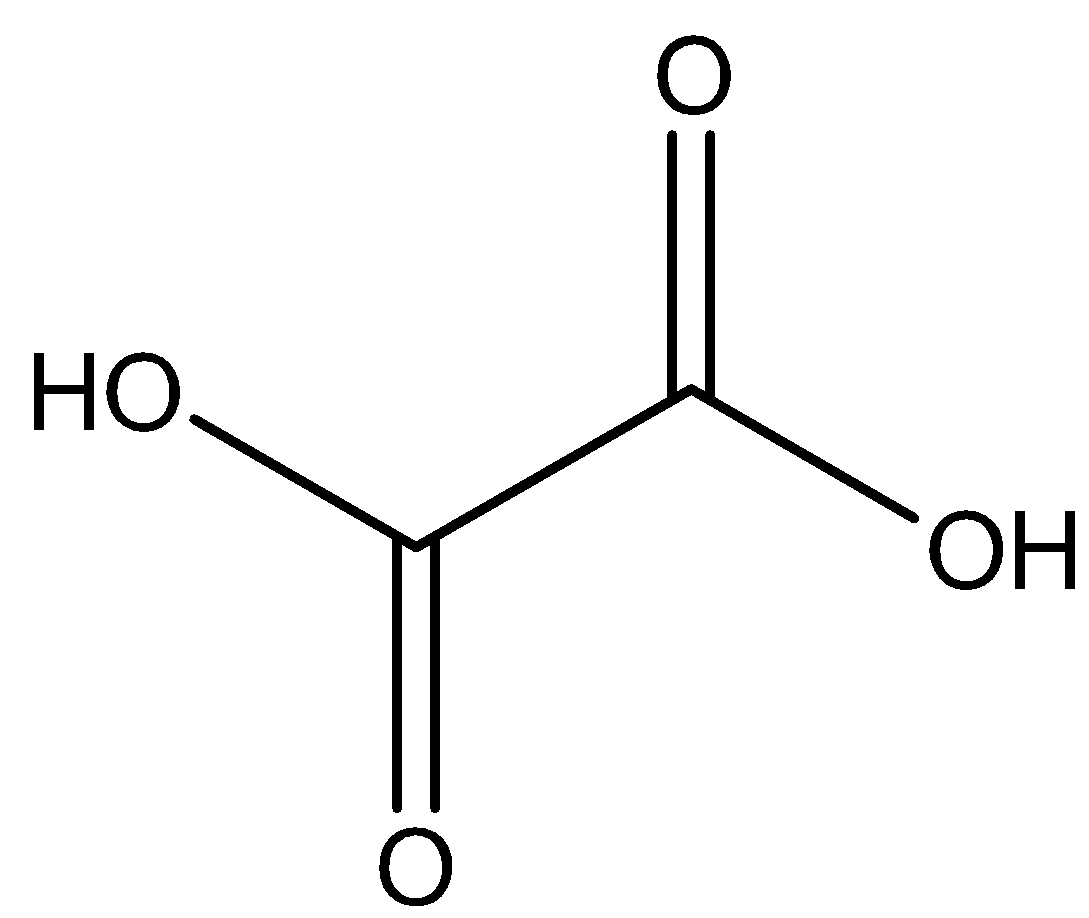
We know that is generally as dihydrate, its chemical formula can be represented as ${C_2}{H_2}{O_4}.2{H_2}O$.
To determine the equivalent weight, we will first divide the molecular weight with the n-factor of the given molecule. The n-factor is defined as the number of ${H^ + }$ ions replaced by $1mol$ of acid in a reaction and the number of $O{H^ - }$ replaced by $1mol$ of base in a reaction.
Oxalic acid is acidic in nature.
Also, Molecular mass of hydrate oxalic acid is calculated as,
$2C + 6H + 5O$
Molecular mass \[ = \left( {2 \times 12} \right) + \left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {6 \times 16} \right) = 126\]
Since, the oxalic acid has two moles of acidic ${H^ + }$ , that means one mole of oxalic acid can neutralize two moles of $O{H^ - }$ (base).
Hence, the number of equivalent moles is $2$.
The formula of equivalent weight is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\text{Molecular mass}}}}{{{\text{Number of equivalent moles}}}}$
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
$ = \dfrac{{126}}{2}$
On simplification we get,
Equivalent weight$ = 63g/eq{\text{ }}mol$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
We need to know that the oxalic acid is a strong reducing agent and its conjugate base is known as oxalate (when we remove the hydrogen ions from the formula).The concept of equivalent weight has dimensions and units of mass. It is generally defined as the mass of one equivalent of a given substance which will combine with or displace a fixed quantity of another substance. For acid-base reactions, the substituting element is the acidic and the basic ions which are involved in the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the chemical structure of oxalic acid as,

We know that is generally as dihydrate, its chemical formula can be represented as ${C_2}{H_2}{O_4}.2{H_2}O$.
To determine the equivalent weight, we will first divide the molecular weight with the n-factor of the given molecule. The n-factor is defined as the number of ${H^ + }$ ions replaced by $1mol$ of acid in a reaction and the number of $O{H^ - }$ replaced by $1mol$ of base in a reaction.
Oxalic acid is acidic in nature.
Also, Molecular mass of hydrate oxalic acid is calculated as,
$2C + 6H + 5O$
Molecular mass \[ = \left( {2 \times 12} \right) + \left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {6 \times 16} \right) = 126\]
Since, the oxalic acid has two moles of acidic ${H^ + }$ , that means one mole of oxalic acid can neutralize two moles of $O{H^ - }$ (base).
Hence, the number of equivalent moles is $2$.
The formula of equivalent weight is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\text{Molecular mass}}}}{{{\text{Number of equivalent moles}}}}$
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
$ = \dfrac{{126}}{2}$
On simplification we get,
Equivalent weight$ = 63g/eq{\text{ }}mol$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
We need to know that the oxalic acid is a strong reducing agent and its conjugate base is known as oxalate (when we remove the hydrogen ions from the formula).The concept of equivalent weight has dimensions and units of mass. It is generally defined as the mass of one equivalent of a given substance which will combine with or displace a fixed quantity of another substance. For acid-base reactions, the substituting element is the acidic and the basic ions which are involved in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




