
Energy is not carried by which of the following waves
A. stationary
B. progressive
C. transverse
D. electromagnetic
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: In order to transport energy, there needs to be a net flow of energy in a certain direction due to the wave. Out of the given options, the type of waves which do not cause net flow of certain direction cannot carry energy.
Complete answer:
A stationary wave is formed when two progressive waves travelling in opposite directions interfere with each other.
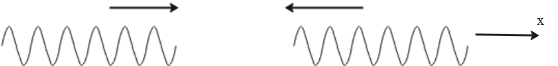
Consider two waves having the same amplitude and frequency travelling towards each other as shown in the diagram.
When they reach each other, they undergo interference where they superimpose on each other. The resultant of this type of superimposition is the stationary waves. As the name implies, they are not travelling but stay stationary.
These two waves carry equal amounts of energy but in opposite directions and after they superimpose, the net energy comes out to be zero. Hence, the stationary waves cannot carry energy with them.
Therefore, based on the above discussion the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:
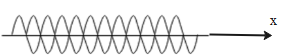
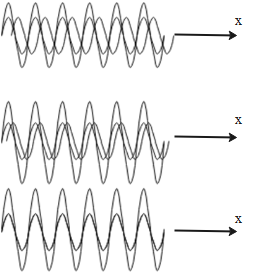
These diagrams show the resultant stationary waves formed when incident and reflected waves superimpose at different phase angles.
The waves are stationary because they are formed by two waves having equal motion but in opposite directions. The equal and opposite nature of two waves results in stationary nature of the stationary waves. This phenomenon is observed when incidents and reflected waves superimpose on each other.
Note:
The electromagnetic waves are transverse waves which can form both progressive waves and the stationary waves. The stationary waves are formed when electromagnetic waves get reflected from an obstruction and interfere with each other.
Complete answer:
A stationary wave is formed when two progressive waves travelling in opposite directions interfere with each other.

Consider two waves having the same amplitude and frequency travelling towards each other as shown in the diagram.
When they reach each other, they undergo interference where they superimpose on each other. The resultant of this type of superimposition is the stationary waves. As the name implies, they are not travelling but stay stationary.
These two waves carry equal amounts of energy but in opposite directions and after they superimpose, the net energy comes out to be zero. Hence, the stationary waves cannot carry energy with them.
Therefore, based on the above discussion the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:


These diagrams show the resultant stationary waves formed when incident and reflected waves superimpose at different phase angles.
The waves are stationary because they are formed by two waves having equal motion but in opposite directions. The equal and opposite nature of two waves results in stationary nature of the stationary waves. This phenomenon is observed when incidents and reflected waves superimpose on each other.
Note:
The electromagnetic waves are transverse waves which can form both progressive waves and the stationary waves. The stationary waves are formed when electromagnetic waves get reflected from an obstruction and interfere with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




