
Edible part of a plum fruit is
A) Endosperm
B) Epicarp and mesocarp
C) Embryo
D) Cotyledons
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: Plum fruit is a simple, fleshy fruit. It is an example of Drupe type. Other examples of drupe are Peach, Mango and Apricot etc.
Complete Answer:
- In botanical terms, a fruit is a ripened ovary that bears seeds. The fruit consists of – Pericarp and seed. Pericarp develops from the ovarian wall. It may be fleshy as in mango, guava and plum or it may be dry as in walnut.
- Seeds are developed from fertilized ovules. The pericarp or the fruit wall is differentiated into three parts – Epicarp (the outermost layer), Mesocarp (the middle layer) and Endocarp (innermost layer).
- On the basis of number and position of ovaries and number of flowers involved in the formation of fruits, the fruits are classified into three major types –
(i) Simple fruits
(ii) Aggregate fruits
(iii) Composite fruits.
- These major types are again classified into different subtypes. Simple fruits are divided into Dry fruits and Fleshy fruits.
- Plum or Prunus domestica is simple, fleshy fruit. Among different types of fleshy fruits, Plum belongs to a type called “Drupe”. Drupes are also known as stone fruits due to the presence of a very hard and stony endocarp.
- In the fruit of Plum, epicarp, i.e., the outermost thin layer and mesocarp, i.e., the middle fleshy layer are edible.
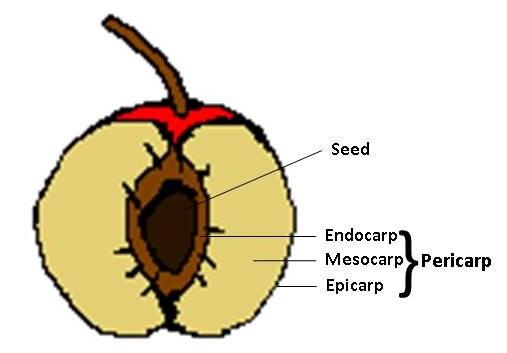
Fig: Parts of a Drupe fruit
Embryo and cotyledons of Plum are not edible. The seeds of Plum are non-endospermic (exalbuminous), i.e., they do not contain endosperm.
Thus, the correct answer is B, i.e., Epicarp and mesocarp.
Note: Drupes develop from mono or multicarpellary, syncarpous and superior ovary. These fruits are known for being one seeded.
Complete Answer:
- In botanical terms, a fruit is a ripened ovary that bears seeds. The fruit consists of – Pericarp and seed. Pericarp develops from the ovarian wall. It may be fleshy as in mango, guava and plum or it may be dry as in walnut.
- Seeds are developed from fertilized ovules. The pericarp or the fruit wall is differentiated into three parts – Epicarp (the outermost layer), Mesocarp (the middle layer) and Endocarp (innermost layer).
- On the basis of number and position of ovaries and number of flowers involved in the formation of fruits, the fruits are classified into three major types –
(i) Simple fruits
(ii) Aggregate fruits
(iii) Composite fruits.
- These major types are again classified into different subtypes. Simple fruits are divided into Dry fruits and Fleshy fruits.
- Plum or Prunus domestica is simple, fleshy fruit. Among different types of fleshy fruits, Plum belongs to a type called “Drupe”. Drupes are also known as stone fruits due to the presence of a very hard and stony endocarp.
- In the fruit of Plum, epicarp, i.e., the outermost thin layer and mesocarp, i.e., the middle fleshy layer are edible.

Fig: Parts of a Drupe fruit
Embryo and cotyledons of Plum are not edible. The seeds of Plum are non-endospermic (exalbuminous), i.e., they do not contain endosperm.
Thus, the correct answer is B, i.e., Epicarp and mesocarp.
Note: Drupes develop from mono or multicarpellary, syncarpous and superior ovary. These fruits are known for being one seeded.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




