
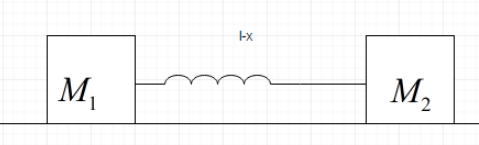
Equation of length of the spring as a function of time is given by x?
A. \[1-{{A}_{1}}\cos wt\]
B. \[1-({{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}})\cos wt\]
C. \[({{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}})\cos wt\]
D. \[1-{{A}_{2}}\cos wt\]

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint:We are given a stretched spring between the two masses. The spring constant of the spring is k.We have to take some point as origin and then from that point we can measure the equilibrium length which is unstretched and also the extension of the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
We know spring has a spring of force constant, $k$ and it has the tendency to return to its equilibrium position that is the unstretched position when it is either compressed or stretched. The energy possessed by the spring when it is either stretched or compressed is called its potential energy.We assume that the equilibrium position of 1st particle be at origin i.e. x = 0. $x$ coordinate of particles can be written as:
\[{{x}_{1}}={{A}_{1}}\cos wt\] and \[{{x}_{2}}=1-{{A}_{1}}\cos wt\]
Thus, the length of spring at time t can be written as:
\[\therefore{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}=1-({{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}})\cos wt\]
So, the correct option is B.
Note: The equilibrium state of the spring corresponds to the situation in which the spring is stretched or we can say that the spring is unextended. But if the spring is perturbed from its equilibrium state then a restoring force comes into play which can be written in the form: \[f(x)=-kx\], where k is the spring constant and x is the extension in the length. Using second law, \[m\dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}x}{\partial {{t}^{2}}}=-kx\]
This differential equation is we say as the simple harmonic oscillator equation, and its solution is known to us. The solution is \[x=A\cos wt\]. Thus, from here we came to use cos to write the solution that we have done in this problem.
Complete step by step answer:
We know spring has a spring of force constant, $k$ and it has the tendency to return to its equilibrium position that is the unstretched position when it is either compressed or stretched. The energy possessed by the spring when it is either stretched or compressed is called its potential energy.We assume that the equilibrium position of 1st particle be at origin i.e. x = 0. $x$ coordinate of particles can be written as:
\[{{x}_{1}}={{A}_{1}}\cos wt\] and \[{{x}_{2}}=1-{{A}_{1}}\cos wt\]
Thus, the length of spring at time t can be written as:
\[\therefore{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}=1-({{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}})\cos wt\]
So, the correct option is B.
Note: The equilibrium state of the spring corresponds to the situation in which the spring is stretched or we can say that the spring is unextended. But if the spring is perturbed from its equilibrium state then a restoring force comes into play which can be written in the form: \[f(x)=-kx\], where k is the spring constant and x is the extension in the length. Using second law, \[m\dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}x}{\partial {{t}^{2}}}=-kx\]
This differential equation is we say as the simple harmonic oscillator equation, and its solution is known to us. The solution is \[x=A\cos wt\]. Thus, from here we came to use cos to write the solution that we have done in this problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




