
How many energetically equivalent resonance structures exist for oxalate dianion?
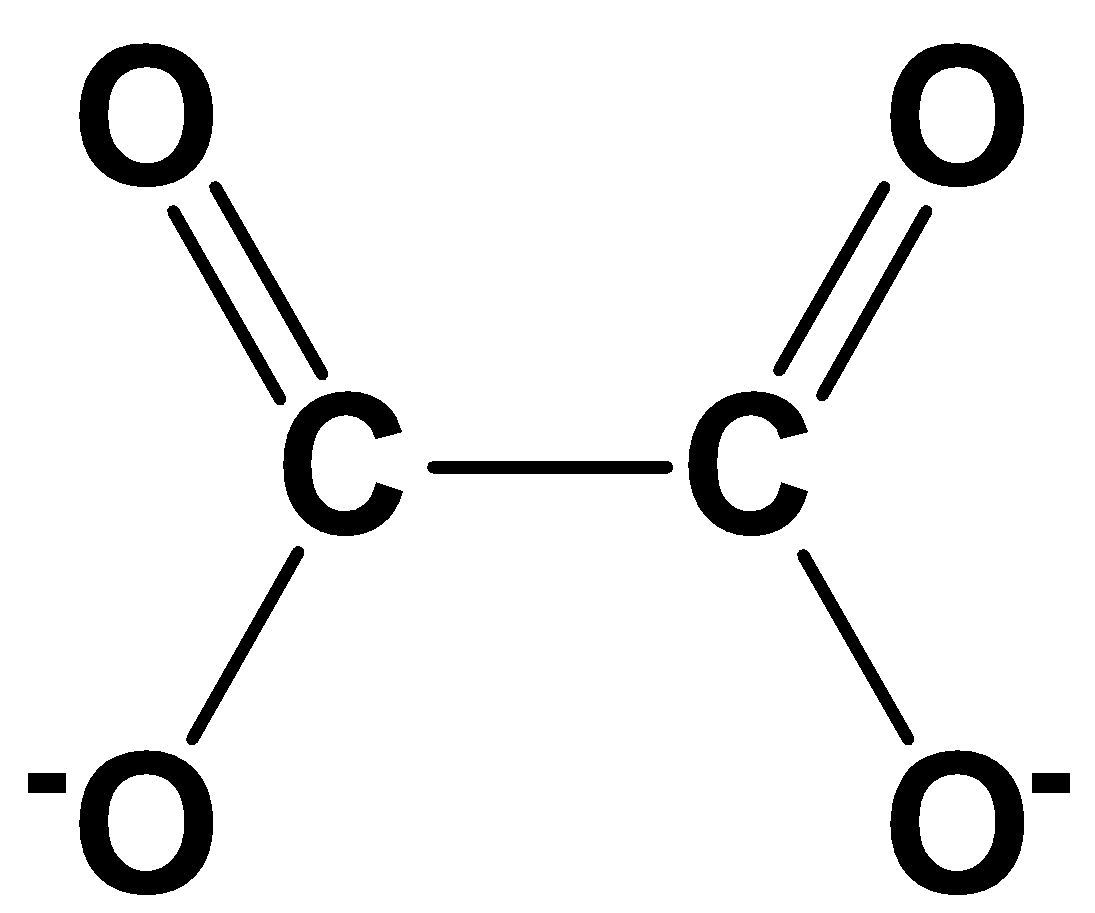
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4

Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Resonance structures are the hybrid of two or more structures obtained by a single compound. It differs in the position of electrons. Resonance mainly involves the delocalization of electrons within the molecules. Anion carries a negative charge and it symbolizes the excess of electrons present in the molecule. On the other hand, cation carries a positive charge and it symbolizes the deficiency of electrons present in the molecule.
Complete answer:
Oxalate dianion has the molecular formula \[{C_{^2}}{O_{^4}}^{2 - }\] and it is obtained by the removal of two protons from oxalic acid. The possible resonance structures involved in oxalate dianion are,
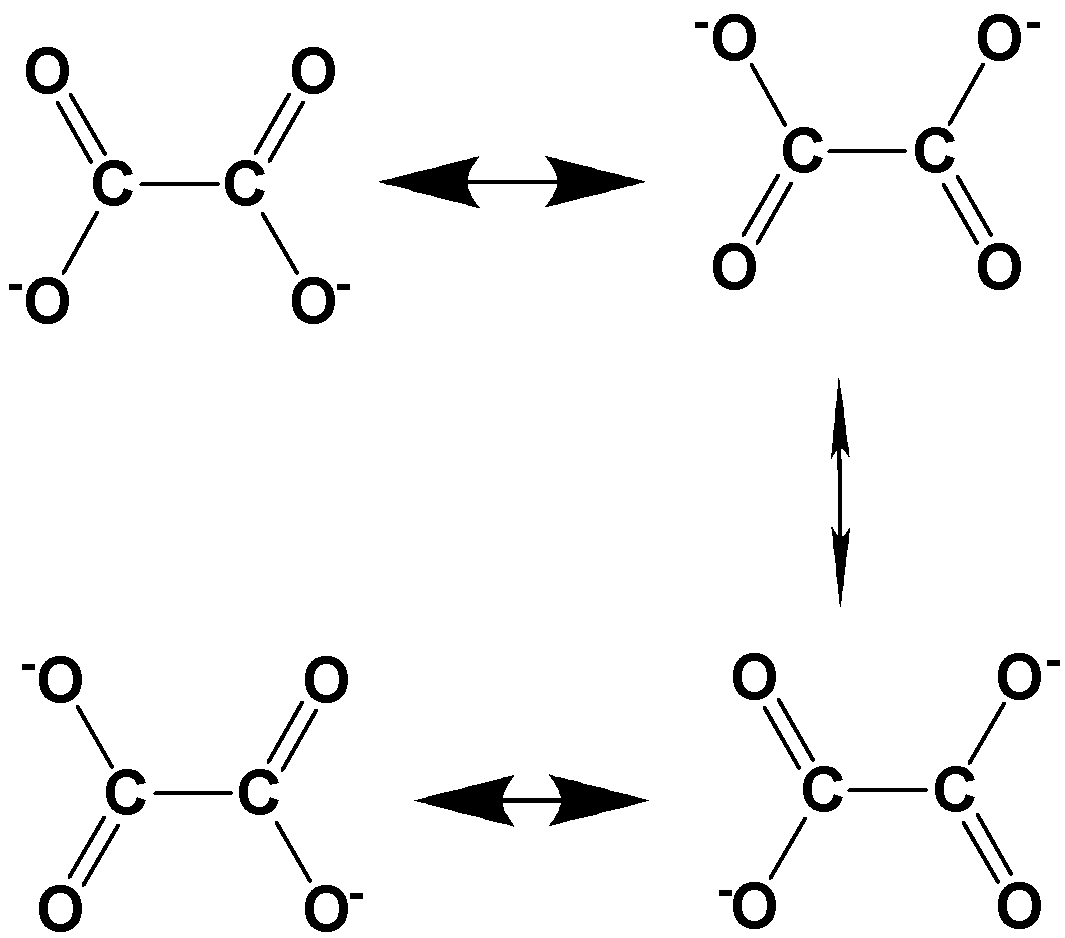
Thus, 4 energetically equivalent resonance structures exist for oxalate dianion.
Hence, option D is the correct option..
Note: It is already known that resonance is the delocalization of electrons within the molecules. Thus, the number of pi electrons present in the molecules must undergo resonating structures. This can be calculated by formula- \[P = 6n + 2 - V\]
Where,
P-number of pi electrons
n-number of atoms present
V-total number of valence electrons in the molecule.
Here, \[n = 6\] since two carbons and four oxygen atoms are present in oxalate dianion.
A total number of valence electrons can be calculated by subtracting the charge of the given molecule to the sum of valence electrons present in the molecule.
\[V = (4 + 4 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6) - ( - 2)\]
Since a carbon atom has four valence electrons and an oxygen atom has six valence electrons. The charge of oxalate dianion is negative and it has the value of \[ - 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 32 + 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 34\]
Thus, the total number of valence electrons can be calculated as,
\[P = 6(6) + 2 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow P = 36 + 2 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow P = 4\]
Four electrons in oxalate dianion are involved in the delocalization of electrons and therefore, the given oxalate dianion possesses four resonating structures.
Complete answer:
Oxalate dianion has the molecular formula \[{C_{^2}}{O_{^4}}^{2 - }\] and it is obtained by the removal of two protons from oxalic acid. The possible resonance structures involved in oxalate dianion are,

Thus, 4 energetically equivalent resonance structures exist for oxalate dianion.
Hence, option D is the correct option..
Note: It is already known that resonance is the delocalization of electrons within the molecules. Thus, the number of pi electrons present in the molecules must undergo resonating structures. This can be calculated by formula- \[P = 6n + 2 - V\]
Where,
P-number of pi electrons
n-number of atoms present
V-total number of valence electrons in the molecule.
Here, \[n = 6\] since two carbons and four oxygen atoms are present in oxalate dianion.
A total number of valence electrons can be calculated by subtracting the charge of the given molecule to the sum of valence electrons present in the molecule.
\[V = (4 + 4 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6) - ( - 2)\]
Since a carbon atom has four valence electrons and an oxygen atom has six valence electrons. The charge of oxalate dianion is negative and it has the value of \[ - 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 32 + 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 34\]
Thus, the total number of valence electrons can be calculated as,
\[P = 6(6) + 2 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow P = 36 + 2 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow P = 4\]
Four electrons in oxalate dianion are involved in the delocalization of electrons and therefore, the given oxalate dianion possesses four resonating structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




