
During exhalation, the ribs
(a)Move outwards
(b)Move downwards
(c)Move upwards
(d)Do not move at all
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The outer intercostal muscles return the diaphragm and ribs to their full thoracic volume during this process. The diaphragm acquires its characteristic dome shape.
Complete answer:
Exhalation is the process of exhaling or breathing out in an organism. In humans, it is the passage of air out of the airways from the lungs to the external atmosphere during respiration. The diaphragm relaxes during exhalation and goes up into the chest cavity. Even the intercostal muscles between the ribs relax to decrease chest cavity volume. If the gap in the chest cavity becomes smaller, the carbon-rich air is pushed out of your lungs and windpipe, then out of your mouth or nose.
They place rib cage downwards and inwards as they relax. Hence the ribs pass downwards during exhalation.
Additional Information: The outer intercostal muscles contract and raise ribs outward during inhalation, while the diaphragm becomes flat and falls thus raising the thoracic cavity length.
Our diaphragm contracts at breathing in and shifts downward. This is why the space in our chest cavity is rising, through which the lungs extend. The intercostal muscles also help to widen the chest cavity between our ribs.
The ribs are long, flat bones that form the bulk of the thoracic cage. They are extremely small, but highly resilient; contributing to their function in protecting thoracic organs within themselves. There are 12 pairs of ribs, all articulating with the vertebral column. The rib cage is the arrangement of ribs in the thorax of most vertebrates attached to the vertebral column and sternum, which encloses and protects the heart and the lungs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Move downwards’.
Note: -Forced breathing is also known as hyperpnea. It is a breathing mode that can occur during exercise or actions that involve active breathing manipulation, such as singing. Inspiration and expiration both occur during forced breathing due to muscle contractions. Muscles of the spine, including the scalenes, contract and raise the thoracic wall during forced inspiration, increasing lung volume.
-Accessory abdominal muscles, including obliques, contract during forced expiration, pulling abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. This helps drive the diaphragm into the thorax, even more, forcing out more air. In addition, the accessory muscles help to compress the rib cage and also decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity.
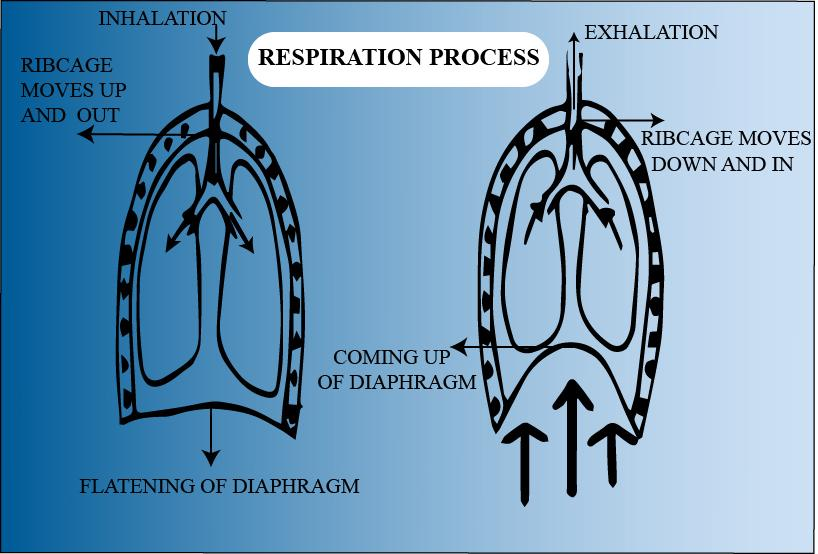
Complete answer:
Exhalation is the process of exhaling or breathing out in an organism. In humans, it is the passage of air out of the airways from the lungs to the external atmosphere during respiration. The diaphragm relaxes during exhalation and goes up into the chest cavity. Even the intercostal muscles between the ribs relax to decrease chest cavity volume. If the gap in the chest cavity becomes smaller, the carbon-rich air is pushed out of your lungs and windpipe, then out of your mouth or nose.
They place rib cage downwards and inwards as they relax. Hence the ribs pass downwards during exhalation.
Additional Information: The outer intercostal muscles contract and raise ribs outward during inhalation, while the diaphragm becomes flat and falls thus raising the thoracic cavity length.
Our diaphragm contracts at breathing in and shifts downward. This is why the space in our chest cavity is rising, through which the lungs extend. The intercostal muscles also help to widen the chest cavity between our ribs.
The ribs are long, flat bones that form the bulk of the thoracic cage. They are extremely small, but highly resilient; contributing to their function in protecting thoracic organs within themselves. There are 12 pairs of ribs, all articulating with the vertebral column. The rib cage is the arrangement of ribs in the thorax of most vertebrates attached to the vertebral column and sternum, which encloses and protects the heart and the lungs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Move downwards’.
Note: -Forced breathing is also known as hyperpnea. It is a breathing mode that can occur during exercise or actions that involve active breathing manipulation, such as singing. Inspiration and expiration both occur during forced breathing due to muscle contractions. Muscles of the spine, including the scalenes, contract and raise the thoracic wall during forced inspiration, increasing lung volume.
-Accessory abdominal muscles, including obliques, contract during forced expiration, pulling abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. This helps drive the diaphragm into the thorax, even more, forcing out more air. In addition, the accessory muscles help to compress the rib cage and also decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




