
Equation of oblique projectile can be written as:
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: In oblique projectile, horizontal plane of projectile motion is at some angle with the x- axis. As we get the equation of motion of the oblique projectile, we will simplify it in terms of x, R (range) and the angle of the projectile. First, we will multiply sin terms in the second term of the right-hand side of the equation, then simplify to make a formula of range in the denominator. This gives another form of equation of motion.
Complete answer:
A projectile is thrown with the velocity u at an angle $\theta$ with the x-axis. The velocity u can be resolved into two components $u cos \theta$ component along X-axis and $u sin \theta$ component along Y-axis.
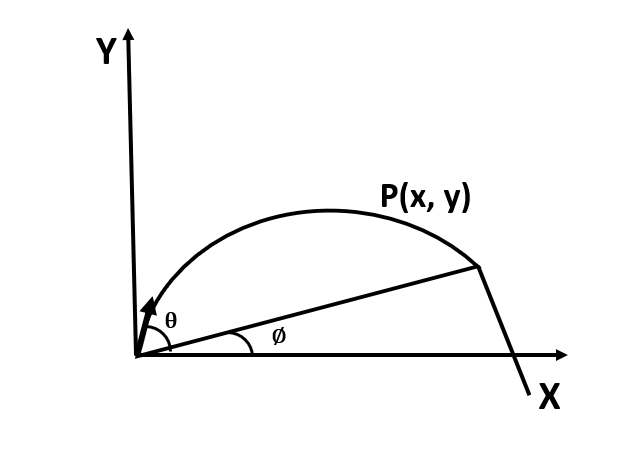
$u_{x} = u cos \theta$ and $u_{y} = u sin \theta$
Equation of trajectory is:
$ y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{g x^{2} }{2 u^{2}cos^{2} \theta }$
Multiply by $sin \theta$ in the second term of the right-hand side.
$ y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{ x^{2} sin \theta }{\dfrac{2 sin \theta u^{2}cos^{2} \theta }{g} }$
$\implies y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{ x^{2} sin \theta }{ cos \theta \dfrac{ u^{2}sin 2 \theta }{g} }$
$\implies y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{x^{2} tan \theta}{R}$, R is the range of projectiles.
$\implies y = x tan \theta \left( 1 - \dfrac{x}{R} \right)$
Equation of oblique projectile can be written as
$ y = x tan \theta \left( 1 - \dfrac{x}{R} \right)$
Note:
When a particle is dropped in the air with speed, the only force performing on it during its air time is the acceleration due to gravity acting vertically downwards. There is no acceleration in the horizontal, which means that the particle's velocity in the horizontal direction lives constantly.
Complete answer:
A projectile is thrown with the velocity u at an angle $\theta$ with the x-axis. The velocity u can be resolved into two components $u cos \theta$ component along X-axis and $u sin \theta$ component along Y-axis.

$u_{x} = u cos \theta$ and $u_{y} = u sin \theta$
Equation of trajectory is:
$ y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{g x^{2} }{2 u^{2}cos^{2} \theta }$
Multiply by $sin \theta$ in the second term of the right-hand side.
$ y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{ x^{2} sin \theta }{\dfrac{2 sin \theta u^{2}cos^{2} \theta }{g} }$
$\implies y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{ x^{2} sin \theta }{ cos \theta \dfrac{ u^{2}sin 2 \theta }{g} }$
$\implies y = x tan \theta - \dfrac{x^{2} tan \theta}{R}$, R is the range of projectiles.
$\implies y = x tan \theta \left( 1 - \dfrac{x}{R} \right)$
Equation of oblique projectile can be written as
$ y = x tan \theta \left( 1 - \dfrac{x}{R} \right)$
Note:
When a particle is dropped in the air with speed, the only force performing on it during its air time is the acceleration due to gravity acting vertically downwards. There is no acceleration in the horizontal, which means that the particle's velocity in the horizontal direction lives constantly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




