
What is the endothermic reaction of aerobic respiration in a living cell?
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Aerobic respiration is the process of producing energy in the presence of oxygen. The carbohydrates in the presence of oxygen break down into various end products like carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
Complete answer
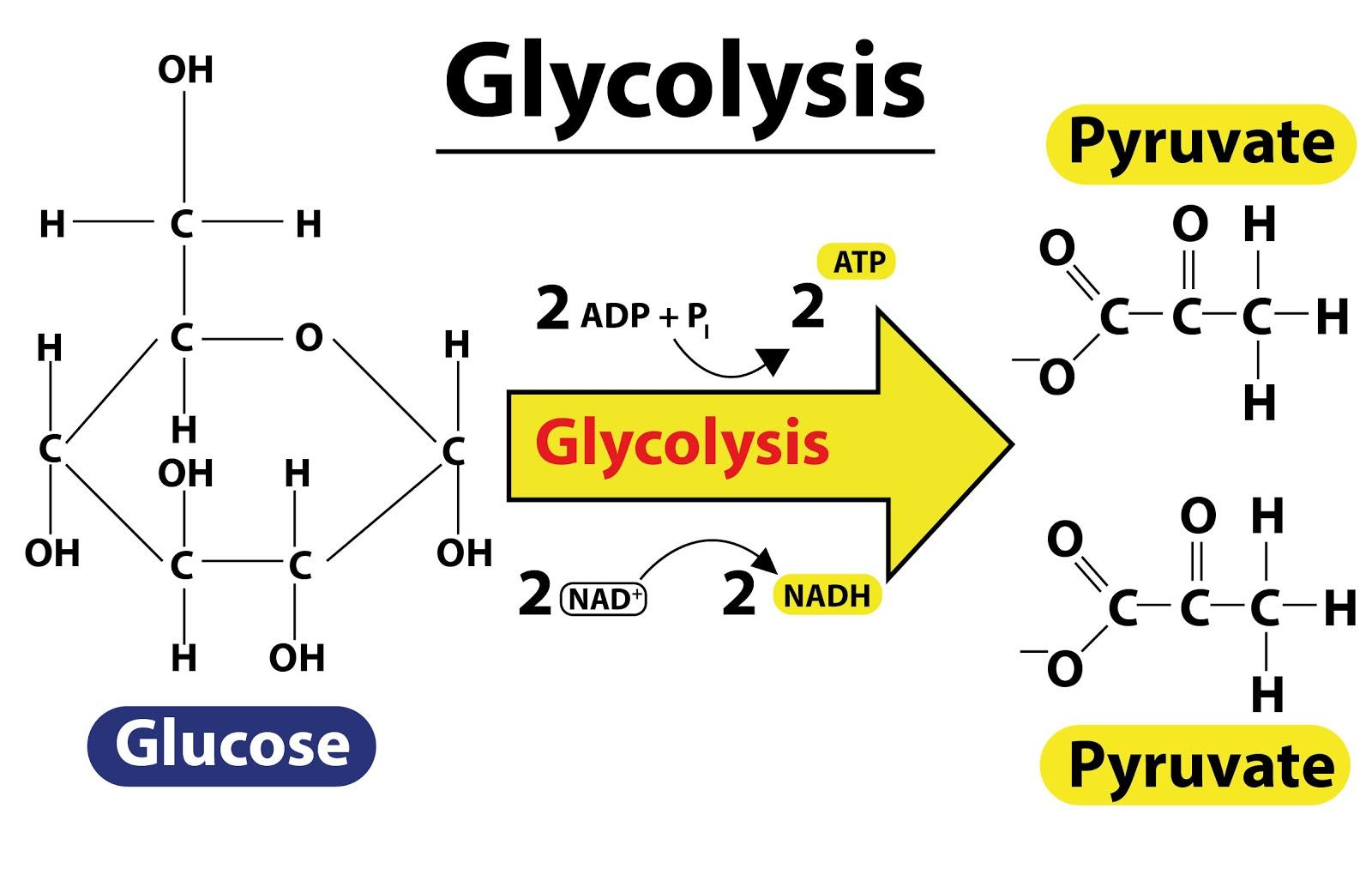
The metabolic pathway that includes the oxidation of the glucose molecule partially is known as the Glycolysis cycle. This cycle occurs outside the mitochondria. In this cycle, the glucose molecule will break down to form two molecules of pyruvate. The beginning of the glycolysis cycle occurs when, due to certain conditions provided the glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. In this whole cycle, a total of 4 ATP molecules are generated, out of which 2 ATP molecules are utilized in the process itself this process is called endothermic reaction while the remaining 2 ATP molecules will be the net gain of the glycolysis cycle thus it is called an exothermic reaction.
The endothermic reaction is also called cellular respiration. It has three stages.
1) Glycolysis - This is an anaerobic process that takes place in the cell cytoplasm. Glycolysis is the stage where 1 glucose molecule is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate.
2) Kreb’s Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle: The pyruvate produced in glycolysis is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix to form Acetyl CoA, which then enters the second stage of cellular respiration, Kreb’s cycle. This is an aerobic process comprising 8 steps of chemical reactions and yield energy.
3) Electron Transport Chain: The final stage takes place across the inner membrane of a mitochondrion and is an aerobic reaction. The ETC is a protein complex that transports electrons and protons across the mitochondrial membrane creating a proton gradient, which facilitates the production of ATP molecules.
Thus the endothermic reaction aerobic respiration in a living cell occurs only in the starting stage of the glycolysis cycle.
Note:
The process of Glycolysis involves catalyzed reactions that involve ten enzymes. Other monosaccharides like fructose and galactose after breakdown will change into their intermediates as in the case of the breakdown of the glucose molecule. The glycolysis has an evolutionary history as it is found in almost all the living organisms as a metabolic pathway and is dependent upon the presence of oxygen.
Complete answer
The metabolic pathway that includes the oxidation of the glucose molecule partially is known as the Glycolysis cycle. This cycle occurs outside the mitochondria. In this cycle, the glucose molecule will break down to form two molecules of pyruvate. The beginning of the glycolysis cycle occurs when, due to certain conditions provided the glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. In this whole cycle, a total of 4 ATP molecules are generated, out of which 2 ATP molecules are utilized in the process itself this process is called endothermic reaction while the remaining 2 ATP molecules will be the net gain of the glycolysis cycle thus it is called an exothermic reaction.
The endothermic reaction is also called cellular respiration. It has three stages.
1) Glycolysis - This is an anaerobic process that takes place in the cell cytoplasm. Glycolysis is the stage where 1 glucose molecule is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate.
2) Kreb’s Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle: The pyruvate produced in glycolysis is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix to form Acetyl CoA, which then enters the second stage of cellular respiration, Kreb’s cycle. This is an aerobic process comprising 8 steps of chemical reactions and yield energy.
3) Electron Transport Chain: The final stage takes place across the inner membrane of a mitochondrion and is an aerobic reaction. The ETC is a protein complex that transports electrons and protons across the mitochondrial membrane creating a proton gradient, which facilitates the production of ATP molecules.
Thus the endothermic reaction aerobic respiration in a living cell occurs only in the starting stage of the glycolysis cycle.

Note:
The process of Glycolysis involves catalyzed reactions that involve ten enzymes. Other monosaccharides like fructose and galactose after breakdown will change into their intermediates as in the case of the breakdown of the glucose molecule. The glycolysis has an evolutionary history as it is found in almost all the living organisms as a metabolic pathway and is dependent upon the presence of oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




