
Enumerate the physiological properties of the heart (cardiac) muscles.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: It is similar to skeletal muscle, another major muscle type, in that it possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres; this feature, however, also distinguishes it from smooth muscle, the third muscle type. It varies from skeletal muscle in that it displays rhythmic compressions and isn't under voluntary control.
Complete answer:
The physiological properties of the heart muscle are 1. Rhythmicity 2. Excitability 3. Contractility 4. Conductivity.
Property 1. Rhythmicity/Automaticity/Chronotropism:
In the myocardium, automaticity is the capacity of the heart muscles to depolarize immediately, without outside electrical incitement from the nervous system.
Property 2. Excitability (Bathmotropic):
Is the ability of the cardiac muscle to respond to adequate stimuli by generating an action potential.
Property 3. Contractility/Inotropism:
It is the power of the heart muscle to convert electricity into mechanical work. Myocardial fibers have ‘functional syncytium’ and not ‘anatomical syncytium’, because they present in touch but not in continuity.
Property 4. Conductivity (Dromotropism):
Is the ability of cardiac muscle fibers to conduct the cardiac impulses that are initiated in the SA node (the pacemaker of the heart)
Additional Information: The heart consists mostly of heart muscle cells (or myocardium). The outstanding characteristics of the action of the guts are its contractility, which is the basis for its pumping action, and therefore the rhythmicity of the contraction. The amount of blood pumped by the guts every moment (the heart yield) differs to fulfill the metabolic requirements of peripheral tissues, especially the skeletal muscles, liver, kidneys, mind, skin, heart, and gastrointestinal tract. The flow is decided by the contractile force developed by the heart muscle cells, also as by the frequency at which they're activated (rhythmicity).
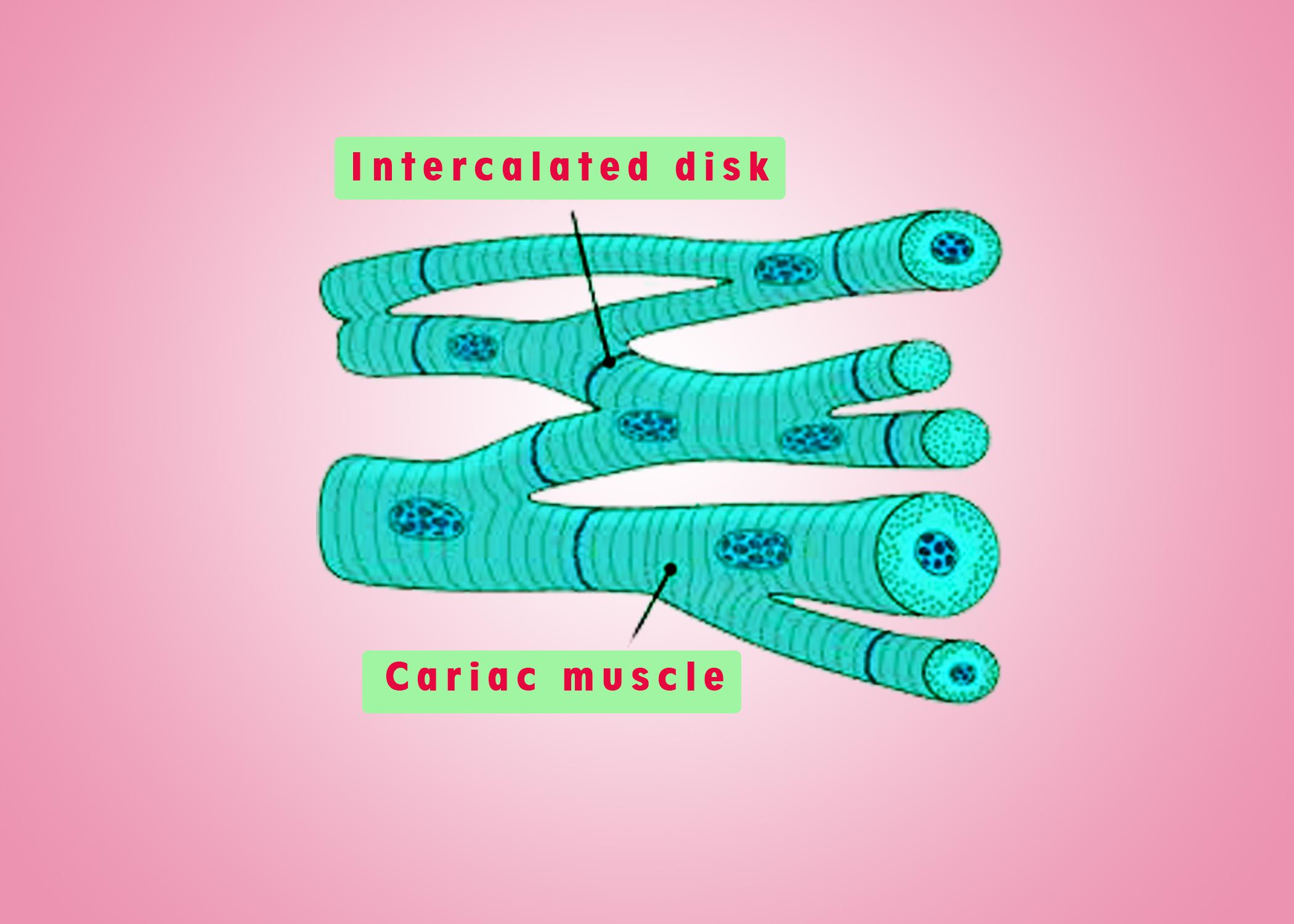
Note: Cardiac muscle cells form a highly branched cellular network in the heart. They are connected end to finish by intercalated disks and are organized into layers of myocardial tissue that are wrapped around the chambers of the guts. The constriction of individual heart muscle cells produces power and shortening in these groups of muscle, with a resultant decrement inside the heart chamber size and accordingly the subsequent discharge of the blood into the pulmonary and systemic vessels.
Complete answer:
The physiological properties of the heart muscle are 1. Rhythmicity 2. Excitability 3. Contractility 4. Conductivity.
Property 1. Rhythmicity/Automaticity/Chronotropism:
In the myocardium, automaticity is the capacity of the heart muscles to depolarize immediately, without outside electrical incitement from the nervous system.
Property 2. Excitability (Bathmotropic):
Is the ability of the cardiac muscle to respond to adequate stimuli by generating an action potential.
Property 3. Contractility/Inotropism:
It is the power of the heart muscle to convert electricity into mechanical work. Myocardial fibers have ‘functional syncytium’ and not ‘anatomical syncytium’, because they present in touch but not in continuity.
Property 4. Conductivity (Dromotropism):
Is the ability of cardiac muscle fibers to conduct the cardiac impulses that are initiated in the SA node (the pacemaker of the heart)
Additional Information: The heart consists mostly of heart muscle cells (or myocardium). The outstanding characteristics of the action of the guts are its contractility, which is the basis for its pumping action, and therefore the rhythmicity of the contraction. The amount of blood pumped by the guts every moment (the heart yield) differs to fulfill the metabolic requirements of peripheral tissues, especially the skeletal muscles, liver, kidneys, mind, skin, heart, and gastrointestinal tract. The flow is decided by the contractile force developed by the heart muscle cells, also as by the frequency at which they're activated (rhythmicity).
Note: Cardiac muscle cells form a highly branched cellular network in the heart. They are connected end to finish by intercalated disks and are organized into layers of myocardial tissue that are wrapped around the chambers of the guts. The constriction of individual heart muscle cells produces power and shortening in these groups of muscle, with a resultant decrement inside the heart chamber size and accordingly the subsequent discharge of the blood into the pulmonary and systemic vessels.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




