
What is the effect of p${ CO }_{ 2 }$ on oxygen transport?
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The partial pressure of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ (p${ CO }_{ 2 }$) and the partial pressure of ${ O }_{ 2 }$ (p${ O }_{ 2 }$) and the relative difference between their values is what decides the rate and direction of diffusion at the different parts of our body.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Oxygen is transported in the blood by hemoglobin which forms a complex known as oxyhemoglobin while doing so. The binding of oxygen to this hemoglobin depends on a number of factors such as p${ CO }_{ 2 }$, p${ O }_{ 2 }$, and $H^+$ concentration.
If p${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is high, ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration is high and p${ O }_{ 2 }$ is low along with high temperature, then in such conditions, the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin is favored. This means that oxygen will be used for cellular respiration instead of being transported.
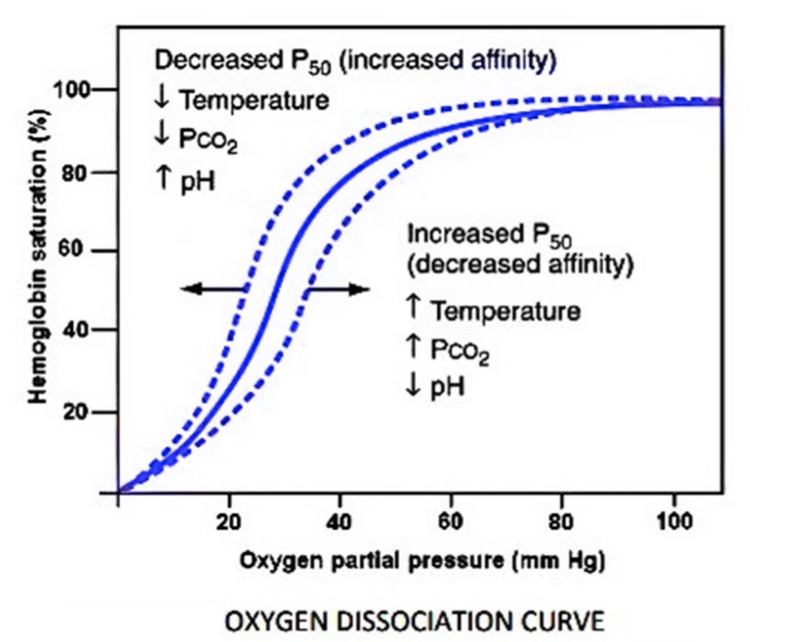
If p${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is low, ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration is low and p${ O }_{ 2 }$ is high along with low temperature, such conditions favor the formation of oxyhemoglobin and thus oxygen is likely to be transported.
Additional information: Regulation of oxygen transport is also done via the neural system.
Respiratory rhythm center: This is a specialized region present in the medulla region of the brain which can detect ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration increase in the blood and thus make changes to reduce them.
Pneumotaxic center: Pneumotaxic region helps in the functioning of the respiratory rhythm organ by signaling it in the case of high ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration.
There are not many roles of the ${ O }_{ 2 }$ in the regulation of its transport.
Note:
- $97\%$ of oxygen is transported in the blood in the form of oxyhemoglobin. The other $3\%$ is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- $20\% - 25\%$ of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is transported by hemoglobin and $70\%$ of it is transported as bicarbonate ions. And the remaining $7\%$ is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- The formation of bicarbonate ions from ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }{ O }$ is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Oxygen is transported in the blood by hemoglobin which forms a complex known as oxyhemoglobin while doing so. The binding of oxygen to this hemoglobin depends on a number of factors such as p${ CO }_{ 2 }$, p${ O }_{ 2 }$, and $H^+$ concentration.
If p${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is high, ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration is high and p${ O }_{ 2 }$ is low along with high temperature, then in such conditions, the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin is favored. This means that oxygen will be used for cellular respiration instead of being transported.

If p${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is low, ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration is low and p${ O }_{ 2 }$ is high along with low temperature, such conditions favor the formation of oxyhemoglobin and thus oxygen is likely to be transported.
Additional information: Regulation of oxygen transport is also done via the neural system.
Respiratory rhythm center: This is a specialized region present in the medulla region of the brain which can detect ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration increase in the blood and thus make changes to reduce them.
Pneumotaxic center: Pneumotaxic region helps in the functioning of the respiratory rhythm organ by signaling it in the case of high ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }^{ + }$ concentration.
There are not many roles of the ${ O }_{ 2 }$ in the regulation of its transport.
Note:
- $97\%$ of oxygen is transported in the blood in the form of oxyhemoglobin. The other $3\%$ is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- $20\% - 25\%$ of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is transported by hemoglobin and $70\%$ of it is transported as bicarbonate ions. And the remaining $7\%$ is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- The formation of bicarbonate ions from ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }{ O }$ is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




