
How is the energy level of the products affected by the presence of a catalyst ?
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: A catalyst is a substance that is added to a reaction mixture to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the entire process. From this information try to determine how the presence of the catalyst will affect the energy of the reactant, products and the reaction as a whole.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. According to intermediate complex theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has transitory existence and decomposes to yield products and the catalyst.
Now, collisions can only result if the particles collide with a certain minimum energy called the activation energy for the reaction. The position of activation energy can be determined by Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
To increase the rate of reaction we need to increase the number of successful collisions and one possible way of doing this is to provide an alternative pathway or reaction mechanism for the reaction by reducing the activation energy between the reactants and products and hence lowering the potential energy barrier.
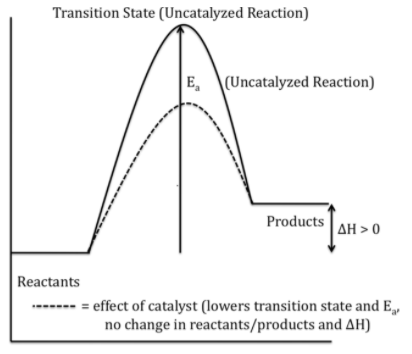
Also from Arrhenius equation $(k=\,A{{e}^{-\dfrac{{{E}_{a}}}{RT}}}$, where ${{E}_{a}}$ is the activation energy and $k$ is the rate constant of a reaction$)$ we can say that lowering the value of activation energy faster will be the rate of a reaction. So we can say that catalyst only lowers the activation energy of a reaction, it does not affect the energy of either the reactant or the product.
Hence the energy level of the products is unaffected by the presence of a catalyst.
Note: You should not confuse the term catalyst with that of inhibitors which actually reduces the rate of a reaction when added to a reaction mixture. Also you should remember the catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant or the Gibbs free energy associated with a given reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. According to intermediate complex theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has transitory existence and decomposes to yield products and the catalyst.
Now, collisions can only result if the particles collide with a certain minimum energy called the activation energy for the reaction. The position of activation energy can be determined by Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
To increase the rate of reaction we need to increase the number of successful collisions and one possible way of doing this is to provide an alternative pathway or reaction mechanism for the reaction by reducing the activation energy between the reactants and products and hence lowering the potential energy barrier.

Also from Arrhenius equation $(k=\,A{{e}^{-\dfrac{{{E}_{a}}}{RT}}}$, where ${{E}_{a}}$ is the activation energy and $k$ is the rate constant of a reaction$)$ we can say that lowering the value of activation energy faster will be the rate of a reaction. So we can say that catalyst only lowers the activation energy of a reaction, it does not affect the energy of either the reactant or the product.
Hence the energy level of the products is unaffected by the presence of a catalyst.
Note: You should not confuse the term catalyst with that of inhibitors which actually reduces the rate of a reaction when added to a reaction mixture. Also you should remember the catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant or the Gibbs free energy associated with a given reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




