
Due to friction, the system as shown in the diagram remains motionless. Calculate the static coefficient of friction?
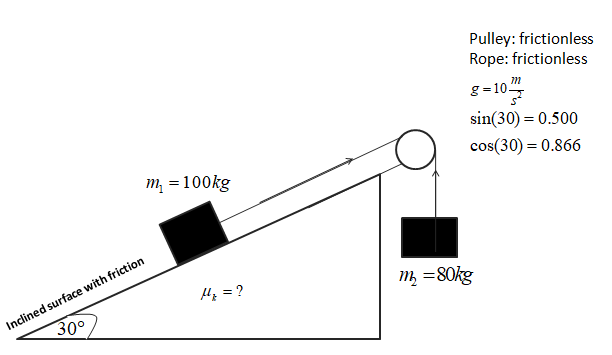

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint:First, the weights of the given masses have to be divided into two components: horizontal and vertical. Thereafter, the forces acting on the masses have to be concluded. The formula of the frictional force has to be known in terms of the static coefficient of friction. The value of the static coefficient of friction can be found in the equation of forces.
Formula used:
The static frictional force, ${f_s} = T - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$T$is the tension of the string.
${m_1}g\sin \theta $ is the sine component of the weight of mass ${m_1}$
${f_s} = \mu N$ $\mu $is the static coefficient of friction.
The normal force, $N = {m_1}g\cos \theta $
$T = {m_2}g$
Complete step-by-step solution:
The diagram in the problem is given by,
First, the diagram has to be modified by showing the components of the forces acting on the two masses ${m_1}$and ${m_2}$ .
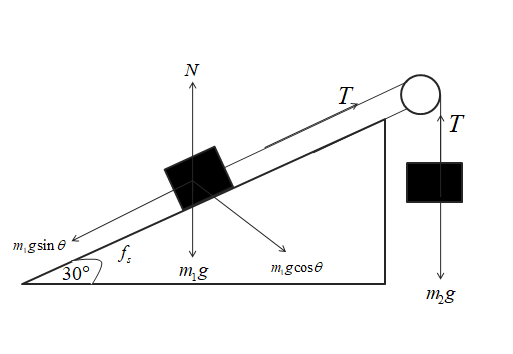
The weight of the mass ${m_1}$is ${m_1}g$ . It is divided into two components horizontal and vertical at an angle $\theta ( = 30^\circ )$ i.e. ${m_1}g\cos \theta $ and ${m_1}g\sin \theta $.
The tension of the string is $T$.
Now, The static frictional force, ${f_s} = T - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
From the diagram, it is shown that $T = {m_2}g$
$ \Rightarrow {f_s} = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
Now, the formula of the static frictional force in terms of the static coefficient of friction $\mu $,
${f_s} = \mu N$
The normal force, $N = {m_1}g\cos \theta $
Now put the values of ${f_s}$ and $N$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \mu N = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu {m_1}g\cos \theta = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu {m_1}\cos \theta = {m_2} - {m_1}\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{{m_2} - {m_1}\sin \theta }}{{{m_1}\cos \theta }}$
Given that, ${m_1} = 100kg$
${m_2} = 80kg$
$\sin \theta = \sin 30 = 0.500$
$\cos \theta = \cos 30 = 0.866$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{80 - \left( {100 \times 0.500} \right)}}{{\left( {100 \times 0.866} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{80 - 50}}{{86.6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{30}}{{86.6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 0.346$
Hence the static coefficient of friction $ \Rightarrow \mu = 0.346$.
Note:The frictional force is the constraint to the motion of a body having motion relative to another. like gravitational force or electromagnetism, It is not a fundamental force. It is the force between two surfaces that are sliding, or going to slide, across each other. The direction of the frictional force is opposite to the direction of the surface.
There are two types of friction: 1. Static Friction is the highest force by a surface on a body until it remains stationary.
2. Sliding friction is the minimum force needed to keep the body having motion over a surface such that it moves similar distances in equal time.
Formula used:
The static frictional force, ${f_s} = T - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$T$is the tension of the string.
${m_1}g\sin \theta $ is the sine component of the weight of mass ${m_1}$
${f_s} = \mu N$ $\mu $is the static coefficient of friction.
The normal force, $N = {m_1}g\cos \theta $
$T = {m_2}g$
Complete step-by-step solution:
The diagram in the problem is given by,

First, the diagram has to be modified by showing the components of the forces acting on the two masses ${m_1}$and ${m_2}$ .

The weight of the mass ${m_1}$is ${m_1}g$ . It is divided into two components horizontal and vertical at an angle $\theta ( = 30^\circ )$ i.e. ${m_1}g\cos \theta $ and ${m_1}g\sin \theta $.
The tension of the string is $T$.
Now, The static frictional force, ${f_s} = T - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
From the diagram, it is shown that $T = {m_2}g$
$ \Rightarrow {f_s} = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
Now, the formula of the static frictional force in terms of the static coefficient of friction $\mu $,
${f_s} = \mu N$
The normal force, $N = {m_1}g\cos \theta $
Now put the values of ${f_s}$ and $N$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \mu N = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu {m_1}g\cos \theta = {m_2}g - {m_1}g\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu {m_1}\cos \theta = {m_2} - {m_1}\sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{{m_2} - {m_1}\sin \theta }}{{{m_1}\cos \theta }}$
Given that, ${m_1} = 100kg$
${m_2} = 80kg$
$\sin \theta = \sin 30 = 0.500$
$\cos \theta = \cos 30 = 0.866$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{80 - \left( {100 \times 0.500} \right)}}{{\left( {100 \times 0.866} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{80 - 50}}{{86.6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{30}}{{86.6}}$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 0.346$
Hence the static coefficient of friction $ \Rightarrow \mu = 0.346$.
Note:The frictional force is the constraint to the motion of a body having motion relative to another. like gravitational force or electromagnetism, It is not a fundamental force. It is the force between two surfaces that are sliding, or going to slide, across each other. The direction of the frictional force is opposite to the direction of the surface.
There are two types of friction: 1. Static Friction is the highest force by a surface on a body until it remains stationary.
2. Sliding friction is the minimum force needed to keep the body having motion over a surface such that it moves similar distances in equal time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




