
During Mitosis, metaphase differs from anaphase in having
(a) The same number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids.
(b)Half the number of chromosomes and half the number of chromatids.
(c)Half the number of chromosomes and the same number of chromatids.
(d)The same number of chromosomes and the same number of chromatids.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: A type of cell division that leads to two daughter cells each having an equivalent number and type of chromosomes because of the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. Mitosis is known to involve five phases, supporting the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Complete answer:
In the metaphase stage, all the chromosomes are arranged at the cell equator. All the chromosomes have two chromatids, joined at the centromere. These are called sister chromatids. The centromere splits in the anaphase stage and the two sister chromatids go to opposite poles. They are now called chromosomes. They have a single chromatid which will duplicate into two sister chromatids in the S phase. Thus, at the anaphase stage, the number of chromosomes remains the same even as the number of chromatids is reduced to one-half due to the splitting of the centromere.
Additional Information:
Stages in mitosis:
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis.
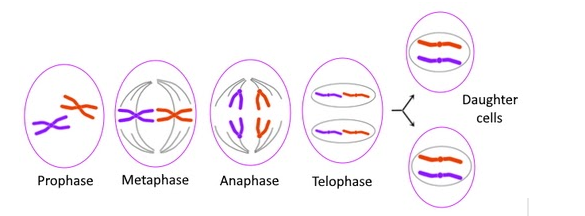
So, the correct answer is, “The same number of chromosomes and half the number of chromatids”.
Note:
Complete answer:
In the metaphase stage, all the chromosomes are arranged at the cell equator. All the chromosomes have two chromatids, joined at the centromere. These are called sister chromatids. The centromere splits in the anaphase stage and the two sister chromatids go to opposite poles. They are now called chromosomes. They have a single chromatid which will duplicate into two sister chromatids in the S phase. Thus, at the anaphase stage, the number of chromosomes remains the same even as the number of chromatids is reduced to one-half due to the splitting of the centromere.
Additional Information:
Stages in mitosis:
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis.

So, the correct answer is, “The same number of chromosomes and half the number of chromatids”.
Note:
| Mitosis | Similarities | Meiosis |
| 4 Stages in total (plus interphase). | Production of new cells | 8 stages in total (plus interphase). |
| Happens in somatic cells | Similar basic steps | Happens in germ cells. |
| The purpose is cellular proliferation. | Start with a single parent cell. | The purpose is sexual reproduction. |
| Produces two diploid daughter cells. | Produces 4 haploid daughter cells. | |
| Chromosome number remains the same. | Chromosome numbers get halved in each daughter cell. | |
| Genetic variation doesn’t change. | Genetic variation seems to be increasing. |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




