
Where is the electron transport system operative in mitochondria? Explain the system highlighting the role of oxygen.
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The Electron transport system is an important component of the energy production metabolism inside the cell. The Electron transport system is a series of events happening inside the powerhouse of the cell. Oxygen is the most electronegative acceptor and thus plays a major role in the electron transport system or ETS.
Complete answer: The electron transport system or ETS is a series of complexes that are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. These complexes consist of serially placed electron donors and electron acceptors. The Mitochondria is referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. The energy molecule ATP or adenosine Triphosphate is produced inside it by an electron transport system. The residual energy products of the respiration process such as NADH and FDA. These molecules get reduced to water in the mitochondria by transferring their electrons through the complexes placed inside the mitochondrial membrane.
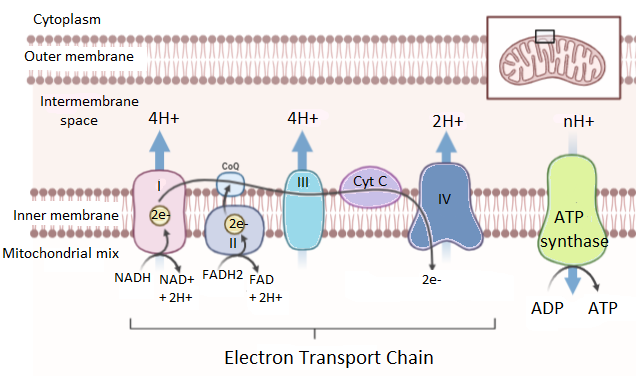
The electrons from NADH and FAD are passed from one electron donor to one electron acceptor. This process continues until the electrons reach the most electronegative electron acceptor that is oxygen. This results in the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. This gradient results in a thermodynamic state and this is called oxidative phosphorylation. Thus, ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is turned into ATP. So, oxygen acts as a terminator acceptor molecule that ends the process of ATP production.
Note: Oxygen also has an important role in the maintenance of membrane potential. It does so by removing de-energized molecules from the inside of the mitochondrial matrix. It should be noted that ETS performs in the presence of oxygen thus it is an aerobic process. It is the last step of the aerobic respiration cycle. Thus, it is also called the ‘Respiratory chain’.
Complete answer: The electron transport system or ETS is a series of complexes that are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. These complexes consist of serially placed electron donors and electron acceptors. The Mitochondria is referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. The energy molecule ATP or adenosine Triphosphate is produced inside it by an electron transport system. The residual energy products of the respiration process such as NADH and FDA. These molecules get reduced to water in the mitochondria by transferring their electrons through the complexes placed inside the mitochondrial membrane.

The electrons from NADH and FAD are passed from one electron donor to one electron acceptor. This process continues until the electrons reach the most electronegative electron acceptor that is oxygen. This results in the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. This gradient results in a thermodynamic state and this is called oxidative phosphorylation. Thus, ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is turned into ATP. So, oxygen acts as a terminator acceptor molecule that ends the process of ATP production.
Note: Oxygen also has an important role in the maintenance of membrane potential. It does so by removing de-energized molecules from the inside of the mitochondrial matrix. It should be noted that ETS performs in the presence of oxygen thus it is an aerobic process. It is the last step of the aerobic respiration cycle. Thus, it is also called the ‘Respiratory chain’.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




