
Electric field outside a long wire carrying charge q is proportional to:
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{r} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{{{r^{\dfrac{1}{{3/5}}}}}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{{{r^{\dfrac{1}{{3/2}}}}}} \\
$
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: We need to use the Gauss law to obtain the expression for the electric field outside a long wire carrying a charge q. From the obtained expression, we can check the dependence of the electric field on distance r from the wire which will give us the required answer.
Formula used:
Gauss law is given as
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}} $
Complete answer:
We are given a long cylindrical wire as shown in the following diagram.
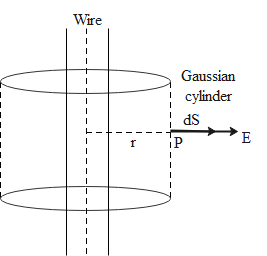
It carries a total charge q and the amount of charge per unit length of the wire can be written as
$
\lambda = \dfrac{q}{l} \\
q = \lambda l \\
$
Here l signifies the length of the wire. Now consider a point P outside this wire at distance r where we want to calculate the electric field due to the wire. Since we are going to use the Gauss law for this, we also need to construct a Gaussian surface around it.
For a cylindrical wire the Gaussian surface will look like a cylinder whose radius is r. Now we can apply the Gauss law to this cylinder in the following way.
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}} $
Here dS is the small area element on the Gaussian cylinder. We can solve this in the following way.
$
E\int {dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}} = \dfrac{{\lambda l}}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E \times 2\pi rl = \dfrac{{\lambda l}}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\therefore E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi { \in _0}r}} \\
$
This is the final expression for the electric field due to the wire at a distance r outside it. We see that $E \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$.
Therefore, the correct dependence of E on distance is option A.
Note:
It should be noted that the direction of the electric field and the area element is the same. Due to this, $\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = EdS\cos 0^\circ = EdS$. Also, the electric field due to the wire is constant since the charge on the wire is also constant, so we have taken E out of the integral in the above calculation.
Formula used:
Gauss law is given as
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}} $
Complete answer:
We are given a long cylindrical wire as shown in the following diagram.

It carries a total charge q and the amount of charge per unit length of the wire can be written as
$
\lambda = \dfrac{q}{l} \\
q = \lambda l \\
$
Here l signifies the length of the wire. Now consider a point P outside this wire at distance r where we want to calculate the electric field due to the wire. Since we are going to use the Gauss law for this, we also need to construct a Gaussian surface around it.
For a cylindrical wire the Gaussian surface will look like a cylinder whose radius is r. Now we can apply the Gauss law to this cylinder in the following way.
$\oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}} $
Here dS is the small area element on the Gaussian cylinder. We can solve this in the following way.
$
E\int {dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}} = \dfrac{{\lambda l}}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\Rightarrow E \times 2\pi rl = \dfrac{{\lambda l}}{{{ \in _0}}} \\
\therefore E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi { \in _0}r}} \\
$
This is the final expression for the electric field due to the wire at a distance r outside it. We see that $E \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$.
Therefore, the correct dependence of E on distance is option A.
Note:
It should be noted that the direction of the electric field and the area element is the same. Due to this, $\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = EdS\cos 0^\circ = EdS$. Also, the electric field due to the wire is constant since the charge on the wire is also constant, so we have taken E out of the integral in the above calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




