
What is the effect of electron withdrawing groups on the acidity carboxylic acid?
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Acidity of a carboxylic acid is mainly determined by the factors like resonance and inductive effect. Here, we will see just one factor; that is how inductive effect affects the acidity of carboxylic acids. Acidity is the ability to produce $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ ions and carboxylic acids have $-\text{COOH}$ groups in common.
Complete answer:
There are two groups under inductive effect, one electron donating groups and another is electron withdrawing groups. Electron withdrawing groups are groups which attract or displace the electrons towards it. The examples of electron withdrawing groups are
$-\text{X,}-\text{C}{{\text{X}}_{3}},-\text{NH}_{3}^{+},-\text{NR}_{3}^{+},-\text{CN,}-\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}},-\text{CHO,}-\text{COR,}-\text{COOH,}-\text{COOR}$.
Here, X refers to halogens while R refers to alkyl or aryl groups.
Let us now talk about the effect of electron withdrawing groups in acidic strength:
As, the electron withdrawing groups attract electrons away from other elements. So, such groups help in increasing the polarity of the $-\text{COOH}$ group. We know that oxygen is an electronegative group, so, the $-\text{OH}$ bond of $-\text{COOH}$ group will be polar or ionizable. As the electron withdrawing groups increase the polarity, it seems that electronegativity of oxygen has increased.
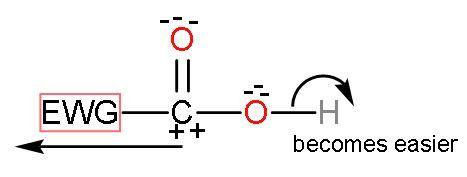
After the release of $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ from the $-\text{COOH}$ group. The compound becomes stable by the resonating structures of carboxylate ions which are stabilised by the negative charge on oxygen atoms.
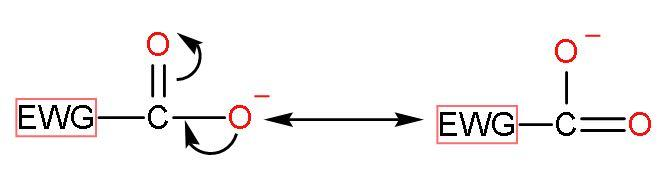
The placement and power of electron withdrawing groups also affect the acidity of compounds:
(1) The inductive effect decreases with increasing carbon chain or increasing distance from the substituted group. So, if an electron withdrawing group is present nearer to the $-\text{COOH}$ group, the compound will be more acidic than the compound where the same electron withdrawing group is placed far from the $-\text{COOH}$ group. Like, $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ClCHCOOH}>\text{ClC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH}$ in acidic strength.
(2) The power of the electron withdrawing group is also taken into account. More is the power of electron withdrawing groups, more will be the acidic strength of carboxylic acids. Like, 2-nitro ethanoic acid is more acidic than 2-chloro ethanoic acid because the –I effect of the nitro group is more than the chloro group.
Note: The electron withdrawing groups increases the acidity of carboxylic acids. On the other hand, electron donating groups decrease the acidity of carboxylic acids as they decrease the polarity of $-\text{OH}$ bond of $-\text{COOH}$ group. The nearer the EWG will be placed less acidic the compound will be and if it is far, it is a little more acidic.
Complete answer:
There are two groups under inductive effect, one electron donating groups and another is electron withdrawing groups. Electron withdrawing groups are groups which attract or displace the electrons towards it. The examples of electron withdrawing groups are
$-\text{X,}-\text{C}{{\text{X}}_{3}},-\text{NH}_{3}^{+},-\text{NR}_{3}^{+},-\text{CN,}-\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}},-\text{CHO,}-\text{COR,}-\text{COOH,}-\text{COOR}$.
Here, X refers to halogens while R refers to alkyl or aryl groups.
Let us now talk about the effect of electron withdrawing groups in acidic strength:
As, the electron withdrawing groups attract electrons away from other elements. So, such groups help in increasing the polarity of the $-\text{COOH}$ group. We know that oxygen is an electronegative group, so, the $-\text{OH}$ bond of $-\text{COOH}$ group will be polar or ionizable. As the electron withdrawing groups increase the polarity, it seems that electronegativity of oxygen has increased.

After the release of $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ from the $-\text{COOH}$ group. The compound becomes stable by the resonating structures of carboxylate ions which are stabilised by the negative charge on oxygen atoms.

The placement and power of electron withdrawing groups also affect the acidity of compounds:
(1) The inductive effect decreases with increasing carbon chain or increasing distance from the substituted group. So, if an electron withdrawing group is present nearer to the $-\text{COOH}$ group, the compound will be more acidic than the compound where the same electron withdrawing group is placed far from the $-\text{COOH}$ group. Like, $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ClCHCOOH}>\text{ClC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH}$ in acidic strength.
(2) The power of the electron withdrawing group is also taken into account. More is the power of electron withdrawing groups, more will be the acidic strength of carboxylic acids. Like, 2-nitro ethanoic acid is more acidic than 2-chloro ethanoic acid because the –I effect of the nitro group is more than the chloro group.
Note: The electron withdrawing groups increases the acidity of carboxylic acids. On the other hand, electron donating groups decrease the acidity of carboxylic acids as they decrease the polarity of $-\text{OH}$ bond of $-\text{COOH}$ group. The nearer the EWG will be placed less acidic the compound will be and if it is far, it is a little more acidic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




