
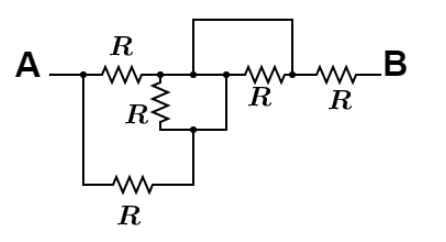
What is equivalent resistance between $A$ and $B$?
A. $\dfrac{{3R}}{2}$
B. $2R$
C. $R$
D. $\dfrac{R}{2}$

Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand current flows.Actually when the wire is subjected to potential difference then an electric field is set up across the wire which binds the electrons to move in the opposite direction so current flows in opposite direction as of electron flows or in direction of applied electric field. Current is defined as the total number of charges flowing across per unit area in unit time interval. Whenever a current flows across wire then wire opposes this behavior and develops opposition known as resistance. Resistance is defined as voltage across a battery divided by current flows.
Complete step by step answer:
Series Equivalent Resistance formula given by, ${R_{eq}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{R_i}} $
Parallel equivalent Resistance formula given by, $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\dfrac{1}{{{R_i}}}} $
To solve this circuit we need to mark the point as shown in figure.
Let the resistance marked between A and C be, ${R_1} = R$
resistance marked between A and E be, ${R_2} = R$
Similarly resistance marked between C and D points be, ${R_3} = R$
And resistance marked between F and G be, ${R_4} = R$
Similarly resistance marked between G and B be, ${R_5} = R$
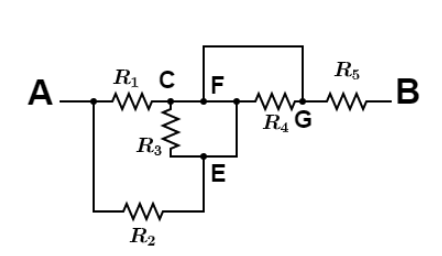
Since the point C, E, F and G are at the same potential as there is only wire connection between these points so resistance ${R_3}\& {R_4}$ could be neglected. So reduced circuit be like this,
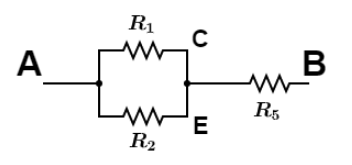
Since the resistance ${R_1}\& {R_2}$are parallel so equivalent resistance is, using equivalent resistance in parallel combination we get,
$R' = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$
Putting values we get,
$R' = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{2R}}$
$\Rightarrow R' = \dfrac{R}{2}$
Now the resistance $R'\& {R_5}$ are in series with each other, so net equivalent resistance would be using series equivalent formula we get, $R'' = \dfrac{R}{2} + R$
$\therefore R'' = \dfrac{{3R}}{2}$
So the correct option is A.
Note: It should be remembered that in series resistance current across all resistors would be the same but the voltage difference would be defined while in parallel resistance voltage difference across all resistors is same and current across all resistors would be different. In series resistance voltage across resistors is divided in inverse ratio of their resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
Series Equivalent Resistance formula given by, ${R_{eq}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{R_i}} $
Parallel equivalent Resistance formula given by, $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\dfrac{1}{{{R_i}}}} $
To solve this circuit we need to mark the point as shown in figure.
Let the resistance marked between A and C be, ${R_1} = R$
resistance marked between A and E be, ${R_2} = R$
Similarly resistance marked between C and D points be, ${R_3} = R$
And resistance marked between F and G be, ${R_4} = R$
Similarly resistance marked between G and B be, ${R_5} = R$

Since the point C, E, F and G are at the same potential as there is only wire connection between these points so resistance ${R_3}\& {R_4}$ could be neglected. So reduced circuit be like this,

Since the resistance ${R_1}\& {R_2}$are parallel so equivalent resistance is, using equivalent resistance in parallel combination we get,
$R' = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$
Putting values we get,
$R' = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{2R}}$
$\Rightarrow R' = \dfrac{R}{2}$
Now the resistance $R'\& {R_5}$ are in series with each other, so net equivalent resistance would be using series equivalent formula we get, $R'' = \dfrac{R}{2} + R$
$\therefore R'' = \dfrac{{3R}}{2}$
So the correct option is A.
Note: It should be remembered that in series resistance current across all resistors would be the same but the voltage difference would be defined while in parallel resistance voltage difference across all resistors is same and current across all resistors would be different. In series resistance voltage across resistors is divided in inverse ratio of their resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

a What type of deviation is shown by a mixture of ethanol class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




