
What is an electromagnet? Name two factors on which the strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet depends and state how it depends on the factors stated by you.
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: The electromagnet converts electrical energy into magnetic energy. To understand the mechanism of conversion, the relationship between the magnetic field produced by the electromagnet and the electric current flowing through it, must be understood clearly, before we understand the strength of the magnet.
Complete answer:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid
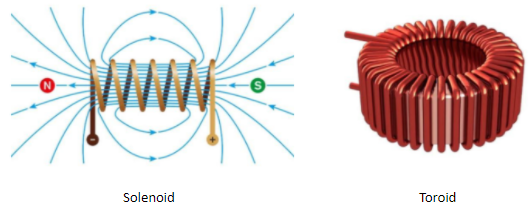
When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid
The magnetic field due to the electric current is dependent on two factors:
A. Current
B. Number of turns per unit length in the solenoid
The expression for magnetic field is given by:
$B = {\mu _0}nI$
where
$n = \dfrac{N}{L}$
where n = number of turns per unit length, N = total number of turns, L = length of the solenoid and I = current in the solenoid and ${\mu _0}$= absolute permeability.
We can see that the magnetic field depends directly on the two factors: $n$ and $I$.
If the number of turns per unit length and the current increase, the magnetic field increases and vice-versa. Thus, we can summarise as:
$B \propto n$
$B \propto I$
Note:
The ${\mu _0}$ in the expression for the magnetic field is called absolute permeability and is defined as a measure of resistance of a material to allow magnetic field lines to infringe them.
The value of absolute permeability, ${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}H{m^{ - 1}}$
Complete answer:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid

When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid
The magnetic field due to the electric current is dependent on two factors:
A. Current
B. Number of turns per unit length in the solenoid
The expression for magnetic field is given by:
$B = {\mu _0}nI$
where
$n = \dfrac{N}{L}$
where n = number of turns per unit length, N = total number of turns, L = length of the solenoid and I = current in the solenoid and ${\mu _0}$= absolute permeability.
We can see that the magnetic field depends directly on the two factors: $n$ and $I$.
If the number of turns per unit length and the current increase, the magnetic field increases and vice-versa. Thus, we can summarise as:
$B \propto n$
$B \propto I$
Note:
The ${\mu _0}$ in the expression for the magnetic field is called absolute permeability and is defined as a measure of resistance of a material to allow magnetic field lines to infringe them.
The value of absolute permeability, ${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}H{m^{ - 1}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




