
What is the equation for formation of dipeptide?
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: Amino acids are found in the human body, which are the simplest unit of proteins. When 2 amino acids link together they form a di – peptide bond. It is a type of condensation reaction, where the peptide bond is formed by removal of a water molecule. These bonds consist of an amide linkage.
Complete answer:
Amino acids are the simplest unit of proteins; they contain an amine group and a carboxylic acid group and hence called amino acids. When two amino acids combine together, they form a bigger network of amino acids. The linkage in the combination of amino acids is through a peptide bond that has a$\left( -\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-NH \right)$ linkage called as peptide or amide linkage. This linkage is a result of condensation of 2 molecules of amino acids that lose a water molecule to form dipeptide. A dipeptide consists of 1 peptide linkage. The equation for formation for dipeptide is as follows:
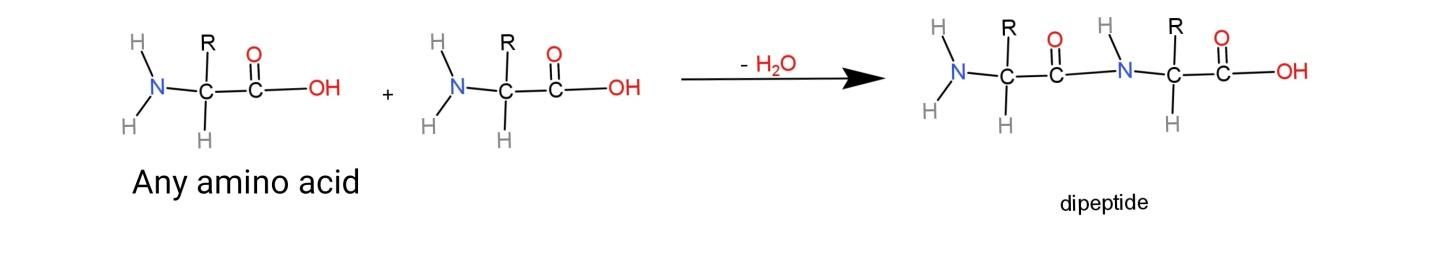
Here, two amino acids having any alkyl group R, combine together and lose a water molecule to form as dipeptide.
The most common example of a dipeptide formation is combination of glycine and alanine as:
$\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}N-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH+{{H}_{2}}N-\overset{C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-COOH\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}{{H}_{2}}N-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-NH-\overset{C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-COOH \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,glycine\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,alanine\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,glycylalanine \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the reaction equation of dipeptide formation involves condensation and removal of water molecules as depicted above.
Note:
When 3 amino acids combine together then a tripeptide is formed that consist of 2 peptide linkages. When more than 10 amino acids join together then they are called polypeptides. The combination of more than 100 amino acids joined together forms a protein. Amino acids can be neutral, acidic or basic.
Complete answer:
Amino acids are the simplest unit of proteins; they contain an amine group and a carboxylic acid group and hence called amino acids. When two amino acids combine together, they form a bigger network of amino acids. The linkage in the combination of amino acids is through a peptide bond that has a$\left( -\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-NH \right)$ linkage called as peptide or amide linkage. This linkage is a result of condensation of 2 molecules of amino acids that lose a water molecule to form dipeptide. A dipeptide consists of 1 peptide linkage. The equation for formation for dipeptide is as follows:

Here, two amino acids having any alkyl group R, combine together and lose a water molecule to form as dipeptide.
The most common example of a dipeptide formation is combination of glycine and alanine as:
$\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}N-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH+{{H}_{2}}N-\overset{C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-COOH\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}{{H}_{2}}N-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-NH-\overset{C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-COOH \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,glycine\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,alanine\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,glycylalanine \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the reaction equation of dipeptide formation involves condensation and removal of water molecules as depicted above.
Note:
When 3 amino acids combine together then a tripeptide is formed that consist of 2 peptide linkages. When more than 10 amino acids join together then they are called polypeptides. The combination of more than 100 amino acids joined together forms a protein. Amino acids can be neutral, acidic or basic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




