
How do electromagnetic waves travel?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the electromagnetic waves and their nature in order to understand the method or the mechanism in which the electromagnetic propagates through a given medium or even in the absence of a medium which is required here.
Complete answer:
The electromagnetic waves are the special transverse type waves which allows the propagation of the light which allows the sensation for vision. The electromagnetic waves are, as the name suggests, the combined versions of the electric field and the magnetic field. The electric field and the magnetic field produced by the acceleration of an electron are in a direction perpendicular to each other. These two mutually perpendicular fields are the binding factor or the cause for the electromagnetic propagation.
The electromagnetic waves propagate in the direction perpendicular to the two fields in the third coordinate. The electromagnetic waves do not require a medium for propagation as they travel by the mutual effect of the moving electric field and the moving magnetic field which goes on infinitely without decaying off.
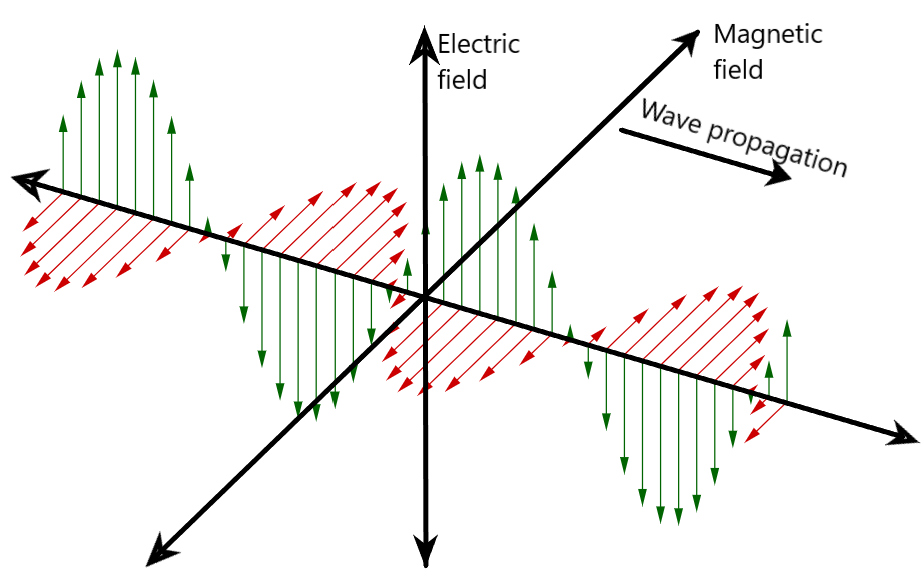
This is directly derived from the electromagnetic induction in which a moving or changing magnetic field creates an induced emf which is the electric field. This electric field varies with time and as a result this cycle goes on thus helping the propagation of the electromagnetic waves without the aid of an external medium or the particle oscillation.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The electromagnetic waves are considered to be transverse waves as the electric field
and the magnetic field are moving in mutually perpendicular directions and in direction perpendicular to the wave propagation as in the case of ordinary transverse waves.
Complete answer:
The electromagnetic waves are the special transverse type waves which allows the propagation of the light which allows the sensation for vision. The electromagnetic waves are, as the name suggests, the combined versions of the electric field and the magnetic field. The electric field and the magnetic field produced by the acceleration of an electron are in a direction perpendicular to each other. These two mutually perpendicular fields are the binding factor or the cause for the electromagnetic propagation.
The electromagnetic waves propagate in the direction perpendicular to the two fields in the third coordinate. The electromagnetic waves do not require a medium for propagation as they travel by the mutual effect of the moving electric field and the moving magnetic field which goes on infinitely without decaying off.

This is directly derived from the electromagnetic induction in which a moving or changing magnetic field creates an induced emf which is the electric field. This electric field varies with time and as a result this cycle goes on thus helping the propagation of the electromagnetic waves without the aid of an external medium or the particle oscillation.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The electromagnetic waves are considered to be transverse waves as the electric field
and the magnetic field are moving in mutually perpendicular directions and in direction perpendicular to the wave propagation as in the case of ordinary transverse waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




